 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI 7nm process, more efficient than GPU, Meta releases first-generation AI inference accelerator
7nm process, more efficient than GPU, Meta releases first-generation AI inference accelerator7nm process, more efficient than GPU, Meta releases first-generation AI inference accelerator
Machine Heart Report
Heart of Machine Editorial Department
Recently, Meta revealed its latest progress in artificial intelligence.
When people think of Meta, they usually think of its apps, including Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, or the upcoming Metaverse. But what many people don't know is that this company designs and builds very sophisticated data centers to operate these services.
Unlike cloud service providers such as AWS, GCP or Azure, Meta is not required to disclose details about its silicon selection, infrastructure or data center design, except that its OCP is designed to impress buyers. Meta's users want a better, more consistent experience, regardless of how it's achieved.
At Meta, AI workloads are everywhere and form the basis for a wide range of use cases, including content understanding, information flow, generative AI, and ad ranking. These workloads run on PyTorch, with best-in-class Python integration, eager-mode development, and API simplicity. In particular, deep learning recommendation models (DLRMs) are very important for improving Meta’s services and application experience. But as the size and complexity of these models increase, the underlying hardware systems need to provide exponential increases in memory and computing power while remaining efficient.
Meta found that for current scale AI operations and specific workloads, GPUs are inefficient and not the best choice. Therefore, the company proposed the inference accelerator MTIA to help train AI systems faster.
MTIA V1

MTIA v1 (inference) chip (die)
In 2020, Meta designed the first generation MTIA ASIC inference accelerator for its internal workloads. The inference accelerator is part of its full-stack solution, which includes silicon, PyTorch and recommendation models.
The MTIA accelerator is fabricated on the TSMC 7nm process and runs at 800 MHz, delivering 102.4 TOPS at INT8 precision and 51.2 TFLOPS at FP16 precision. It has a thermal design power (TDP) of 25 W.
MTIA accelerators consist of processing elements (PEs), on-chip and off-chip memory resources, and interconnects. The accelerator is equipped with a dedicated control subsystem running system firmware. The firmware manages available compute and memory resources, communicates with the host through a dedicated host interface, and coordinates job execution on the accelerator.
The memory subsystem uses LPDDR5 as an off-chip DRAM resource, expandable to 128 GB. The chip also has 128 MB of on-chip SRAM, shared by all PEs, providing higher bandwidth and lower latency for frequently accessed data and instructions.
The MTIA accelerator grid consists of 64 PEs organized in an 8x8 configuration that are connected to each other and to the memory blocks via a mesh network. The entire grid can be used as a whole to run a job, or it can be divided into multiple sub-grids that can run independent jobs.
Each PE is equipped with two processor cores (one of which is equipped with vector extensions) and a number of fixed-function units that are optimized to perform critical operations such as matrix multiplication, accumulation, data movement, and nonlinear function calculations. The processor core is based on the RISC-V open instruction set architecture (ISA) and is heavily customized to perform the necessary computing and control tasks.
Each PE also has 128 KB of local SRAM memory for fast storage and manipulation of data. This architecture maximizes parallelism and data reuse, which are fundamental to running workloads efficiently.
The chip provides both thread- and data-level parallelism (TLP and DLP), leverages instruction-level parallelism (ILP), and enables massive memory-level parallelism (MLP) by allowing large numbers of memory requests to be processed simultaneously.

MTIA v1 system design
MTIA accelerators are mounted on small dual M.2 boards for easier integration into servers. The boards use a PCIe Gen4 x8 link to connect to the host CPU on the server, consuming as little as 35 W.

Sample test board with MTIA
The servers hosting these accelerators use the Yosemite V3 server specification from the Open Compute Project. Each server contains 12 accelerators that are connected to the host CPU and to each other using a PCIe switch hierarchy. Therefore, communication between different accelerators does not need to involve the host CPU. This topology allows workloads to be distributed across multiple accelerators and run in parallel. The number of accelerators and server configuration parameters are carefully selected to best execute current and future workloads.
MTIA Software Stack
MTIA software (SW) stack is designed to provide developers with better development efficiency and high-performance experience. It is fully integrated with PyTorch, giving users a familiar development experience. Using PyTorch with MTIA is as easy as using PyTorch with a CPU or GPU. And, thanks to the thriving PyTorch developer ecosystem and tools, the MTIA SW stack can now use PyTorch FX IR to perform model-level transformations and optimizations, and LLVM IR for low-level optimizations, while also supporting MTIA accelerator custom architectures and ISAs .
The following picture is the MTIA software stack framework diagram:

As part of the SW stack, Meta has also developed a hand-tuned and highly optimized kernel library for performance-critical ML kernels, such as fully connected and embedded package operators. Higher levels in the SW stack have the option of instantiating and using these highly optimized kernels during compilation and code generation.
Additionally, the MTIA SW stack continues to evolve with integration with PyTorch 2.0, which is faster and more Pythonic, but as dynamic as ever. This will enable new features such as TorchDynamo and TorchInductor. Meta is also extending the Triton DSL to support the MTIA accelerator and use MLIR for internal representation and advanced optimization.
MTIA Performance
Meta compared the performance of MTIA with other accelerators and the results are as follows:

Meta uses five different DLRMs (from low to high complexity) to evaluate MTIA
In addition, Meta also compared MTIA with NNPI and GPU, and the results are as follows:

The evaluation found that MTIA is more efficient at processing low-complexity (LC1 and LC2) and medium-complexity (MC1 and MC2) models than NNPI and GPU. In addition, Meta has not been optimized for MTIA for high complexity (HC) models.
Reference link:
https://ai.facebook.com/blog/meta-training-inference-accelerator-AI-MTIA/
The above is the detailed content of 7nm process, more efficient than GPU, Meta releases first-generation AI inference accelerator. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PMThe 2025 Artificial Intelligence Index Report released by the Stanford University Institute for Human-Oriented Artificial Intelligence provides a good overview of the ongoing artificial intelligence revolution. Let’s interpret it in four simple concepts: cognition (understand what is happening), appreciation (seeing benefits), acceptance (face challenges), and responsibility (find our responsibilities). Cognition: Artificial intelligence is everywhere and is developing rapidly We need to be keenly aware of how quickly artificial intelligence is developing and spreading. Artificial intelligence systems are constantly improving, achieving excellent results in math and complex thinking tests, and just a year ago they failed miserably in these tests. Imagine AI solving complex coding problems or graduate-level scientific problems – since 2023
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PMMeta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
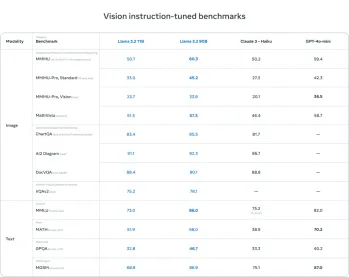 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and MoreApr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and MoreApr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PMThis week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 The Human Cost Of Talking To Machines: Can A Chatbot Really Care?Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:00 PM
The Human Cost Of Talking To Machines: Can A Chatbot Really Care?Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:00 PMThe comforting illusion of connection: Are we truly flourishing in our relationships with AI? This question challenged the optimistic tone of MIT Media Lab's "Advancing Humans with AI (AHA)" symposium. While the event showcased cutting-edg
 Understanding SciPy Library in PythonApr 11, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Understanding SciPy Library in PythonApr 11, 2025 am 11:57 AMIntroduction Imagine you're a scientist or engineer tackling complex problems – differential equations, optimization challenges, or Fourier analysis. Python's ease of use and graphics capabilities are appealing, but these tasks demand powerful tools
 3 Methods to Run Llama 3.2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 11, 2025 am 11:56 AM
3 Methods to Run Llama 3.2 - Analytics VidhyaApr 11, 2025 am 11:56 AMMeta's Llama 3.2: A Multimodal AI Powerhouse Meta's latest multimodal model, Llama 3.2, represents a significant advancement in AI, boasting enhanced language comprehension, improved accuracy, and superior text generation capabilities. Its ability t
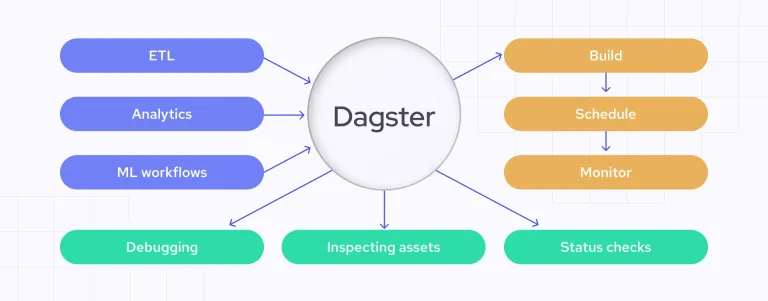 Automating Data Quality Checks with DagsterApr 11, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Automating Data Quality Checks with DagsterApr 11, 2025 am 11:44 AMData Quality Assurance: Automating Checks with Dagster and Great Expectations Maintaining high data quality is critical for data-driven businesses. As data volumes and sources increase, manual quality control becomes inefficient and prone to errors.
 Do Mainframes Have A Role In The AI Era?Apr 11, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Do Mainframes Have A Role In The AI Era?Apr 11, 2025 am 11:42 AMMainframes: The Unsung Heroes of the AI Revolution While servers excel at general-purpose applications and handling multiple clients, mainframes are built for high-volume, mission-critical tasks. These powerful systems are frequently found in heavil


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),




