Home >Operation and Maintenance >Nginx >Nginx Cache configuration plan and how to solve related memory usage problems
Nginx Cache configuration plan and how to solve related memory usage problems
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-23 14:01:382801browse
5 options for nginx cache
1. One of the traditional caches (404)
This method is to direct the 404 error of nginx to the backend, and then use proxy_store to The returned page is saved.
Configuration:
location / {
root /home/html/;#主目录
expires 1d;#网页的过期时间
error_page 404 =200 /fetch$request_uri;#404定向到/fetch目录下
}
location /fetch/ {#404定向到这里
internal;#指明这个目录不能在外部直接访问到
expires 1d;#网页的过期时间
alias /html/;
proxy_store会将文件保存到这目录下
proxy_pass//www.jb51.net/;#后端upstream地址,/fetch同时是一个代理
proxy_set_header accept-encoding '';#让后端不要返回压缩(gzip或deflate)的内容,保存压缩后的内容会引发乱子。
proxy_store on;#指定nginx将代理返回的文件保存
proxy_temp_path /home/tmp;#临时目录,这个目录要和/home/html在同一个硬盘分区内
} When using it, please note that nginx must have permission to write files to /home/tmp and /home/html. In Linux, nginx is generally It will be configured to run as the nobody user, so these two directories must be chown nobody, and set to be exclusive to the nobody user. Of course, you can also chmod 777, but all experienced system administrators will recommend not to use 777 casually.
2. Traditional cache 2 (!-e)
The principle is basically the same as the 404 jump, but more concise:
location / {
root /home/html/;
proxy_store on;
proxy_set_header accept-encoding '';
proxy_temp_path /home/tmp;
if ( !-f $request_filename )
{
proxy_pass//www.jb51.net/;
}
} You can see this The configuration saves a lot of code compared to 404. It uses !-f to determine whether the requested file exists on the file system. If it does not exist, proxy_pass to the backend, and the return is also saved using proxy_store.
Both traditional caches have basically the same advantages and disadvantages:
Disadvantage 1: Dynamic links with parameters are not supported, such as read.php?id=1, because nginx only saves the file name, so this link only Save it as read.php in the file system, so that incorrect results will be returned when users access read.php?id=2. At the same time, it does not support the home page and secondary directory //www.jb51.net/download/ in the form of //www.jb51.net/, because nginx is very honest and will write such a request into the file system according to the link, and this The link is obviously a directory, so saving fails. In these cases, rewrite is required to save correctly.
Disadvantage 2: There is no mechanism for cache expiration and cleanup inside nginx. These cached files will be permanently stored on the machine. If there are a lot of things to be cached, it will fill up the entire hard disk space. For this purpose, you can use a shell script to clean it regularly, and you can write dynamic programs such as php to do real-time updates.
Disadvantage 3: Only 200 status codes can be cached, so status codes such as 301/302/404 returned by the backend will not be cached. If a pseudo-static link with a large number of visits happens to be deleted, it will continue. The penetration causes the rear end to bear considerable pressure.
Disadvantage 4: nginx will not automatically select memory or hard disk as the storage medium. Everything is determined by the configuration. Of course, there will be an operating system-level file caching mechanism in the current operating system, so there is no need to worry too much about file caching on the hard disk. IO performance problems caused by concurrent reads.
The shortcomings of nginx’s traditional caching are also its different features from caching software such as squid, so it can also be regarded as its advantages. In production applications, it is often used as a partner with Squid. Squid is often unable to block links with ?, but nginx can block their access, such as: http://jb51.net/? and http://jb51.net / will be treated as two links on Squid, so it will cause two penetrations; nginx will only save it once, no matter the link becomes http://jb51.net/?1 or http://jb51.net/? 123, cannot be cached by nginx, thus effectively protecting the backend host.
nginx will very faithfully save the link form to the file system, so that for a link, you can easily check its cache status and content on the cache machine, and you can also easily communicate with other file managers such as Used in conjunction with rsync, etc., it is completely a file system structure.
Both of these two traditional caches can save files to /dev/shm under Linux. Generally, I do this, so that the system memory can be used for caching. If the memory is used, the expiration content will be cleaned up faster. Much more. When using /dev/shm/, in addition to pointing the tmp directory to the /dev/shm partition, if there are a large number of small files and directories, you must also modify the number of inodes and the maximum capacity of this memory partition:
mount -o size=2500m -o nr_inodes=480000 -o noatime,nodiratime -o remount /dev/shm
The above command is used on a machine with 3g of memory. Because the default maximum memory of /dev/shm is half of the system memory, which is 1500m, this command will increase it to 2500m. At the same time, the number of shm system inodes is the default It may not be enough in some cases, but the interesting thing is that it can be adjusted at will. The adjustment here is 480000, which is a bit conservative, but it is basically enough.
3. Cache based on memcached
nginx has some support for memcached, but the function is not particularly strong, and the performance is still very good.
location /mem/ {
if ( $uri ~ "^/mem/([0-9a-za-z_]*)$" )
{
set $memcached_key "$1";
memcached_pass 192.168.1.2:11211;
}
expires 70;
} 这个配置会将http://jb51.net/mem/abc指明到memcached的abc这个key去取数据。
nginx目前没有写入memcached的任何机制,所以要往memcached里写入数据得用后台的动态语言完成,可以利用404定向到后端去写入数据。
4、基于第三方插件ncache
ncache是新浪兄弟开发的一个不错的项目,它利用nginx和memcached实现了一部分类似squid缓存的功能,我并没有使用这个插件的经验,可以参考:
http://code.google.com/p/ncache/
5、nginx新开发的proxy_cache功能
从nginx-0.7.44版开始,nginx支持了类似squid较为正规的cache功能,目前还处于开发阶段,支持相当有限,这个缓存是把链接用md5编码hash后保存,所以它可以支持任意链接,同时也支持404/301/302这样的非200状态。
配置:
首先配置一个cache空间:
复制代码 代码如下:
proxy_cache_path /path/to/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=name:10m inactive=5m max_size=2m clean_time=1m;
注意这个配置是在server标签外,levels指定该缓存空间有两层hash目录,第一层目录是1个字母,第二层为2个字母,保存的文件名就会类似/path/to/cache/c/29/b7f54b2df7773722d382f4809d65029c;keys_zone为这个空间起个名字,10m指空间大小为10mb;inactive的5m指缓存默认时长5分钟;max_size的2m是指单个文件超过2m的就不缓存;clean_time指定一分钟清理一次缓存。
location / {
proxy_pass//www.jb51.net/;
proxy_cache name;#使用name这个keys_zone
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 1h;#200和302状态码保存1小时
proxy_cache_valid 301 1d;#301状态码保存一天
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;#其它的保存一分钟
}ps:支持cache的0.7.44到0.7.51这几个版本的稳定性均有问题,访问有些链接会出现错误,所以这几个版本最好不要在生产环境中使用。nginx-0.7下目前所知较为稳定的版本是0.7.39。稳定版0.6.36版也是近期更新,如果在配置里没有使用到0.7的一些新标签新功能,也可以使用0.6.36版。
nginx缓存的内存占用问题的一般解决方法
1、前些日子某服务被刷,每分钟达到上几百万请求;当时采用了nginx cache来解决的;但是因为某服务不能缓存太久,当时设置了5s,那么带来的问题就是产生大量小文件,而且很快就删除了。
2、通过
free -m
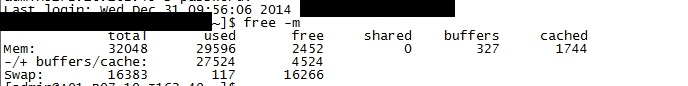
会发现used是27g;但是通过top查看进程占的内存并没有那么多
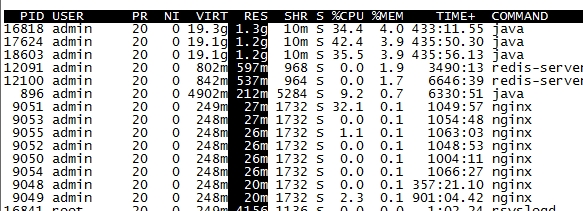
那内存去哪了?
3、通过查阅资料会发现(cat /proc/meminfo)
slab: 22464312 kb
sreclaimable: 16474128 kb (这些是内核保持的但是可以释放的inode和dentry的缓存)
sunreclaim: 5990184 kb
4、这些内存为什么会不自动清理呢?
某机房机器系统版本:linux 2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 #1 smp fri nov 22 03:15:09 utc 2013 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 gnu/linux(正常,没出现内存快到100%的情况)
某机房机器系统版本:linux 2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64 #1 smp fri jun 22 12:19:21 utc 2012 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 gnu/linux (不释放)
5、通过设置如下参数来设置内存阀值
sysctl -w vm.extra_free_kbytes=6436787 sysctl -w vm.vfs_cache_pressure=10000
The above is the detailed content of Nginx Cache configuration plan and how to solve related memory usage problems. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

