 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI The future of artificial intelligence is human-machine environment system intelligence
The future of artificial intelligence is human-machine environment system intelligenceThe future of artificial intelligence is human-machine environment system intelligence

Military intelligence is like war, it is a fog, there is a lot of uncertainty, and it is unpredictable and unpredictable. Judging from the current development trend of artificial intelligence, in the foreseeable future wars, there are many hidden dangers of human-machine integration that have not yet been solved. Specifically, they are:
(1) In complex wars In the information environment, humans and machines absorb, digest, and use limited information within a specific period of time. For humans, the greater the pressure, the more information they misunderstand, and the easier it is to cause confusion, confusion, and accidents. It is still very difficult for machines to learn, understand and predict cross-domain unstructured data.
(2) The information required for decision-making in war is widely distributed in time and space, which determines that some key information is still difficult to obtain. Moreover, it is difficult to coordinate and integrate the important objective physical data collected by machines with the subjectively processed information and knowledge obtained by humans.
(3) In future wars, there will be a large number of nonlinear characteristics and unexpected variability, which often lead to unpredictability in the combat process and results. Based on axioms Formal logical reasoning is far from meeting the needs of decision-making in complex and ever-changing battle situations. In view of the continuous spread and proliferation of nuclear weapons, the cost of future wars between countries, regardless of their size, will become increasingly high. No matter how artificial intelligence develops, the future belongs to mankind. Human beings should jointly define the rules of the game for future wars and determine the fate of artificial intelligence, rather than artificial intelligence deciding the fate of mankind. The reason is that artificial intelligence is logical, and Future wars are not only logical, but also contain a large number of illogical factors.
(4) In view of the different classifications of autonomous equipment in different countries, there is a huge gap in the definition and understanding of the concept of strong artificial intelligence or general artificial intelligence weapons, so the most important work at present is From time to time, it is not about how to solve specific technical problems (technical iterations are updated very quickly), but about how to reach a consensus on the basic concepts and definitions of artificial intelligence applications, such as: ① What is AI? ②What is autonomy? ③What is the difference between automation and intelligence? ④What is the difference between machine calculation and human calculation? ⑤What is the boundary of human-machine function/ability distribution? ⑥What is the relationship between data, AI and risk responsibility? ⑦The difference between computability and decidability, etc.
Some definitions are still very rough and need further refinement. For example, from the perspective of human security, prohibiting autonomous weapons with "people outside the loop" is in line with universal values and reduces the risk of loss of control. It is necessary, but what kind of people are often ignored in the system loop, and some irresponsible people may be worse off in the epidemic prevention system;
(5) For the world On the development of independent technologies, it is recommended to set up a joint assessment team to conduct detailed assessments and early warnings on the development of independent technologies on a regular basis, to check the technological development milestones, to conduct predictive analysis of technological development, and to monitor key institutions and R&D institutions that develop sensitive technologies. personnel to conduct targeted supervision and establish a certain degree of academic openness requirements.
(6) The security risks and challenges faced by the development of AI militarization mainly include:
① Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems may lead to Unexpected escalation of the situation and instability of the crisis;
② Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems will reduce the strategic stability between opponents (such as the strategic relationship between China and the United States, the United States and Russia will become more tense );
③ Different combinations of people and autonomous systems (including people judging human decisions, people judging machine decisions, machines judging human decisions, and machines judging machine decisions) will affect the situation escalation of both parties ;
④Machines have poor understanding of deterrence signals (especially de-escalation signals) sent by humans;
⑤Autonomous systems have no intention of attacking friendly forces or civilians accidents will raise more questions;
⑥ Artificial intelligence and autonomous systems may lead to the instability of an arms race;
⑦ Autonomy The spread of the system could trigger a serious search for countermeasures that would heighten uncertainty and raise security concerns.
Calculation deals with "complexity", and calculation deals with "complexity". Composition writing is a calculation process, but it does not use numbers and graphics, but text symbols.
Human beings cannot completely master the world, but they can try to understand it. This kind of intelligence will give birth to newer philosophical categories and thinking.
In von Neumann's last book on the relationship between the brain and the computer published before his death, "The Computer and the Brain", von Neumann Neumann summarized his views by acknowledging that the brain was not only far more complex than a machine, but that the brain seemed to fulfill its functions along different lines than he originally envisioned. Almost conclusively, he concluded that binary computers were completely unsuitable for simulating the brain. This is because he has almost concluded that the logical structure of the brain is completely different from the logical structure of logic and mathematics. Then, "from the perspective of evaluating the mathematics or logical speech actually used by the central nervous system, the mathematics we use Its external form is completely unsuitable for such work."
Recent scientific research also confirms this. The findings of French neuroscientist Romain Brette fundamentally question the consistency of the underlying architecture of the brain and computers, known as neural coding. Influenced by the metaphor between the brain and the computer, scientists have shifted the connection between stimuli and neurons from a technical sense to a representational sense in which neuronal coding thoroughly represents the stimulus. In fact, how the neural network delivers the signal to the "downstream structure" of the idealized observer in the brain in an optimal way of decoding is still unknown and not clear even in simple models. hypothesis. This metaphor, then, leads scientists to focus only on the connections between sensations and neurons, while ignoring the true impact of animals' behavior on neurons.
The results of the research by Hungarian neuroscientist Gyorgi Bussaki are even more radical. In his book The Brain Inside Out, Bussaki points out that the brain does not actually represent information by encoding it, but rather constructs it. In his view, the brain does not simply passively accept stimuli and then represent them through neural coding, but actively searches for various possibilities to test various possible options. This is undoubtedly a complete overthrow of the metaphor of using computers as a metaphor for the brain.
Whether it is from the perspective of brain science or computer science, the metaphorical lifespan of comparing the brain to a computer may no longer last. Cobb keenly pointed out that this kind of metaphor has been applied to people's research on computers, blinding people and narrowing the scope of the real research.
The above is the detailed content of The future of artificial intelligence is human-machine environment system intelligence. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
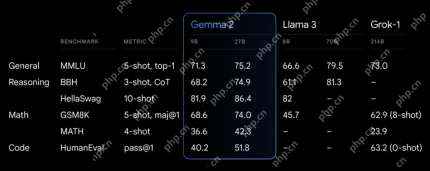 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.




