Home >Operation and Maintenance >Safety >How to analyze and detect Rapid ransomware virus
How to analyze and detect Rapid ransomware virus
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-13 18:10:061583browse
Ransomware has always been a hot topic in the security industry. Recently, security personnel have discovered a ransomware called rapid. This ransomware uses RSA and AES to encrypt files. It will not only infect files already on the computer. Some files will also encrypt newly created files. This article conducts a detailed analysis of the rapid virus, analyzes its encryption mechanism, and parses its encrypted files.
1.Overview
When the rapid virus runs, it will create multiple threads to continuously scan the file system and encrypt files. It will not only infect the computer Existing files on the computer will also be encrypted for newly created files. The encrypted file has a ".rapid" extension added to its file name, and the file size is increased by 0x4D0 bytes.
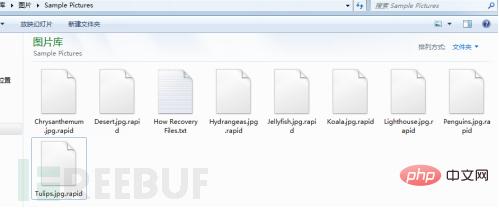
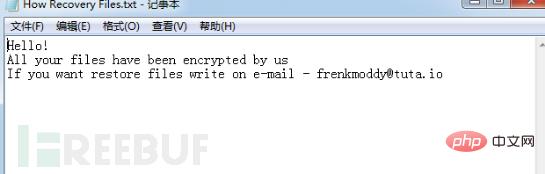
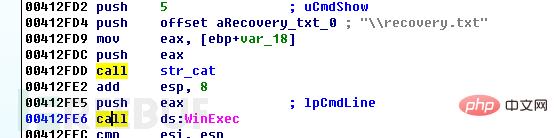
The rapid virus will create a ransom note file named "How Recovery Files.txt" in the encrypted folder, which contains an email. Let the victim contact you on how to complete the payment. When the user restarts the computer, a ransomware prompt file named "recovery.txt" will automatically pop up. Its content is the same as the content of the "How Recovery Files.txt" file.
2.Detailed analysis
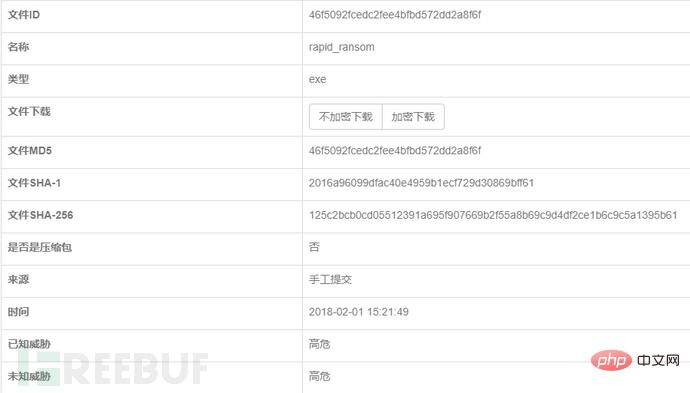
Use the LanyEye next-generation threat perception system to detect rapid programs. In Lan's eyes, the rapid program was marked as high-risk:
Next, conduct a reverse analysis of the rapid program.
First, the program calls ShellExecuteA to execute the command shown in the figure:
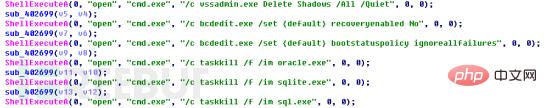
The main function includes clearing Windows volume shadow copies and preventing victims from using shadow volumes Copy the recovery files. Disable system repair and automatic modification functions. Ransomware may encrypt driver files and cause frequent system crashes. Disable repair functions and ignore errors to reduce the probability of system crashes. Terminating the oracle.exe, sqlite.exe, and sql.exe processes can, on the one hand, release memory, and on the other hand, relieve the occupation of certain files by these database processes.
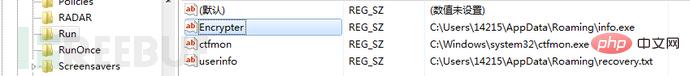
Then the program adds a startup item, and creates new Encrypter and userinfo items under the registry HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run. The Encrypter item value is "%AppData\Romaing\info.exe", userinfo The key value is "%AppData\Romaing\recovery.txt". The "info.exe" file is a copy of the ransomware program itself, and the "recovery.txt" file is a ransomware information file. The content of the file is the same as the "How Recovery Files.txt" file mentioned above.

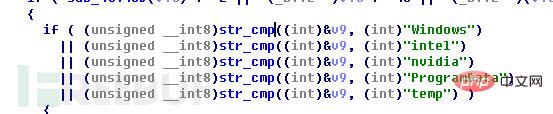
In order to ensure that the system can run normally, the program will not select the folder name "Windows" , "intel", "nvidia", "ProgramData" and "temp" files:
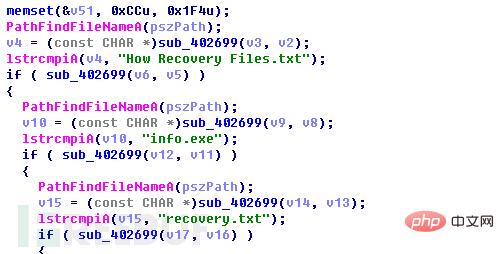
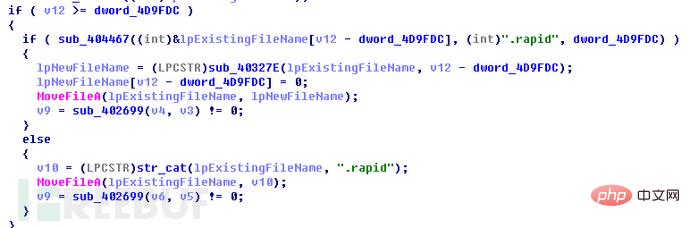
This ransomware does not filter files by suffix name but Determine whether the selected file is "How Recovery Files.txt", "info.exe", or "recovery.txt". If it is three of the files, skip it and the rest are fully encrypted.
2.1.Encryption process
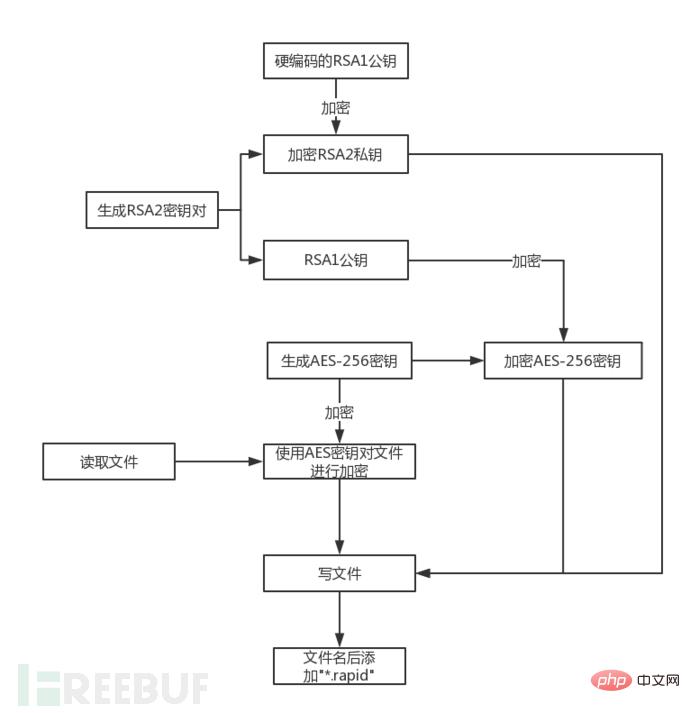
The program is first created A CSP container of type PROV_RSA_FULL and then import the RSA public key (named RSA1) hard-coded in the program via Base64.
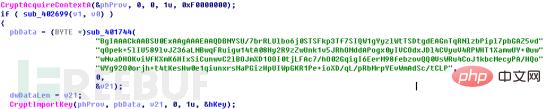
Then the program will check whether the registry key "local_public_key" exists. If not, the registry key "local_public_key" will be created
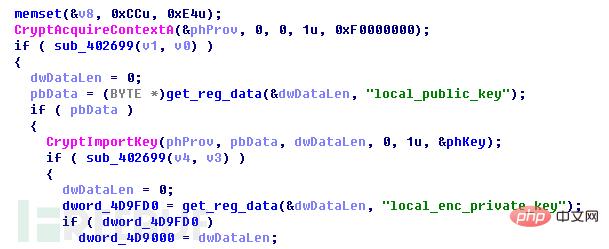
The program creates a CSP container of type PROV_RSA_FULL and calls CryptGenKey() to generate a random RSA key Right (named RSA2).

Then call CryptExportKey() to export the RSA2 private key data just generated, and call the RSA1 public key to encrypt the RSA2 private key. After the encryption is completed, write the RSA private key data to the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\EncryptKeys\local_enc_private_key, and write the data length to the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\EncryptKeys\local_enc_private_key_len
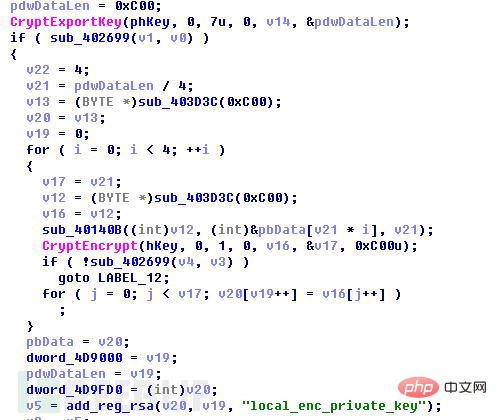
Call CryptExportKey() again to export the random RSA2 public key data just generated. This time no encryption is required, and it is directly written to the registry HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\EncryptKeys\local_public_key and HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\EncryptKeys\local_public_key_len.
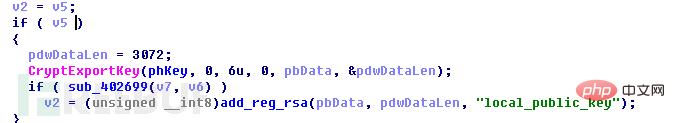
Then start to encrypt the file and get the size of the selected file. If the file size is less than 0x4D0 bytes, enter the encryption process directly; otherwise, read the 0x20 bytes at the end of the file. data, and determine whether this part of the data is the encryption mark "F5 D5 CD CD CD 7D CD CD 95 91 C1 C1 CD AD CD CD 41 CD 41 CD C1 99 FD 1D 59 95 81 FD 99 79 25 A5", if not then Enter the encryption process, otherwise select the next file. Because the encrypted file is larger than 0x4D0, and an encryption flag of 0x20 bytes is added to the end of the file

After the program enters the encryption process, it will first Call CryptGenKey() to generate a random AES key.

And call CryptExportKey() to export the AES key data, BLOBTYPE=PLAINTEXTKEYBLOB:

As shown in the figure, the data length returned is 0x2C, 0x3A42A8-0x3A42AF is BLOBHEADER, 0x3A42B0-0x3A42B3 is keysize, 0x3A42B4-0x3A42D3 is the AES key, 0x3A42D4-0x3A4327 is the data filled with 0xCD:
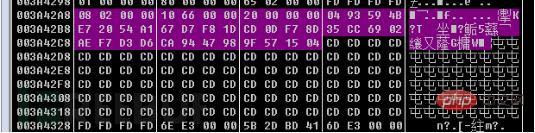
Use the RSA2 public key to encrypt the AES key. What is encrypted is the entire 0x80-byte data of the "BLOB format data AES key padding data" mentioned above:

Read the file data and use the AES key to encrypt the read file data:

AES Encryption is grouped according to 128 bits. When the number of bytes in the original file is not an integer multiple of 128 bits, the encrypted ciphertext data will be larger than the plaintext data, so the program fills 0x10 bytes of 0x00 (a The number of bytes in the AES packet).
Overwrite the encrypted data to the file. First, only the ciphertext data of the original file size is written, and the increased 0x10-byte data is written next;
Continue to write to the file Write data, write 0x4D0 byte data. This 0x4D0 byte data consists of five parts: the first part is 0x10 bytes, which is the variable data; the second part is 0x20 bytes, which contains the source file size string and 0xCD padding data; the third part is 0x80 words. section is the encrypted AES key data; the fourth part, 0x400 bytes, is the encrypted RSA2 private key data; the fifth part, 0x20 bytes, is the file encryption flag data.
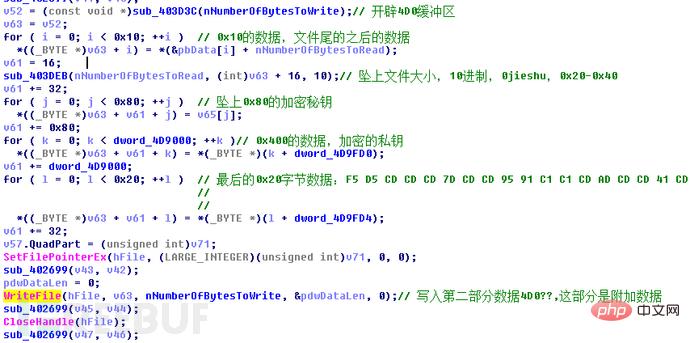
Add ".rapid" extension after the file name:
Show ransomware Information
So far, we have analyzed the file encryption process of rapid ransomware. Next, let’s analyze the encrypted files.
3.Encrypted file analysis
Assume that a file with a size of 0x9000 bytes is encrypted by the rapid program. The encrypted file structure is as follows:
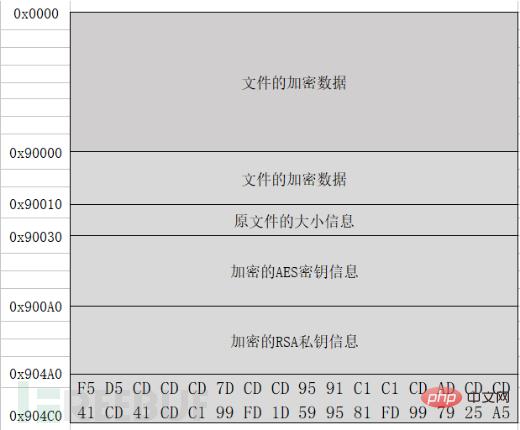
The rapid ransomware virus uses digital signatures (RSA_AES-256) to encrypt files. To decrypt files, you need to obtain the private key of the digital signature. However, the private key of the array signature is encrypted with RSA. Without the RSA private key, it is difficult to obtain the private key of the digital signature, and file recovery is extremely difficult.
2017 was a year of high incidence of ransomware viruses, and it is foreseeable that this situation will continue in 2018. Each of us should be more vigilant, never open attachments from suspicious mailboxes, avoid using third-party software resources, and install Anti-virus software to reduce security risks.
The above is the detailed content of How to analyze and detect Rapid ransomware virus. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

