Home >Java >javaTutorial >How Java and SpringBoot use redis
How Java and SpringBoot use redis
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-12 20:31:041031browse
1. Java connects to redis
What languages does redis support and can be operated (check the redis official website)
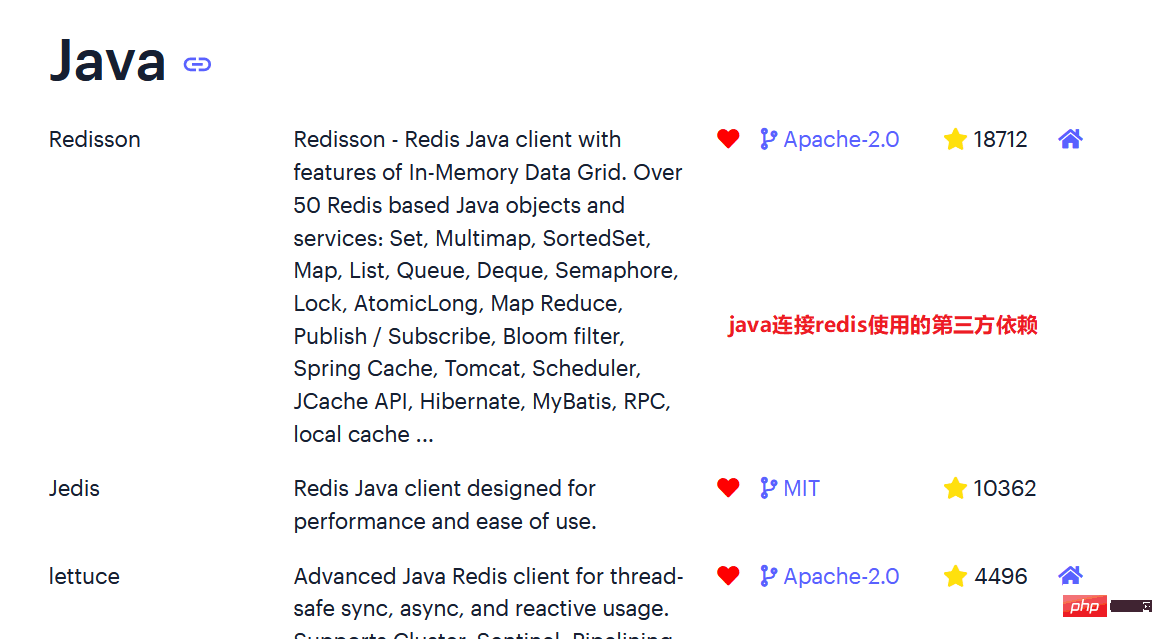
1.1 Use Jedis
(1) Add jedis dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<!--只能在测试类中使用-->
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.6.0</version>
</dependency>(2) Code test
public class TestJedis {
@Test
public void test01(){
//连接redis--必须保证你的redis服务运行远程连接
//该对象把每个redis命令封装成对应的方法
//注意端口号
//xshell中的redis要运行起来,注意防火墙释放端口号,注意配置文件的修改
Jedis jedis=new Jedis("192.168.1.16",6379);
//对于字符串操作的命令
String set = jedis.set("k1", "v1");
System.out.println(set);
String set1 = jedis.set("k2", "v2");
System.out.println(set1);
String set2 = jedis.set("k3", "v3");
System.out.println(set2);
//对于hash的操作
jedis.hset("k4","name","小花");
Long hset = jedis.hset("k4", "age", "18");
System.out.println(hset);
Map<String ,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","小明");
map.put("age","20");
Long k = jedis.hset("k5", map);
System.out.println(k);
jedis.close();
}
}1.2 Use connection pool Connecting to redis
@Test
public void test02(){
//创建连接池的配置类
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig=new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(20);
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(5);
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWait(Duration.ofMillis(3000));
JedisPool jedisPool=new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig,"192.168.1.16",6379);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
//从jedis连接池获取资源
Jedis jedis=jedisPool.getResource();
String ping = jedis.ping();
jedis.close();//是否关闭池子
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
//是为了比较使用池子还是不使用快,结论是使用池子快
System.out.println("总耗时:"+(end-start));
}1.3 Java connecting to redis cluster mode
When connecting to the cluster, make sure there is no value stored in the cluster. If there is a value stored, you need to delete the previously generated file (make sure to delete it cleanly)
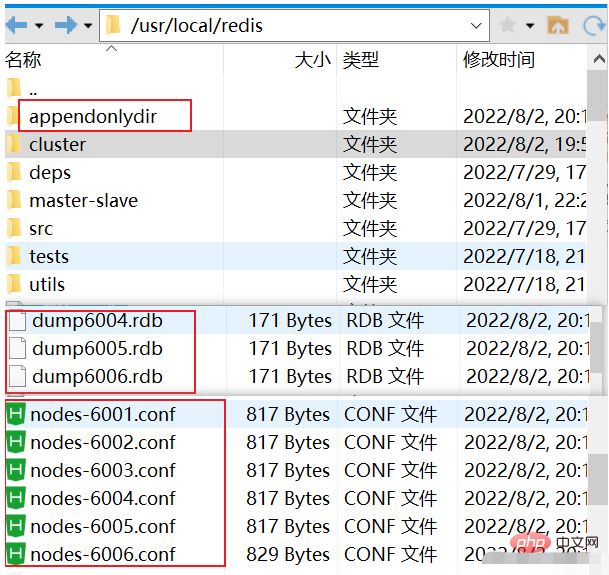
The other is to release the corresponding ports: 6001, 6002, 6003, 6004, 6005, 6006, because the port that was released before was actually 10000. Pay attention to the above two points before you can use the idea to create it successfully. .
@Test
public void test03(){
Set<HostAndPort> nodes=new HashSet<>();
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6001));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6002));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6003));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6004));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6005));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.227.175",6006));
JedisCluster jedisCluster=new JedisCluster(nodes);
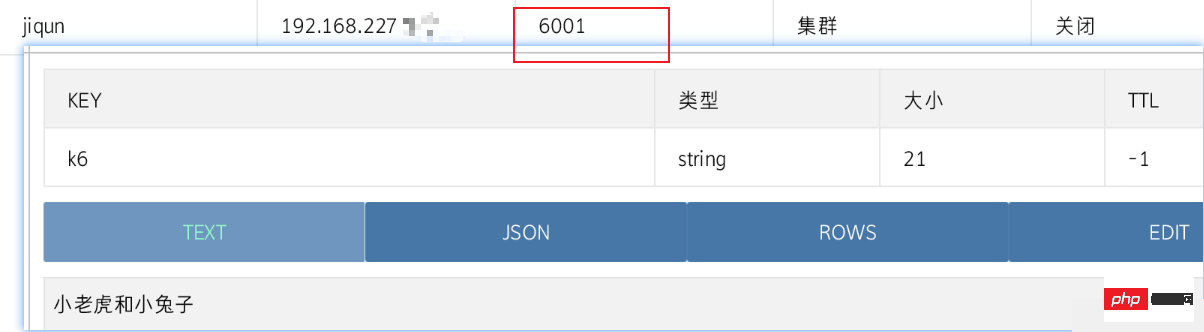
jedisCluster.set("k6", "小老虎和小兔子");
jedisCluster.close();
}
2. SpringBoot integrates redis
springboot’s operation of redis encapsulates two StringRedisTemplate and RedisTemplate classes. StringRedisTemplate is a subclass of RedisTemplate, and StringRedisTemplate it Only string types can be stored, object types cannot be stored. If you want to use StringRedisTemplate to store objects, you must convert the object into a json string.
When springboot integrates redis, it provides two template tool classes, StringRedisTemplate and RedisTemplate.
2.1 StringRedisTemplate
(1) Introduce related dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)Inject StringRedisTemplate object of this class
@Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
(3) Use StringRedisTemplate
This class seals the corresponding internal class separately for operations on each data type.
There will be no garbled characters here because the serialization and deserialization methods have been changed to String type.
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void test01(){
//对hash类型的操作
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> forHash = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash();
forHash.put("k1","name","张三");
forHash.put("k1","age","15");
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","李四");
map.put("age","25");
forHash.putAll("k36",map);
Object o = forHash.get("k1", "name");
System.out.println(o);
Set<Object> k1 = forHash.keys("k1");
System.out.println(k1);
List<Object> k11 = forHash.values("k1");
System.out.println(k11);
//获取k1对于的所有的field和value
Map<Object, Object> k12 = forHash.entries("k1");
System.out.println(k12);
}
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//删除指定的key
// stringRedisTemplate.delete("k");
//查看所有的key
//stringRedisTemplate.keys("k");
//是否存在指定的key
//stringRedisTemplate.hasKey("k");
//对字符串数据类型的操作ValueOperations
ValueOperations<String, String> forValue = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
//存储字符串类型--key value long uint setex()
forValue.set("k1","张三",30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//等价于setnx 存入成功返回true ,失败返回false
Boolean absent = forValue.setIfAbsent("k11", "李四", 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(absent);
//append拼接
Integer append = forValue.append("k11", "真好看");
String k11 = forValue.get("k11");
System.out.println(k11);
}2.2 RedisTemplate
There will be garbled characters here because its serialization and deserialization methods default to JDK.
@SpringBootTest
class SbredisApplicationTests02 {
//当你存储的value类型为对象类型使用redisTemplate
//存储的value类型为字符串。StringRedisTemplate 验证码
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void test01(){
//必须认为指定序列化方式
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class));
//对String类型操作类
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//redis中key和value都变成了乱码
//key和value都没有指定序列化方式,默认采用jdk的序列化方式
forValue.set("k1","张三");
//value默认采用jdk,类必须实现序列化接口
forValue.set("k44",new User(1,"haha",12));
}
}The above RedisTemplate needs to specify the key value and field serialization method every time. Can you create a configuration class that has already specified serialization for RedisTemplate? No need to specify if used later.
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化 filed value
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
return template;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How Java and SpringBoot use redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

