Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to operate the sequence table of Java data structure
How to operate the sequence table of Java data structure
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-12 20:22:04961browse
Preface
A linear list is a finite sequence of n data elements with the same characteristics. Linear tables are a data structure that is widely used in practice. Common linear tables include sequential lists, linked lists, stacks, queues, strings... A linear list is logically a linear structure, that is, a continuous straight line. . However, the physical structure is not necessarily continuous. When linear tables are physically stored, they are usually stored in the form of arrays and linked structures.
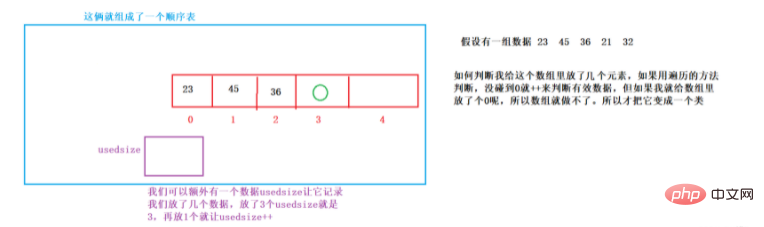
1. What is a sequence table
The concept and structure of a sequence table
A sequence table is a linear structure that uses a storage unit with a continuous physical address to store data elements in sequence. Generally, In this case, array storage is used. Complete the addition, deletion, checking and modification of data on the array
is actually an array. Then why do you need to write a sequence table? Wouldn't it be better to just use an array? The difference is that writing it in a class can be object-oriented.
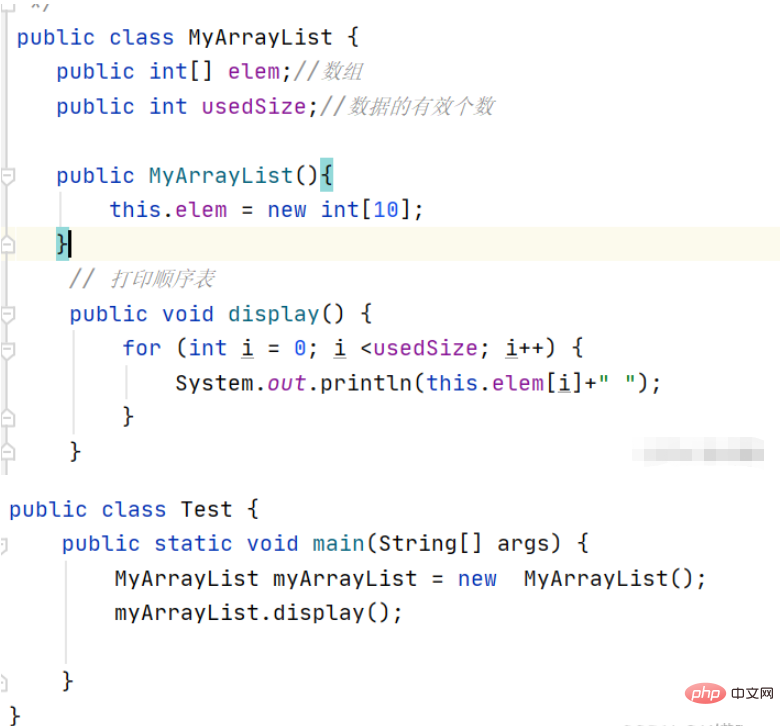
Create sequence table
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;//数组
public int usedSize;//数据的有效个数
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
}Print sequence table

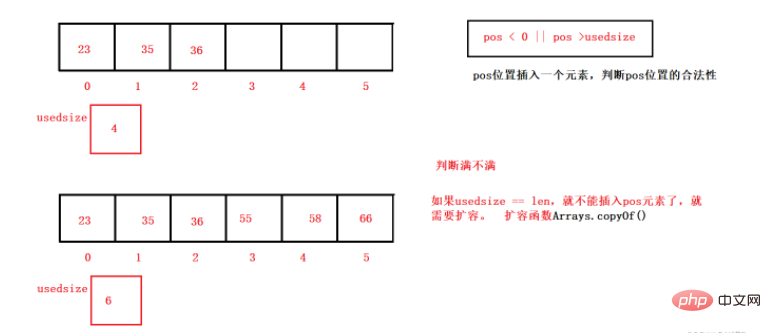
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > usedSize){
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2);
}
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >=pos ; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}Print result:
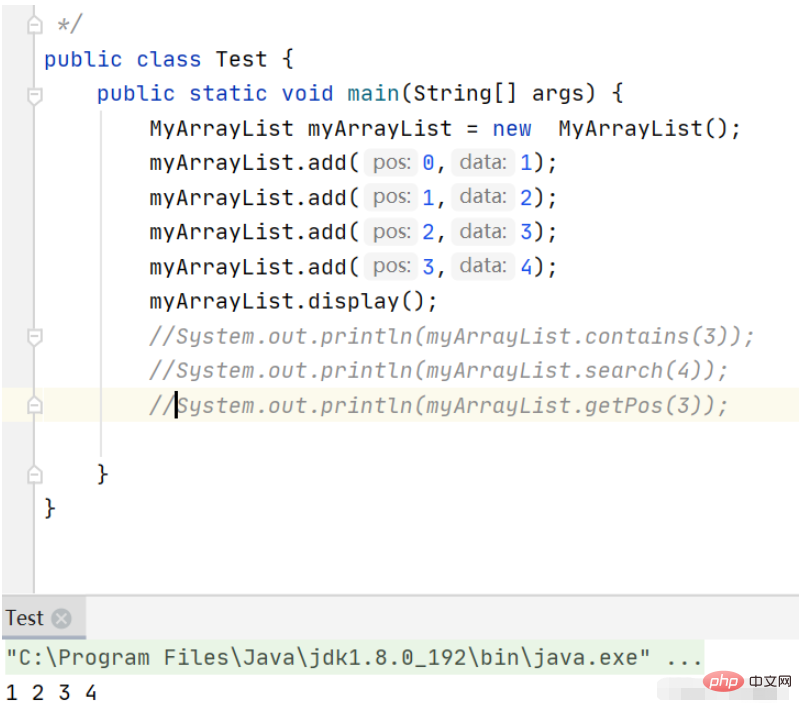
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Print result:
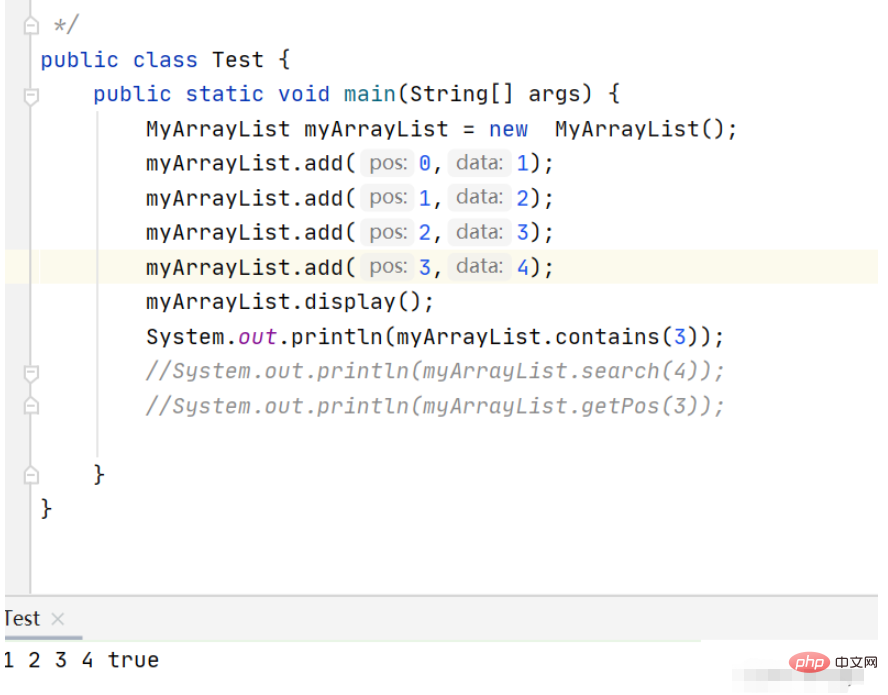
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
Print result:
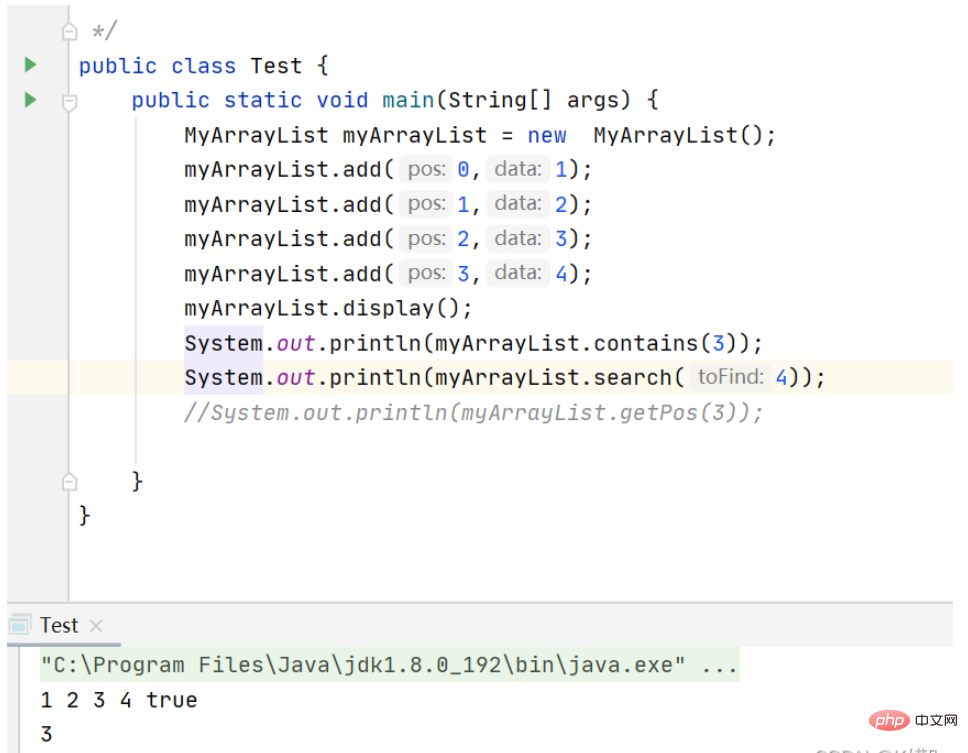 ##Get the element at pos position
##Get the element at pos position
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize){
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return -1;//所以,这里说明一下,业务上的处理,这里不考虑
}
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("顺序表为空");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){//判断为不为空的情况下
return this.usedSize == 0;
}Print result:
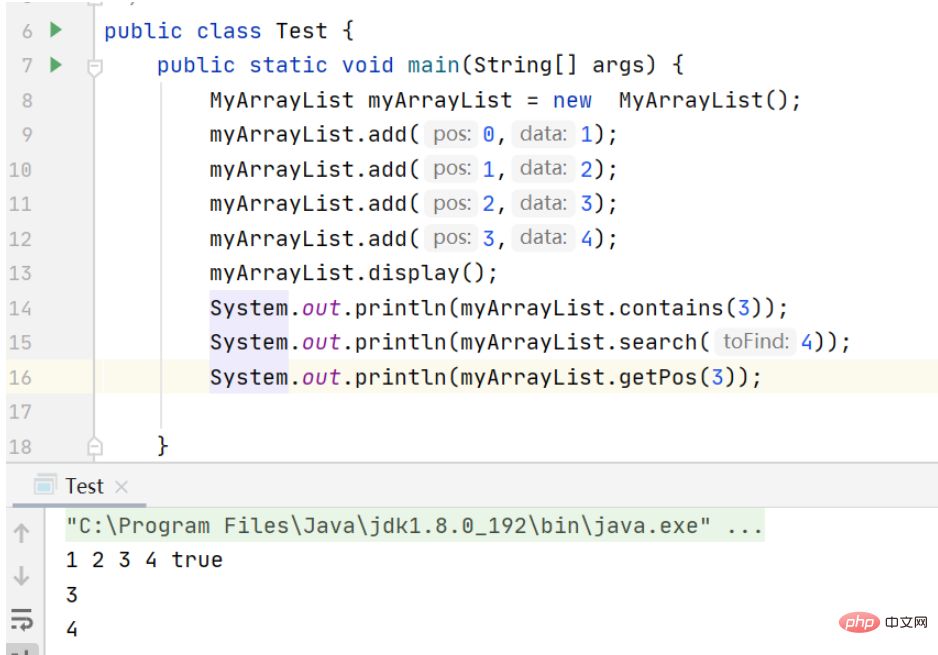 Set the element at pos position to value
Set the element at pos position to value
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return ;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {//判断为不为空的情况下
return this.usedSize == 0;
}Print the result:
##Delete the element you want to delete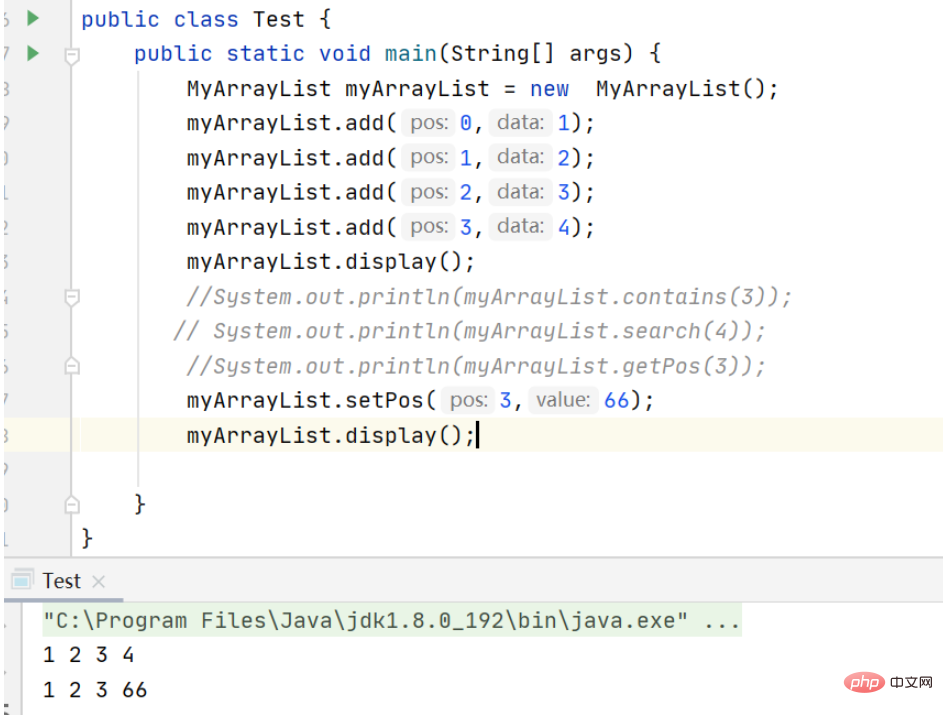
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("顺序表为空");
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);//查找要删除元素对应的位置
if(index == -1){
System.out.println("没有你要找到数字");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <this.usedSize-1 ; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
} Print result:
The above is the detailed content of How to operate the sequence table of Java data structure. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

