Home >Operation and Maintenance >Nginx >How Nginx implements load balancing
How Nginx implements load balancing
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-11 20:07:044629browse
1. Introduction to Nginx
Nginx is a high-performance Http and reverse proxy server, and also an IMAP/POP3 /SMTP server (email proxy), one of the earliest purposes of developing this product is also as a mail proxy server. It is widely used in various production deployments due to its stability, rich feature set, sample configuration files, low system resource consumption and high concurrency performance. Moreover, nginx implements I/O multiplexing based on the event-driven model (epoll), and processes requests in an asynchronous and non-blocking manner. In the case of high connection concurrency, Nginx is a good alternative to the Apache server. And why should we choose Nginx?
2. Nginx features
High concurrency and high performance;
High reliability (can be uninterrupted 7*24 hours Run);
Strong scalability (highly modular design, adding modules smoothly);
As a Web server: Compared with Apache, Nginx uses fewer resources and supports more concurrent connections;
serves as a load balancing server: it can be customized and configured to support virtual hosts, URL redirection, network monitoring, etc. .
Nginx installation is very simple, the configuration file is very concise (it can also support perl syntax), and there are few bugs;
Processes static files and indexes File and automatic indexing;
Reverse proxy acceleration (no cache), simple load balancing and fault tolerance;
Supports hot deployment (can Upgrade nginx without stopping the server).
This is why you should choose Nginx. And the functions and features of Nginx are not limited to these. The above is just a brief list of some common functions.
3. Nginx Load Balancing
In our actual production, the processing power and storage space of a server are limited. Do not try to change to a more powerful server. For large-scale As far as websites are concerned, no matter how powerful the server is, it cannot meet the continuous growth of the business needs of the website. In this case, a more appropriate approach is to add a server to share the access and storage pressure of the original server. In fact, this is what we call Load Balancing. As a load balancing server, Nginx uses a reverse proxy to load balance multiple back-end servers. First, let’s talk about Nginx load balancing strategy and load balancing algorithm.
3.1 Understanding the upstream module
upstream This module writes a set of proxy server addresses (that is, selects a server from the defined back-end server list to accept user requests), and then configures the load balanced algorithm. Let’s take a look at the most basic load balancing example:
upstream test {
server 10.20.151.114:80;
server 10.20.151.115:80;
}
server {
....
location / {
proxy_pass http://test; --请求转向 test 定义的服务器列表
}3.2 Nginx load balancing strategy
(1) Polling
The most basic configuration method, the above example is round robin The query method is the default load balancing strategy of the upstream module. Each request is distributed to a different backend server one by one in chronological order.
upstream test {
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2;
}(2) ip_hash
Each request is assigned according to the hash result of the accessed IP. The same IP client always accesses a back-end server. It can ensure that requests from the same IP are sent to a fixed machine, which can solve the session problem.
upstream test {
ip_hash; --同一个IP客户端固定访问一个后端服务器
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2;
}(3) url_hash
Distribute requests according to the hash result of the accessed URL, so that each URL is directed to the same back-end server. Once the resource is cached, it can be read from the cache when a request is received.
upstream test {
hash $request_uri; --实现每个url定向到同一个后端服务器
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2;
}(4) least_conn
Forward the request to the backend server with fewer connections. The polling algorithm forwards requests to each backend evenly so that their loads are roughly the same; however, some requests take a long time, which will cause the backend where they are located to have a higher load. In this case, least_conn can achieve better load balancing effect.
upstream test {
least_conn; --把请求转发给连接数较少的后端服务器
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2;
}(5) weight
Weight method specifies the probability of polling based on the polling strategy.
upstream test {
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2; --轮询的几率相对上一条要大
}(6) fair
This algorithm can intelligently perform load balancing based on page size and loading time, that is, allocate requests based on the response time of the back-end server, with a short response time priority allocation.
upstream test {
server 10.20.151.114:80; weight=1;
server 10.20.151.115:80; weight=2;
fair; --实现响应时间短的优先分配
}nginx load balancing configuration status parameters
down: Indicates that the current server does not participate in load balancing temporarily.
backup: Reserved backup machine. The backup machine will be requested when all other non-backup machines fail or are busy, so this machine has the least pressure.
max_fails: The number of allowed request failures, the default is 1. When the maximum number of times is exceeded, the error defined by the proxy_next_upstream module is returned.
fail_timeout: After experiencing max_fails failures, the time unit for suspending the service is seconds. max_fails can be used together with fail_timeout.
Nginx可分为二层、三层、四层、七层负载均衡。 所谓的二层就是基于MAC地址的负载均衡, 三层就是基于IP地址的负载均衡,四层就是基于IP+端口的负载均衡,七层就是基于URL等应用层信息的负载均衡。因篇幅较长这里不再做具体的介绍,有兴趣的可自行百度。这里以七层负载均衡来做实例。
3.3 Nginx负载均衡实例
环境准备:准备3台Nginx服务器,一台作为负载均衡服务器,其它两台作为后端服务器。
10.20.151.240 ----proxy_server(负载均衡服务器)
10.20.151.112 ----server1(后端服务器1)
10.20.151.113 ----server2(后端服务器2)
(1)负载均衡服务器配置
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf --配置主配置文件 vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf --配置子配置文件
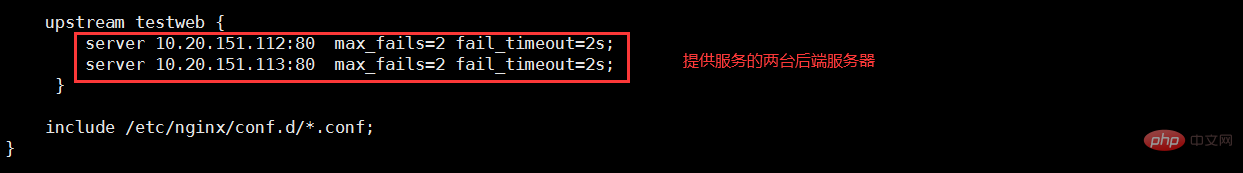
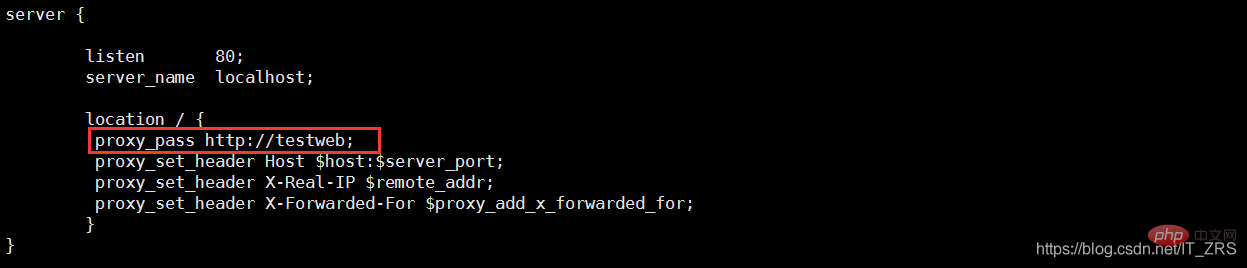
(2)后端服务器配置
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf --修改配置文件 vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html --添加测试数据
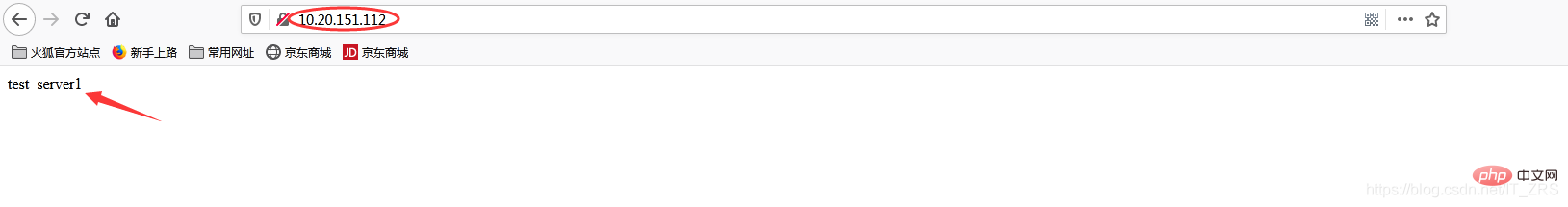
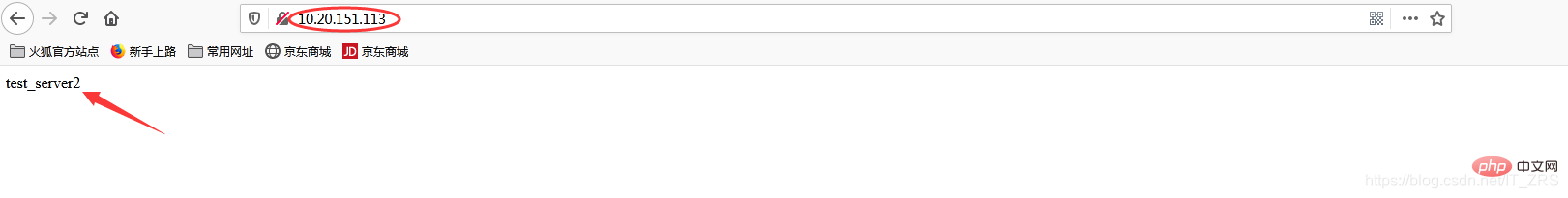
(3)负载均衡测试
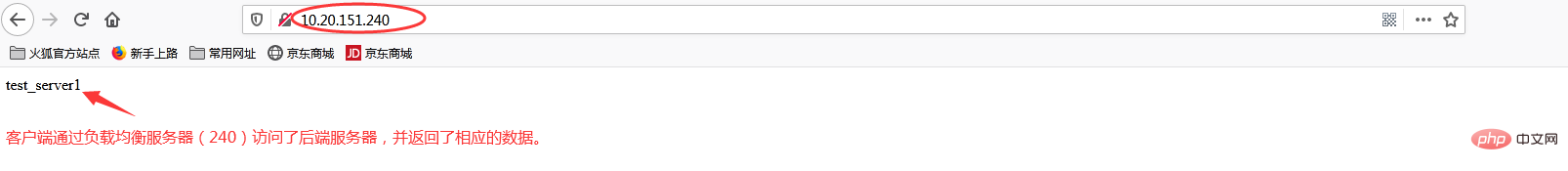
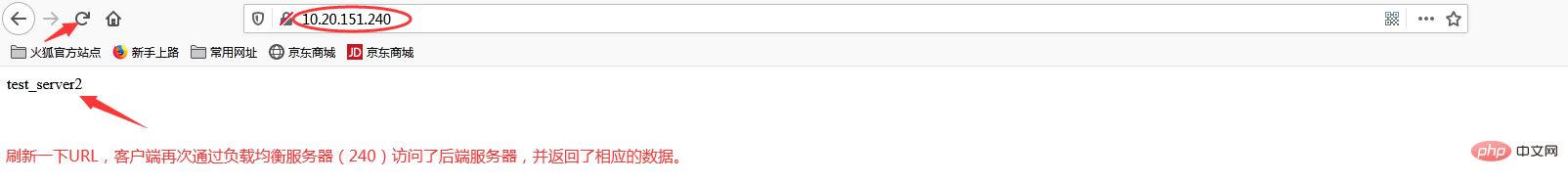
在浏览器端访问http://10.20.151.240/,在实际生产中,这两个页面返回的结果是一样的,这里是为了测试效果,所以返回了不同的内容。而为什么刷新后又会返回不同结果呢?那是因为负载均衡默认的均衡策略(或算法)是轮询,所以每刷新一次就会从不同的后端服务器返回不同的请求结果,减轻单个后端服务器的访问量,提升客户端的访问效率,从而达到负载均衡的效果。
当我添加权重(weight)时

再次访问http://10.20.151.240/
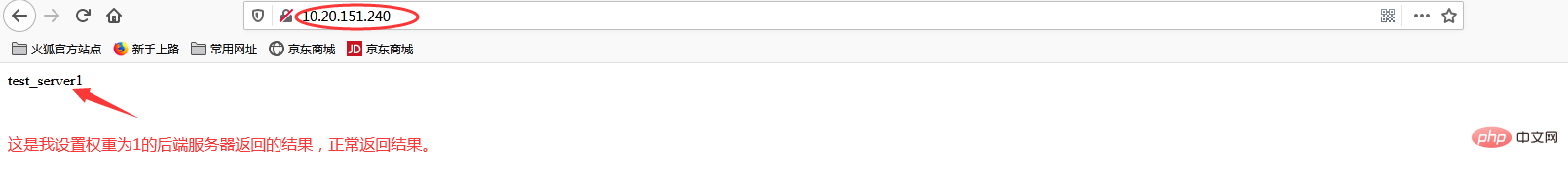
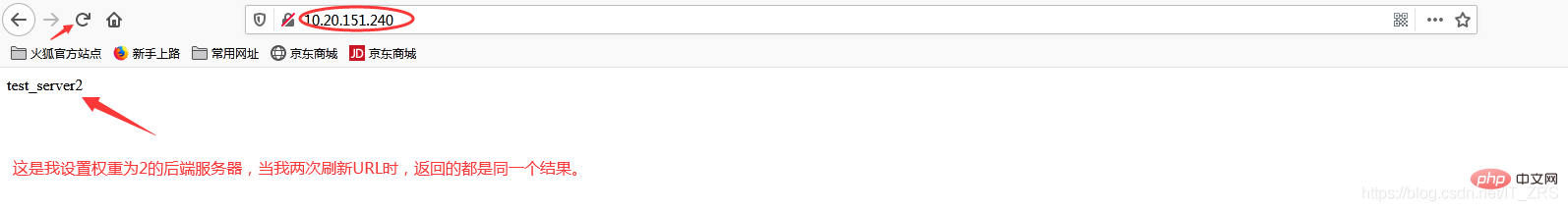
加权重和没加权重有什么区别呢?在实际生产中,我们一般会将配置较高的服务器的权重设置高一点,其实就是客户端在访问时,权重较高的服务器会被多次请求,这样能减轻配置较低的服务器的请求量,从而更好的实现负载均衡。
当我添加backup状态参数时

再次访问http://10.20.151.240/
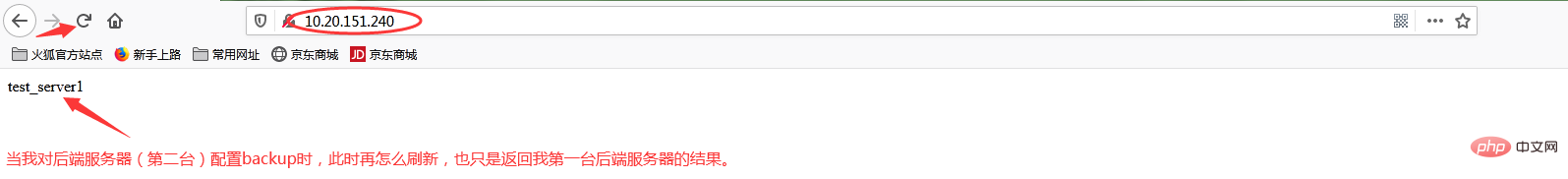
此时我故意停掉第一台后端服务器,继续访问http://10.20.151.240/
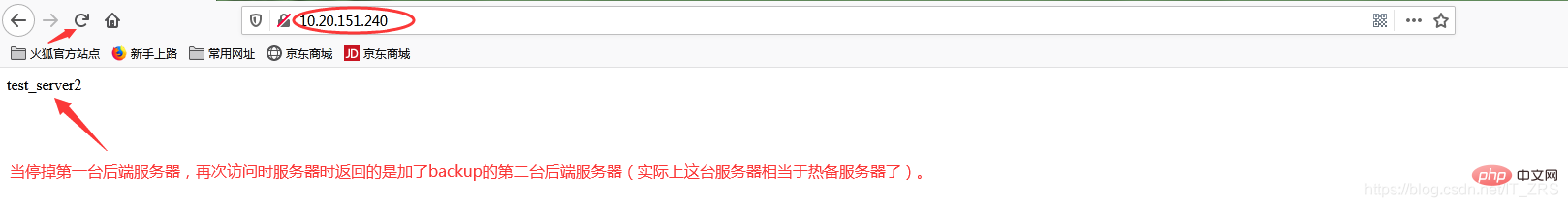
当我给113这台后端服务器添加backup后,它就会作为热备服务器,添加的主要目的就是当我其他后端服务器都宕机的情况下,我的热备服务器还能继续提供同样的服务(注意:在其他后端服务器还未宕机之前,该热备服务器是不工作的)。因此负载均衡不仅能达到各个后端服务器负载的均衡,同时通过配置相关转态参数还能保证客户端请求时不造成服务器宕机的情况,保证了后端服务器的稳定性。其他状态参数这里我不再做演示(因为配置方式都一样)。
The above is the detailed content of How Nginx implements load balancing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

