Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to implement dichotomy in Java
How to implement dichotomy in Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-03 10:04:06947browse

In an ordered array, find whether a certain number exists

- Since it is an ordered array, you can first get the midpoint position, and the midpoint can divide the array into left and right halves.
- If the value of the midpoint position is equal to the target value, return the midpoint position directly.
- If the value of the midpoint position is less than the target value, go to the left side of the midpoint of the array and search in the same way.
- If the value of the midpoint position is greater than the target value, take the right side of the midpoint of the array and search in the same way.
- If not found at the end, return: -1.
class Solution {
public int search(int[] arr, int t) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 1) {
return -1;
}
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (arr[m] == t) {
return m;
} else if (arr[m] > t) {
r = m - 1;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}Time complexity O(logN).
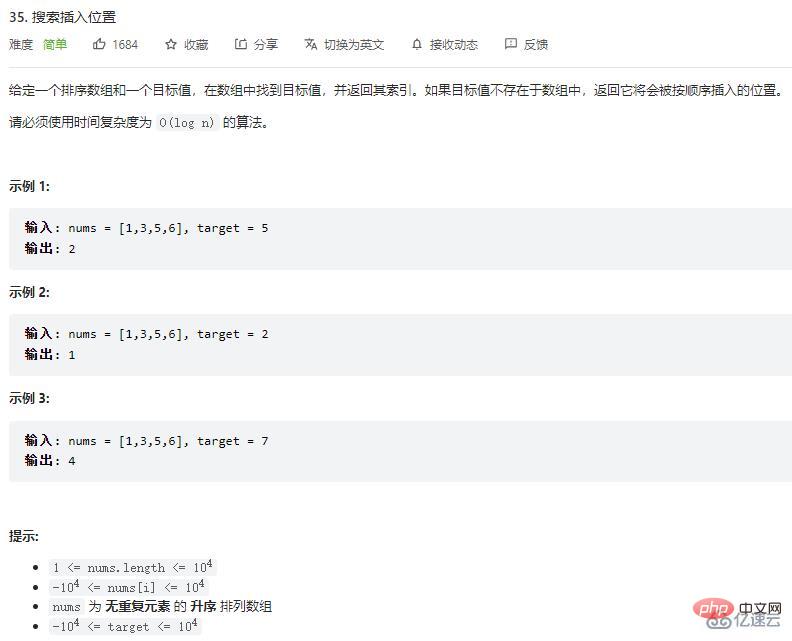
num, It should be inserted between element 3 and element 5, that is, position 2.
num, it should be inserted at the position between element 1 and element 3, that is, position 1.
num, it should be inserted at the end of the array, that is, at position 4.
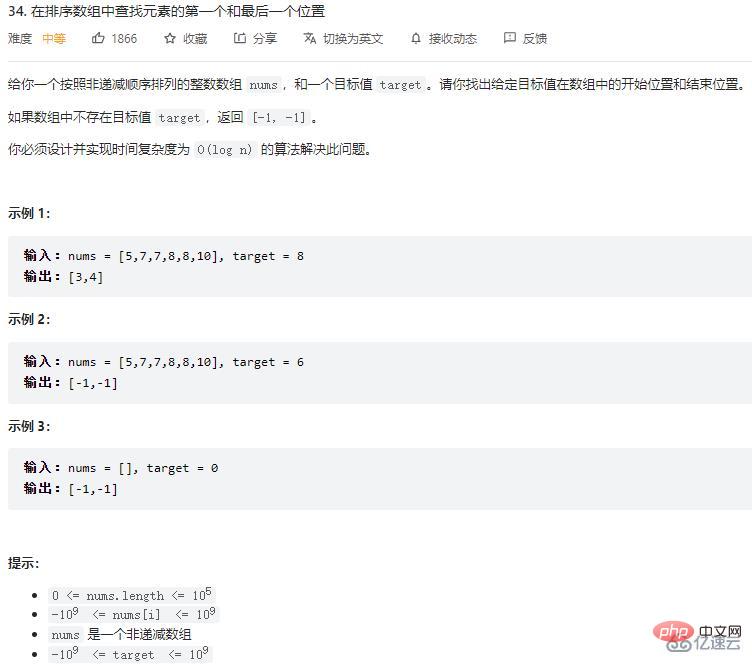
In an ordered array, find the leftmost position that is greater than or equal to a certain number. If it does not exist, return the length of the array (representing Insert at the end position)
We only need to make simple changes based on the above example. In the above example, if we find the position that meets the conditions, we can directlyreturn
if (arr[m] == t) {
return m;
}In this question, because we need to find the leftmost position, when encounters equality, we only need to record the position first, without returning directly, and then continue to search on the left Is there any position further to the left that meets the conditions?
At the same time, when encounteringarr[m] > t, you also need to record the m position at this time, because this may also is a location that satisfies the conditions.
class Solution {
public static int searchInsert(int[] arr, int t) {
int ans = arr.length;
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + ((r - l)>>1);
if (arr[m] >= t) {
ans = m;
r = m - 1;
} else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}The time complexity of the entire algorithm is O(logN).
class Solution {
public static int[] searchRange(int[] arr, int t) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 1) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
return new int[]{left(arr,t),right(arr,t)};
}
public static int left(int[] arr, int t) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 1) {
return -1;
}
int ans = -1;
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (arr[m] == t) {
ans = m;
r = m - 1;
} else if (arr[m] < t) {
l = m +1;
} else {
// arr[m] > t
r = m - 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static int right(int[] arr, int t) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 1) {
return -1;
}
int ans = -1;
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (arr[m] == t) {
ans = m;
l = m + 1;
} else if (arr[m] < t) {
l = m +1;
} else {
// arr[m] > t
r = m - 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}Time complexity O(logN).
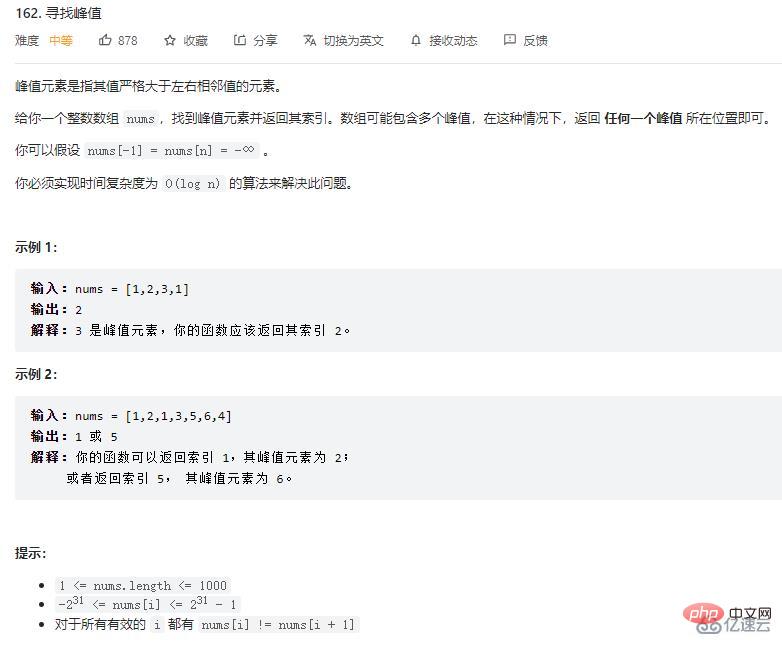
N, first determine 0 Are the number at position and the number at position N-1 the peak position? The
0 position only needs to be compared with the 1 position. If the 0 position is larger, the 0 position It is the peak position and can be returned directly. The
N-1 position only needs to be compared with the N-2 position. If the N-1 position is larger, Position N-1 is the peak position and can be returned directly.
0 position and N-1 are both minimum values in the last round of comparison, then the array must look like the following:

[0..1] interval is a growth trend, [N-2...N-1] Within the range is a downward trend.
[1...N-2].
bisection, first go to the midpoint position, assuming it is mid, if the value of the midpoint position is greater than the value of the left and right sides Duda:
arr[mid] > arr[mid+1] && arr[mid] > arr[mid-1]then the
mid position is the peak position and returns directly.

[1...(mid-1)] interval.

则在[(mid+1)...(N-2)]区间内继续上述二分。
完整代码
public class LeetCode_0162_FindPeakElement {
public static int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) {
return 0;
}
int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
if (nums[l] > nums[l + 1]) {
return l;
}
if (nums[r] > nums[r - 1]) {
return r;
}
l = l + 1;
r = r - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1] && nums[mid] > nums[mid - 1]) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[mid] < nums[mid + 1]) {
l = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[mid - 1]) {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}时间复杂度O(logN)。
The above is the detailed content of How to implement dichotomy in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

