 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI With full coverage of values and privacy protection, the Cyberspace Administration of China plans to 'establish rules” for generative AI
With full coverage of values and privacy protection, the Cyberspace Administration of China plans to 'establish rules” for generative AIWith full coverage of values and privacy protection, the Cyberspace Administration of China plans to 'establish rules” for generative AI
On April 11, the Cyberspace Administration of China (hereinafter referred to as the Cyberspace Administration of China) drafted and released the "Measures for the Management of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services (Draft for Comments)" and launched a month-long solicitation of opinions from the public. .

This management method (draft for comments) has a total of 21 articles. From the scope of application, it includes both the entities that provide generative artificial intelligence services and the users of these services. organizations and individuals; the management measures cover the value orientation of generative artificial intelligence output content, training principles for service providers, protection of privacy/intellectual property rights and other rights, etc.
The emergence of GPT-type generative natural language large models and products has not only allowed the public to experience the leaps and bounds of artificial intelligence, but also exposed security risks, including the generation of biased and discriminatory content, data leaks, Issues such as privacy invasion and AI fraud. Globally, the regulation of artificial intelligence in various countries has gradually become a trend.
In China, once the "Generative Artificial Intelligence Service Management Measures" are promulgated, the large models and product providers of domestic generative AI can no longer be "rolled" in disorder, and adopters will also have problems when using generative AI. the normative circle.
1. Set up "restricted areas" for generated content
"These Measures shall apply to those who develop and utilize generative artificial intelligence products to provide services to the public within the territory of the People's Republic of China.
The term “generative artificial intelligence” as mentioned in these Measures refers to the technology that generates text, pictures, sounds, videos, codes and other content based on algorithms, models, and rules.”
On April 11, the Cyberspace Administration of China released The "Measures for the Administration of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services (Draft for Comments)" (hereinafter referred to as the "Measures") clarifies the applicable subjects of the "Measures" and the definition of "generative artificial intelligence" in the second article.
Judging from the content of this article, companies such as Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, and Huawei that have publicly stated that they have generative large models and products will be governed by the "Measures" if they provide services to users in China. Within the scope, users also need to comply with the provisions of the Measures when using relevant products and services.
The "Measures" also emphasize that the state supports independent innovation, promotion and application, and international cooperation of basic technologies such as artificial intelligence algorithms and frameworks, and encourages the priority use of safe and trustworthy software, tools, computing and data resources.
Under this premise, the "Measures" delineates "restricted areas" for providers of generative artificial intelligence products or services, including generated content and basic principles of research and development.
In terms of content, the "Measures" require: Content generated using generative artificial intelligence should reflect the core socialist values, and must not contain content that subverts state power, overthrows the socialist system, incites to split the country, undermines national unity, or promotes Terrorism, extremism, promotion of ethnic hatred, ethnic discrimination, violence, obscene pornographic information, false information, and content that may disrupt economic and social order; content generated using generative artificial intelligence should be true and accurate, and measures should be taken to prevent the generation of false information information.
In terms of research and development, the "Measures" require providers to take measures to prevent the occurrence of racial, ethnic, religious, national, regional, Discrimination based on gender, age, occupation, etc.
Judging from these requirements, the "Measures" basically cover the safety and ethical issues exposed by users of large-scale natural language model products on the market, including the generation of discriminatory bias, false information, etc.
Questionable content produced by humans through generative AI has appeared endlessly on the Internet.
For example, ChatGPT once provided steps for users to inquire about "how to shoplift", even though it included "tips on illegal shoplifting"; its "role-playing" function was once induced by users to DAN (Do Anyting Now) answered questions with the identity of "Do Anyting Now", and the answers given included "expletives"; some people also used ChatGPT to test fake news spread in the country, which became the content of "refuting rumors".
Microsoft's chatbot integrated into the search engine Bing was exposed by overseas media as "abusive to users"; the AI photo-generating application Midjourney was even used to create "The Pope wears a Balenciaga down jacket" and "Horse Some people even used it to create various non-existent earthquake histories, solar storm disasters, etc.

Fake pictures of the Pope (left) and Musk
Regarding false information and identifying AI-generated content, the "Measures" require providers to start from the source "Able to ensure the authenticity, accuracy, objectivity and diversity of data"; generative pictures, videos and other content should be labeled in accordance with the "Internet Information Services Deep Synthesis Management Regulations"; while generative artificial intelligence products are being developed When manual annotation is used, the provider shall formulate clear, specific, and operable annotation rules that comply with the requirements of these Measures, conduct necessary training for annotators, and verify the correctness of the annotated content on a sample basis.
Chinese regulation has set up restricted areas for generative artificial intelligence content. To some extent, it also requires companies that provide large models and products to control pre-training and data.
2. Emphasis on data sources and personal information protection
In addition to emphasizing value orientation, social ethics, compliance with laws and anti-discrimination for generated content, the "Measures" also emphasizes on generative artificial intelligence-related Requirements for pre-training and data sources, personal information protection and other rights and interests.
For example, the "Measures" require that providers should be responsible for the legality of the sources of pre-training data and optimization training data for generative artificial intelligence products, and do not contain content that infringes on intellectual property rights; if the data contains personal information, The consent of the personal information subject shall be obtained; the obligation to protect user input information and usage records shall not be illegally retained; input information that can be used to determine the user's identity shall not be illegally retained; user input information shall not be profiled based on user input information and usage; user input information shall not be provided to others.
The problem of data infringement caused by generative AI does exist. For example, when users use conversational robots to meet some work needs, they will inevitably upload company information. If they are not careful, it is likely to cause the leakage of business secrets. . Previously, South Korean electronics giant Samsung stated that internal data was leaked due to employees' interactions with the application after it filed a "restriction order" on ChatGPT.
The "Measures" not only point to providers of generative artificial intelligence products and services, but also stipulate principles for users of products and services.
For example, do not use generated content to damage the image, reputation and other legitimate rights and interests of others, and do not engage in commercial hype or unfair marketing.
Since the "Measures" were formulated in accordance with the higher-level laws "Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China", "Data Security Law of the People's Republic of China", "Personal Information Protection Law of the People's Republic of China" and other laws and administrative regulations, these laws and regulations will Applicable to violations of the Measures, including infringement of intellectual property rights, infringement of personal information and other illegal activities.
The "Measures" have a total of 21 articles, 13 of which explicitly target "providers", that is, organizations and individuals who use generative artificial intelligence products to provide services such as chat and text, image, and sound generation.

The public can provide feedback through three channels
It can be seen that once the "Measures" are officially promulgated, domestic companies that make large generative models and products will Adopting parties will be required to act within the rules. According to the official website of the Cyberspace Administration of China, the public can provide feedback through three channels, and the deadline for feedback is May 10, 2023.
The above is the detailed content of With full coverage of values and privacy protection, the Cyberspace Administration of China plans to 'establish rules” for generative AI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AM
How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AMRunning large language models at home with ease: LM Studio User Guide In recent years, advances in software and hardware have made it possible to run large language models (LLMs) on personal computers. LM Studio is an excellent tool to make this process easy and convenient. This article will dive into how to run LLM locally using LM Studio, covering key steps, potential challenges, and the benefits of having LLM locally. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or are curious about the latest AI technologies, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical tips. Let's get started! Overview Understand the basic requirements for running LLM locally. Set up LM Studi on your computer
 Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AMGuy Peri is McCormick’s Chief Information and Digital Officer. Though only seven months into his role, Peri is rapidly advancing a comprehensive transformation of the company’s digital capabilities. His career-long focus on data and analytics informs
 What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AM
What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AMIntroduction Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving to understand not just words, but also emotions, responding with a human touch. This sophisticated interaction is crucial in the rapidly advancing field of AI and natural language processing. Th
 12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AM
12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AMIntroduction In today's data-centric world, leveraging advanced AI technologies is crucial for businesses seeking a competitive edge and enhanced efficiency. A range of powerful tools empowers data scientists, analysts, and developers to build, depl
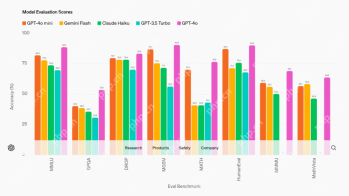 AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AM
AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AMThis week's AI landscape exploded with groundbreaking releases from industry giants like OpenAI, Mistral AI, NVIDIA, DeepSeek, and Hugging Face. These new models promise increased power, affordability, and accessibility, fueled by advancements in tr
 Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AMBut the company’s Android app, which offers not only search capabilities but also acts as an AI assistant, is riddled with a host of security issues that could expose its users to data theft, account takeovers and impersonation attacks from malicious
 Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AMYou can look at what’s happening in conferences and at trade shows. You can ask engineers what they’re doing, or consult with a CEO. Everywhere you look, things are changing at breakneck speed. Engineers, and Non-Engineers What’s the difference be
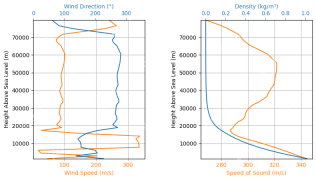 Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AMSimulate Rocket Launches with RocketPy: A Comprehensive Guide This article guides you through simulating high-power rocket launches using RocketPy, a powerful Python library. We'll cover everything from defining rocket components to analyzing simula


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools





