
We can use artificial intelligence to automate complex, repetitive tasks faster than humans can.
Artificial intelligence technology can logically sort complex and repeated inputs. This is why artificial intelligence is used in facial recognition and self-driving cars. But this capability also paves the way for AI cybersecurity. This is particularly useful for assessing threats in complex organizations. When business structures are constantly changing, administrators often fail to identify weaknesses.
In addition, the network structure of enterprises is becoming more and more complex. This means there are more vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit against us. We can see this in highly automated Manufacturing 3.0 enterprises or integrated companies such as the oil and gas industry. To this end, various security companies have developed AI cybersecurity tools to help protect businesses.
This article will take an in-depth look at what artificial intelligence is and how it is applied to cybersecurity. We will also look at the advantages and disadvantages of this promising technology. Next, let’s first take a look at what artificial intelligence is!
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is a rationalization method that uses statistical weighting matrices. This matrix is also called a neural network. You can first think of this network as a decision matrix, where the nodes have weighted biases for each filtering process. The neural network will receive a database of precompiled data. The data will also contain answers to potential questions that AI can solve. In this way, AI can become biased.
For example, a database containing different images. Suppose it has a face image and other watermelon images. Additionally, each image has a tag to check each item. As the AI "learns" whether its guesses are correct, the system increases node weights. This process continues until the system reaches a predefined error rate. This is often called deep learning, which refers to the creation of deep layers of decision-making.
Next, look at the steps used to process the data.
Key steps in artificial intelligence data processing
The entire data workflow can be condensed into the following process:
1. Input the sensor to receive data.
2. The data passes through the CPU and is redirected to the artificial intelligence process.
3. Data enters the statistical weighting matrix of the artificial intelligence solution. Each node processes this information and then makes a decision using each respective filter.
4. The data reaches the last node of the statistical weighting matrix. This determines the final decision.
However, this process is slightly different from deep learning. Step 1 will include data from the precompiled database, tagged with the correct response. Additionally, deep learning will repeat steps 1 to 4 to reach a predefined fault tolerance value.
Let’s look at this through an example of how to process AI data.
AI data filtering example
Suppose a picture reaches an AI node. This node will filter the data into a usable format, such as 255 grayscale. Then, a script is run to identify the characteristics. If these characteristics match other characteristics in the filter, the node can make a decision. For example, it will indicate whether it found a face or a watermelon.
Then, the data goes to the next node. This particular node can have a color filter confirming the first decision. This process continues until the data reaches the last node. At that point, the AI will make the final decision to ensure it finds a face or a watermelon.
The important thing is that artificial intelligence systems will always have a certain degree of error. Nothing is absolutely correct, ever. But sometimes, the error percentage is acceptable.
After understanding how artificial intelligence works, let’s take a look at artificial intelligence’s network security solutions.
Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity addresses the need to automatically assess threats in complex environments. Specifically, here are two AI use cases in cybersecurity:
1. Detect anomalies. Artificial intelligence often detects anomalies in the day-to-day operations of a network. This helps understand when and where users access the network. The gateway device also features AI integration for analytics. Some solutions lock out users if unusual behavior occurs. Other solutions only send alerts.
2. Classified data. Artificial intelligence is actually a classification utility. This speeds up the screening process for malware or bad behavior. This is useful in organizations with large amounts of data.
These are the two main uses of artificial intelligence in network security. Let’s take a look at its advantages and disadvantages!
The advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence
As before As mentioned, artificial intelligence has many benefits. It can run repetitive tasks to identify anomalies or classify data. That said, some big drawbacks may outweigh its benefits. So let’s look at the shortcomings.
AI Accuracy vs Resource Requirements
The first disadvantage is the accuracy of AI cybersecurity solutions. This accuracy also depends on many factors. This includes the size of the neural network and the decisions defined for filtering. It also depends on the number of iterations required to reach a predefined error rate.
Suppose there is a three-level decision tree. Each layer has multiple nodes for each decision path. Even though this is a fairly simple matrix, it requires a lot of calculations. The system's limited resources compromise the intelligence of the solution.
Artificial intelligence cybersecurity solution providers may hinder the intelligence/accuracy of their solutions to satisfy the target population. But sometimes, the problem isn't IQ. Instead, it has low latency and security vulnerabilities. When looking for AI cybersecurity solutions, consider its security within the network.
Static and Continuous Training
Once the artificial intelligence statistical weighting matrix is trained, it is usually not retrained in the service. This was found to be caused by a lack of available processing resources in the hardware. Sometimes the system learns something that makes the situation worse, making it less efficient. In contrast, humans learn iteratively. This means a lot of accidents. Therefore, solution providers must ensure that the software meets specification requirements during use.
Cybersecurity often needs to be updated to respond to new attacks. To do this, a lot of power is needed to train the AI. Additionally, AI cybersecurity vendors will need regular updates to address cyber threats.
That is, the artificial intelligence component of an artificial intelligence cybersecurity solution is used to classify data and evaluate anomalies in baseline data. Therefore, it does not cause problems with malware list updates. This means AI cybersecurity can still be used.
After reading the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence network security, let’s take a look at some uses of this technology!
Where to find AI network security
As before As mentioned above, highly automated enterprise network security is the weakest. Generally speaking, automation environments overlap information technology (IT), operational technology (OT), and the Internet of Things (IoT). This is to increase productivity, reduce the unit cost of the product, and undercut the competition.
But this can also create loopholes. To this end, AI cybersecurity can be helpful in uncovering potential vulnerabilities in these companies. The solution is to either notify the administrator or apply the patch automatically.
However, this may not be enough. Cybercriminals are currently targeting large, highly integrated companies. To do this, they leverage OT without security. This OT is for wired networks to send commands to hardware, such as factory equipment. This means it never constituted a security vulnerability. But today, attackers use OT to gain access to the rest of the network or take factory equipment offline.
OT Risk Management for Manufacturing and Automated Factories
OT risk management tools are becoming more and more popular due to the above reasons. These systems effectively take a live clone of the production environment and then run countless simulations to find vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities are often found in the AI part of the system. In this case, the administrator will provide a solution. OT risk management software continuously operates as manufacturing plant schedules change to meet order, project, or supply needs.
In this case, the AI system uses known malware from antivirus lists to try to find an entry path into the system. This task requires the automated, repetitive capabilities of complex systems, which is ideally suited for artificial intelligence.
So, when should you implement AI cybersecurity?
When should you use AI cybersecurity
As mentioned above, businesses using manufacturing and factory equipment should Using artificial intelligence for cybersecurity. In most cases, one also needs to look for an OT risk management solution to reduce the risks associated with OT.
If enterprises use IoT and IT, they can also use artificial intelligence cybersecurity. In this way, the risk of network attacks can be reduced. IoT devices are often sold at a lower price than competitors, so the cost of adding adequate security measures is also eliminated.
Finally, even companies that only use IT can also use AI. Artificial intelligence can help assess irregular traffic to protect gateways. In addition, AI data analysis can also be used. This way, you can tell if someone is using the hardware maliciously.
In summary, that’s all about artificial intelligence network security, a brief summary!
Summary
We may use artificial intelligence wherever repetitive tasks need to be automated intelligent. Artificial intelligence also helps in decision-making on complex tasks. This is why many cybersecurity solution providers use artificial intelligence. In fact, these providers' tools help address the challenges of highly complex and poorly secured systems.
We can always benefit from AI cybersecurity, no matter how integrated the business technology is. AI capabilities are also great for classifying data using intelligent operations. This way, you can speed up your search for malware. AI cybersecurity can also help detect abnormal usage of the network.
The above is the detailed content of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity: Pros and Cons. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
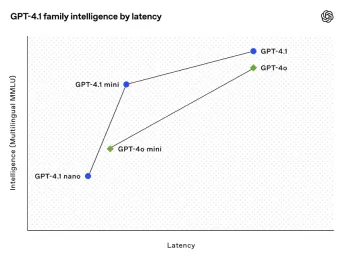 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools







