
Today, industrial robots are used in almost all industries. They bring many benefits to manufacturing facilities and pave the way for the smart factories of the future. However, there are some limitations that manufacturers should consider when selecting robotic equipment.
Demand for automated processes is increasing, with the industrial robot market expected to reach $31.3 billion in 2028, according to Fortune Business Insights. Manufacturers are increasingly aware of the potential business and production benefits of implementing robots. However, industrial robots are not without their drawbacks. Here are some of the most common limitations, along with some suggestions from manufacturers on how to overcome them.
Affordability
Generally speaking, industrial robots require a large upfront investment, including additional installation and configuration costs. Manufacturers also need to consider future maintenance costs and the need for additional components.
Similarly, robotics is an ever-evolving industry, and upgraded machines are always appearing on the market. For some companies, investing in new robots on a regular basis can be a daunting task, especially smaller ones that could go out of business trying to keep up with industry trends.
However, industrial robots can help manufacturers cut costs in different areas. They can reduce production costs and increase profits by optimizing work. With a clear investment strategy and financial plan, bots are more likely to deliver a quick return on investment.
Another smart option is to invest in refurbished robots. Typically, used robots cost half the price of new robots while maintaining their efficiency and maneuverability.
Safety
In factories, industrial robots are always considered dangerous. And for good reason - they're huge, bulky devices that can also move very fast. Older machines even lack the sentience to detect nearby humans, making them prone to dangerous collisions and accidents. For this reason, many manufacturers add cages or partitions to isolate robots from their human colleagues.
Recently, safety has become one of the main priorities in industrial automation with the introduction of collaborative robots that are smaller, lighter and designed to work alongside humans. More regulatory measures are already in place for bulky industrial robots and collaborative robots.
While there is still a long way to go to achieve absolute safety in factories, there is no doubt that progress is still being made. New technologies such as light curtains, laser scanners and presence-sensing devices are widely regarded as a way to improve human safety.
A good practice for manufacturers is to conduct a risk assessment on their production lines and train workers on how to respond to potential accidents.
Difficult to train
Industrial robots require expert programming and training to perform tasks, so companies need to hire experienced engineers and programmers to be responsible for the installation of the robots. On top of that, even experienced personnel may need to be retrained when newly developed software or new robots appear on the market. If a robot is not programmed correctly, it can cause malfunctions and harm those around it.
However, in recent years a new method of training robots has been implemented - no-code or low-code programming. It allows employees with less coding experience to configure robots using visual modeling and a drag-and-drop user interface. Thanks to the easy-to-use format of no-code and low-code platforms, robots can also be reprogrammed for different jobs by adjusting their arms.
The trend for low-code and no-code platforms is on the rise, with 84% of businesses in the US, UK, Canada and Australia implementing low-code development platforms to reduce the need for coding.
Industrial robots have been proven to simplify human tasks, provide manufacturers with a rapid return on investment, and streamline production. However, they are not without limitations. They are more difficult to train than humans, require high investment and maintenance costs, and pose safety challenges. While these are legitimate concerns for manufacturers, they can be overcome with careful planning and new technology.
The above is the detailed content of Limitations of industrial robots. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
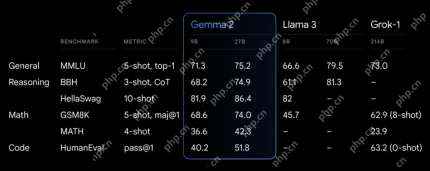 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software






