EU's AI bill: Will regulation hinder innovation?

- Open source AI regulations are mentioned in the Artificial Intelligence Act (AIA), which is currently being discussed in the EU.
- However, severely restricting the use, sharing and distribution of General Open Source AI (GPAI) could be seen as a step backwards.
- Free exchange of open source information licenses, such as the MIT license, are intended to share knowledge and concepts, not to retail finished, proven merchandise.
- Expanding the legal obligations on open source GPAI researchers and developers will only hinder technological innovation and development.
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AIA) currently under discussion mentions the regulation of open source artificial intelligence. However, imposing strict restrictions on the use, sharing, and distribution of open source general artificial intelligence (GPAI) can be considered a step backwards.
Objectives of the EU Artificial Intelligence Act
The only way humanity can advance technology at such a rapid pace is through open source culture. Until recently, it has been acceptable for AI researchers to release their source code to increase openness and verifiability; however, limiting this trend could reverse the cultural progress made by the scientific community.
Two objectives of the proposed regulatory structure of the Artificial Intelligence Bill stand out in particular:
- "Ensuring legal certainty to promote investment and innovation in artificial intelligence"
- " Promote the development of a single market for legal, safe and trustworthy artificial intelligence applications and prevent market fragmentation”
The GPAI regulations in the Artificial Intelligence Bill appear to contradict these claims. GPAI encourages innovation and the exchange of information without fear of costly and negative legal consequences. So instead of building a security market that resists fragmentation, some serious regulatory restrictions that simultaneously hinder open source development and further monopolize AI development by the major tech giants may actually occur.
Should open source development of artificial intelligence be more strictly regulated?
This is more likely to lead to less transparency in the market, making it difficult to determine whether an artificial intelligence application is "legal, safe and trustworthy" be more challenging. Of course, none of this is good for GPAI. Instead, there is a growing and troubling fear that the disparity this imposition could create would give more power to large corporations.
It is also important to recognize that some may interpret this opposition to the changes as an attempt by businesses to get around the rules. There is no doubt that regulations such as the Artificial Intelligence Act are necessary to curb risky misconduct. Without regulations, will AI fall into the wrong hands?
It should be noted that regulations like the Artificial Intelligence Bill are undoubtedly necessary to deter risky misconduct…
This is a legitimate concern and, of course, rules are necessary. However, rather than applying this law to all models simultaneously, it is better to apply it one by one. Rather than regulating open source at the source and limiting innovation, each model should be assessed for potential damage and managed accordingly.
The implementation of the Act is nuanced, complex and multi-dimensional. Even those who generally agreed differed in other ways. However, the fact that GPAI is open to the public is a major sticking point. This open, collaborative approach is the main driver for progress, transparency and technological development, for the collective and individual benefit of society rather than commercial gain.
Share Information Freely
Open source licenses like the MIT License are intended for information and idea sharing, not for selling a polished, proven product. Therefore, they should not be handled in a similar manner. There is a real need for an ideal regulatory mix. This is to increase reliability and openness about how these AI models are developed, the types of data used to train them, and whether there are any known limitations. However, this must not be at the expense of the freedom of exchange of information.
The form of the Artificial Intelligence Act needs to be tailored to attract more cautious users of open source software.
The Artificial Intelligence Act should be structured to encourage users of open source software to be more cautious and conduct their own research and testing before making it available to a large audience. This can catch bad actors trying to commercially exploit a creator's work without conducting more investigation or applying quality standards.
In fact, it should be the responsibility and obligation of the final developer to thoroughly check everything before delivering it to consumers. These people will ultimately benefit financially from open source initiatives. However, the framework does not explicitly seek to achieve this in its current state. A core principle of open source is the free exchange of information and expertise for personal and non-commercial purposes.
Expanding the legal liability of open source GPAI developers and researchers will only stifle technological progress and innovation. This will prevent developers from exchanging knowledge and ideas, making it harder for new businesses or aspiring individuals to gain access to cutting-edge technology. They will not be able to build on their own knowledge or be motivated by what others have gained.
Nowadays, artificial intelligence is widely used, including in smart buildings, which also involves safety issues. Recently, the 23rd China International Building Intelligence Summit in 2022, hosted by Qianjia.com, will officially kick off. The theme of this summit is "Digital Intelligence Empowerment, Carbon Solving a New Future", in which how to create safer smart buildings will It has become one of the main topics discussed at this summit.
The summit will be held grandly in the five major cities of Xi'an, Chengdu, Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou from November 8 to December 8, 2022. At that time, we will join hands with world-renowned building intelligence brands and experts to share hot topics and the latest technology applications such as AI, cloud computing, big data, IoT, smart cities, smart homes, and smart security, and discuss how to create a "lower carbon, A safer, more stable and more open industry ecology will help achieve the "double carbon" goal.
The above is the detailed content of EU's AI bill: Will regulation hinder innovation?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
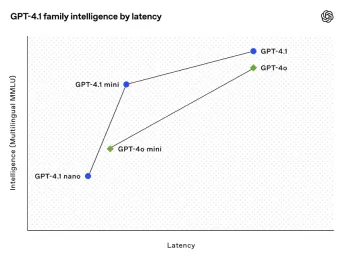 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools







