Overview: Collaborative sensing technology for autonomous driving
arXiv review paper "Collaborative Perception for Autonomous Driving: Current Status and Future Trend", August 23, 2022, Shanghai Jiao Tong University.

Perception is one of the key modules of the autonomous driving system. However, the limited capabilities of bicycles create a bottleneck in improving perception performance. In order to break through the limitations of single perception, collaborative perception is proposed to enable vehicles to share information and perceive the environment outside the line of sight and outside the field of view. This article reviews promising work related to collaborative sensing technology, including basic concepts, collaborative models, and key elements and applications. Finally, open challenges and issues in this research area are discussed and further directions are given.
As shown in the figure, two important problems with single perception are long-distance occlusion and sparse data. The solution to these problems is that vehicles in the same area share common perception information (CPM, collective perception message) with each other and collaboratively perceive the environment, which is called collaborative sensing or collaborative sensing.

Thanks to the construction of communication infrastructure and the development of communication technologies such as V2X, vehicles can exchange information in a reliable way, thereby achieving collaboration. Recent work has shown that collaborative sensing between vehicles can improve the accuracy of environmental perception as well as the robustness and safety of transportation systems.
In addition, autonomous vehicles are usually equipped with high-fidelity sensors for reliable perception, resulting in expensive costs. Collaborative sensing can alleviate the stringent requirements of a single vehicle on sensing equipment.
Cooperative sensing shares information with nearby vehicles and infrastructure, enabling autonomous vehicles to overcome certain perception limitations such as occlusion and short field of view. However, achieving real-time and robust collaborative sensing requires solving some challenges caused by communication capacity and noise. Recently, some work has studied strategies for collaborative sensing, including what is collaboration, when to collaborate, how to collaborate, alignment of shared information, etc.
Similar to fusion, there are four categories of collaboration:
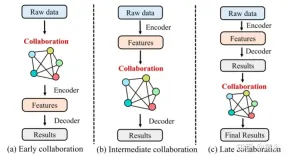
##1 Early collaboration
Early collaboration in Collaborate in the input space to share raw sensory data between vehicles and infrastructure. It aggregates the raw measurements of all vehicles and infrastructure to get a holistic view. Therefore, each vehicle can perform the following processing and complete perception based on the overall perspective, which can fundamentally solve the occlusion and long-distance problems that arise in single perception. However, sharing raw sensory data requires extensive communication and easily congests the communication network with excessive data load, which hinders its practical application in most cases.2. Late Collaboration
Later collaboration collaborates in the output space, which promotes the fusion of the perception results output by each agent and achieves refinement. Although late stage collaboration is bandwidth economical, it is very sensitive to positioning errors of agents and suffers from high estimation errors and noise due to incomplete local observations.3 Intermediate collaboration
Intermediate collaboration performs collaboration in the intermediate feature space. It is capable of transmitting intermediate features generated by individual agent prediction models. After fusing these features, each agent decodes the fused features and produces a perceptual result. Conceptually, representative information can be compressed into these features, saving communication bandwidth compared to early collaboration and improving perception compared to late collaboration. In practice, the design of this collaborative strategy is algorithmically challenging in two aspects: i) how to select the most effective and compact features from raw measurements for transmission; and ii) how to maximize Integrate the characteristics of other intelligences to enhance the perception ability of each intelligence.4 Hybrid Synergy
As mentioned above, each synergy mode has its advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, some works adopt hybrid collaboration, combining two or more collaboration modes to optimize collaboration strategies. The main factors of collaborative sensing include:1 Collaborative graph
The graph is a powerful tool for collaborative sensing modeling because it models non-European The data structure has good interpretability. In some works, the vehicles participating in collaborative sensing form a complete collaborative graph, in which each vehicle is a node and the collaborative relationship between two vehicles is the edge between the two nodes.2 Attitude Alignment
Since collaborative sensing requires fusing data from vehicles and infrastructure at different locations and at different times, achieving accurate data alignment is critical to successful collaborative sensing. It's important.3 Information Fusion
Information fusion is the core component of the multi-agent system. Its goal is to fuse the largest amount of information from other agents in an effective way. part.4 Resource allocation based on reinforcement learning
The limited communication bandwidth in real environments requires full utilization of available communication resources, which makes resource allocation and spectrum sharing very important. In vehicular communication environments, rapidly changing channel conditions and growing service demands make the optimization of allocation problems very complex and difficult to solve using traditional optimization methods. Some works utilize multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to solve optimization problems.
Applications of collaborative sensing:
1 3D target detection
3D target detection based on lidar point cloud is the most popular in collaborative sensing research The problem. The reasons are as follows: i) LiDAR point clouds have more spatial dimensions than images and videos. ii) LiDAR point clouds can preserve personal information, such as faces and license plate numbers, to a certain extent. iii) Point cloud data is an appropriate data type for fusion because it loses less than pixels when aligned from different poses. iv) 3D object detection is a basic task for autonomous driving perception, on which many tasks such as tracking and motion prediction are based.
2 Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation of 3D scenes is also a key task required for autonomous driving. Collaborative semantic segmentation of 3D scene objects. Given 3D scene observations (images, lidar point clouds, etc.) from multiple agents, a semantic segmentation mask is generated for each agent.
Challenging issues:
1 Communication robustness
Effective co-unification relies on reliable communication between agents. However, communication is not perfect in practice: i) as the number of vehicles in the network increases, the available communication bandwidth of each vehicle is limited; ii) due to inevitable communication delays, it is difficult for vehicles to receive real-time information from other vehicles; iii) Communication may sometimes be interrupted, resulting in communication interruption; iv) V2X communication is damaged and reliable services cannot always be provided. Although communication technology continues to develop and the quality of communication services continues to improve, the above problems will still exist for a long time. However, most existing works assume that information can be shared in a real-time and lossless manner, so it is of great significance for further work to consider these communication constraints and design robust collaborative sensing systems.
2 Heterogeneity and cross-modality
Most collaborative perception work focuses on lidar point cloud-based perception. However, there are many more types of data available for sensing, such as images and millimeter-wave radar point clouds. This is a potential way to leverage multimodal sensor data for more effective collaboration. Furthermore, in some scenarios, there are different levels of autonomous vehicles providing different qualities of information. Therefore, how to collaborate in heterogeneous vehicle networks is a problem for further practical application of collaborative sensing. Unfortunately, few works focus on heterogeneous and cross-modal collaborative sensing, which also becomes an open challenge.
3 Large-scale data sets
The development of large-scale data sets and deep learning methods has improved perceptual performance. However, existing datasets in the field of collaborative sensing research are either small in size or not publicly available.
The lack of public large-scale data sets hinders further development of collaborative sensing. Furthermore, most data sets are based on simulations. Although simulation is an economical and safe method to verify algorithms, real data sets are also needed to apply collaborative sensing in practice.
The above is the detailed content of Overview: Collaborative sensing technology for autonomous driving. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AM
How to Run LLM Locally Using LM Studio? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:38 AMRunning large language models at home with ease: LM Studio User Guide In recent years, advances in software and hardware have made it possible to run large language models (LLMs) on personal computers. LM Studio is an excellent tool to make this process easy and convenient. This article will dive into how to run LLM locally using LM Studio, covering key steps, potential challenges, and the benefits of having LLM locally. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or are curious about the latest AI technologies, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical tips. Let's get started! Overview Understand the basic requirements for running LLM locally. Set up LM Studi on your computer
 Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Guy Peri Helps Flavor McCormick's Future Through Data TransformationApr 19, 2025 am 11:35 AMGuy Peri is McCormick’s Chief Information and Digital Officer. Though only seven months into his role, Peri is rapidly advancing a comprehensive transformation of the company’s digital capabilities. His career-long focus on data and analytics informs
 What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AM
What is the Chain of Emotion in Prompt Engineering? - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:33 AMIntroduction Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving to understand not just words, but also emotions, responding with a human touch. This sophisticated interaction is crucial in the rapidly advancing field of AI and natural language processing. Th
 12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AM
12 Best AI Tools for Data Science Workflow - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:31 AMIntroduction In today's data-centric world, leveraging advanced AI technologies is crucial for businesses seeking a competitive edge and enhanced efficiency. A range of powerful tools empowers data scientists, analysts, and developers to build, depl
 AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AM
AV Byte: OpenAI's GPT-4o Mini and Other AI InnovationsApr 19, 2025 am 11:30 AMThis week's AI landscape exploded with groundbreaking releases from industry giants like OpenAI, Mistral AI, NVIDIA, DeepSeek, and Hugging Face. These new models promise increased power, affordability, and accessibility, fueled by advancements in tr
 Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Perplexity's Android App Is Infested With Security Flaws, Report FindsApr 19, 2025 am 11:24 AMBut the company’s Android app, which offers not only search capabilities but also acts as an AI assistant, is riddled with a host of security issues that could expose its users to data theft, account takeovers and impersonation attacks from malicious
 Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Everyone's Getting Better At Using AI: Thoughts On Vibe CodingApr 19, 2025 am 11:17 AMYou can look at what’s happening in conferences and at trade shows. You can ask engineers what they’re doing, or consult with a CEO. Everywhere you look, things are changing at breakneck speed. Engineers, and Non-Engineers What’s the difference be
 Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics VidhyaApr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AMSimulate Rocket Launches with RocketPy: A Comprehensive Guide This article guides you through simulating high-power rocket launches using RocketPy, a powerful Python library. We'll cover everything from defining rocket components to analyzing simula


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.





