Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >Linux vim has several working modes
Linux vim has several working modes
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2023-02-02 19:00:143599browse
Linux vim has 3 working modes: 1. Command mode (command mode). You can use the direction keys (up, down, left, right keys) or k, j, h, i to move the cursor position, and also You can copy, paste, replace, delete and other operations on the file content. 2. Input mode, you can perform writing operations on files, similar to entering content in a document on a Windows system. 3. Edit mode, used to perform operations such as saving, searching or replacing specified content in the file.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is vi?
vi is the abbreviation of Visual Editor;
is a text editor under the command line interface;
In the early Unix In the operating system, vi is used as the default editor of the system
So what is vim?
Abbreviation of Vi IMproved;
Upgraded version of Vi;
The biggest difference between Vim and Vi is that when we edit When a text is displayed, vi will not display colors, but vim will display colors.
In addition, vim can also perform program editing functions such as shell scripts, C language, etc.; therefore, you can regard vim as a program editor. Device
Then the CentOS system we installed already has the vim command, so there is no need to install it; if there is no vim command in the Linux system, then you need to use the command yum install -y after connecting to the Internet vim-enhanced installs itself.
Three working modes of vim
When using Vim to edit files, there are three working modes, namely command mode, Input mode and editing mode, these three working modes can be switched at will, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Vim’s three working modes
Vim’s command mode
When using Vim to edit files, the default is Command mode. In this mode, you can use the direction keys (up, down, left, right keys) or k, j, h, i to move the cursor position, and you can also copy, paste, replace, delete and other operations on the file content.
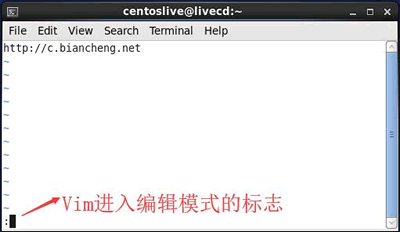
Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of Vim in command mode in CentOS 6.x system.
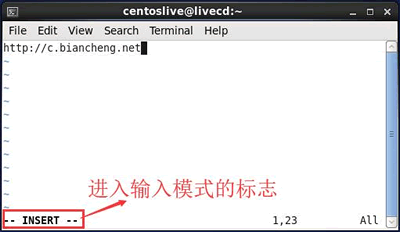
Figure 2 Vim in command state
Vim’s input mode
In input mode, Vim can execute files The writing operation is similar to typing in a document on Windows systems.
The way to put Vim into input mode is to enter i, I, a, A, o, O and other insertion commands in the command mode state (the specific functions of each command are shown in Table 3). When editing a file Press Esc when finished to return to command mode.
| Shortcut keys | Function description |
|---|---|
| i | Insert the subsequently entered text at the current cursor position, and the text after the cursor moves to the right accordingly |
| I | Insert the line where the cursor is Insert the text entered subsequently at the beginning of the line. The beginning of the line is the first non-blank character of the line, which is equivalent to moving the cursor to the beginning of the line and executing the i command |
| o | Insert a new line below the line where the cursor is. The cursor stops at the beginning of the empty line, waiting for the input text |
| O | to insert a new line above the line where the cursor is. The cursor stops at the beginning of the empty line, waiting for input text |
| a | Inserts the subsequently entered text after the current cursor position |
| A | Insert the subsequently entered text at the end of the line where the cursor is located, which is equivalent to moving the cursor to the end of the line and then executing the a command |
The above is the detailed content of Linux vim has several working modes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!