Home >Web Front-end >Front-end Q&A >What does vue's cross-domain mean?
What does vue's cross-domain mean?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2022-12-21 14:00:013185browse
In vue, cross-domain means that the browser cannot execute scripts from other websites; it is caused by the browser's same-origin policy and is the security restriction imposed by the browser on JS. The nature of cross-domain is a security method based on the same-origin policy of the browser; the same-origin policy is a convention, which is the core and most basic security function of the browser. Vue cross-domain solutions: 1. JSONP; 2. CORS; 3. Proxy.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue3 version, DELL G3 computer.
1. What is cross-domain
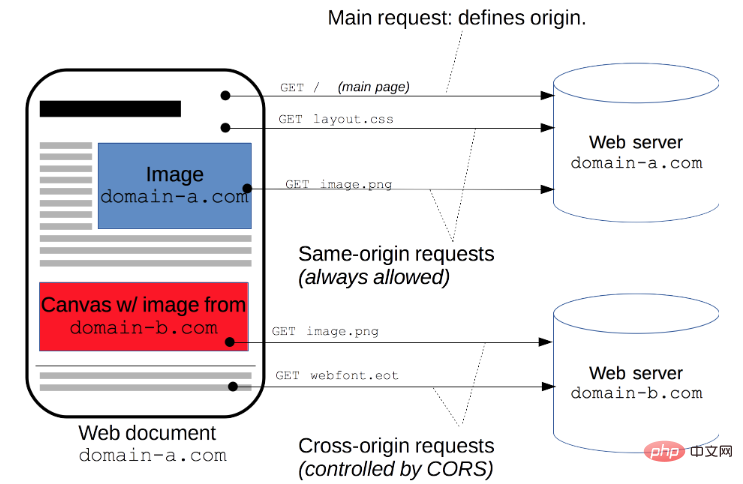
Cross-domain means that the browser cannot execute scripts from other websites. It is caused by the browser's same-origin policy, which is a security restriction imposed by the browser on JS.
The nature of cross-domain is a security method used by browsers based on Same origin policy
Sameorigin policy (Sameoriginpolicy) is an agreement, which is the most important thing for browsers The core and most basic security function
The so-called same origin (that is, in the same domain) has the following three similarities
- The same protocol (protocol)
- The host is the same (host)
- The port is the same (port)
On the contrary, non-source requests, that is, when one of the protocols, ports, and hosts are different, then there will be Cross-domain generation
Be sure to note that cross-domain is a limitation of the browser. If you use a packet capture tool to capture the interface data, you can see that the interface has returned the data, but it is only a limitation of the browser. , you cannot get the data. Data can be requested using the postman request interface. These once again confirm that cross-domain is a limitation of browsers.
2. How to solve it
There are many ways to solve cross-domain issues. Three are listed below:
- JSONP
- CORS
- Proxy
In the vue project, we mainly focus on CORS or ProxyExpand these two solutions
CORS
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, cross-domain resource sharing) is a system. It consists of a series of transmitted HTTP headers. These HTTP headers determine whether the browser prevents the front-end JavaScript code from obtaining responses to cross-domain requests.
CORS It is very convenient to implement and only needs to add someHTTP header, allowing the server to declare allowed access sources
As long as the backend implements CORS, cross-domain is achieved
Take koaframework as an example
Add middleware and directly set Access-Control-Allow-OriginRequest header
app.use(async (ctx, next)=> {
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type, Content-Length, Authorization, Accept, X-Requested-With , yourHeaderFeild');
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'PUT, POST, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS');
if (ctx.method == 'OPTIONS') {
ctx.body = 200;
} else {
await next();
}
})ps: Access-Control-Allow-Origin Setting it to * actually has little meaning. It can be said to be useless. In actual application, we will set Access-Control-Allow before going online. -Origin value is set to our targethost
Proxy
Proxy (Proxy) is also called a network proxy , is a special network service that allows one (usually a client) to make an indirect connection with another network terminal (usually a server) through this service. Some network devices such as gateways and routers have network proxy functions. It is generally believed that proxy services are helpful to protect the privacy or security of network terminals and prevent attacks
Option 1
If it is through thevue-cliscaffolding tool To build the project, we can use webpack to set up a local server for us as the proxy object of the request.
Forward the request to the target server through the server, get the result and forward it to the front end, but finally publish it online If the web application and interface server are not together, it will still cross domain
In thevue.config.js file, add the following code
amodule.exports = {
devServer: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 8084,
open: true,// vue项目启动时自动打开浏览器
proxy: {
'/api': { // '/api'是代理标识,用于告诉node,url前面是/api的就是使用代理的
target: "http://xxx.xxx.xx.xx:8080", //目标地址,一般是指后台服务器地址
changeOrigin: true, //是否跨域
pathRewrite: { // pathRewrite 的作用是把实际Request Url中的'/api'用""代替
'^/api': ""
}
}
}
}
} When sending a request through axios, configure the root path of the request
axios.defaults.baseURL = '/api'
Option 2
In addition, you can also use the service End-to-end proxy request forwarding
Take theexpressframework as an example
var express = require('express');
const proxy = require('http-proxy-middleware')
const app = express()
app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/'))
app.use('/api', proxy({ target: 'http://localhost:4000', changeOrigin: false
}));
module.exports = appOption 3
passed Configure nginx Implement proxy
server {
listen 80;
# server_name xxx.xxx.com;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
location /api {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}[Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial, web front-end development]
The above is the detailed content of What does vue's cross-domain mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

