A brief analysis of how to use FormArray and modal boxes in Angular
How to use FormArray and modal box together? The following article will introduce to you how to use Angular's FormArray and modal box together. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Business scenario
Use FormArray to create dynamic forms. Every time a form is created, a new input is added to the page to display the title of the form. Click Edit and jump to click the fill-in content of the form. [Related tutorial recommendations: "angular tutorial"]
// 封装获取modelList
get modelList() {
return this.formGroup.get('modelList') as FormArray
}
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {}
ngOnInit() {
// 一开始初始化arr为空数组
this.formGroup = this.fb.group({
// 内部嵌套FormControl、FormArray、FormGroup
modelList: this.fb.array([])
})
}
// 模态框构造内部的表单
function newModel() {
return this.fb.group({
modelName: [''],
// 可以继续嵌套下去,根据业务需求
})
}
// 省略模态框部分代码
// 传递到模态框的FormArray
selectedType: FormArrayForm list

Form Details [Modal Box]

<form [FormGroup]="formGroup">
<div FormArrayName="modelList">
<ng-container *nfFor="let item of modelList.controls;let i = index" [FormGroupName]="i">
<nz-input-group
[nzSuffix]="suffixIconSearch"
>
<input type="text" nz-input formControlName="modelName"/>
</nz-input-group>
<ng-template #suffixIconSearch>
<span
nz-icon
nzType="edit"
class="hover"
(click)="showModal(i)"
></span>
</ng-template>
</ng-container>
</div>
</form>
<nz-modal
[(nzVisible)]="isVisible"
nzTitle="Model"
[nzFooter]="modalFooter"
(nzOnCancel)="handleCancel()"
(nzOnOk)="handleOk()"
>
<ng-container *nzModalContent>
<form nz-form [formGroup]="selectedType">
<nz-form-item>
<nz-form-label nzRequired>Model Test</nz-form-label>
<nz-form-control>
<input
type="text"
nz-input
placeholder="请输入ModelName"
formControlName="modelName"
/>
</nz-form-control>
</nz-form-item>
<nz-form-item>
<nz-form-control>
<product-config></product-config>
</nz-form-control>
</nz-form-item>
</form>
</ng-container>
<ng-template #modalFooter>
<button *ngIf="!isNewModel" nzDanger nz-button nzType="default" (click)="handleDelete()">删除</button>
<button *ngIf="isNewModel" nz-button nzType="default" (click)="handleCancel()">取消</button>
<button nz-button nzType="primary" (click)="handleOk()">保存</button>
</ng-template>
</nz-modal>Because this kind of modal box is special, it separates the relationship between the FormGroup of the form and needs to be passed when clicking. The parameters are sent to the modal box to display part of the value. If you simply pass the parameters and use this.modelList.at(index) to obtain the entity and assign the value to the modal box for modification, you will find the modification after clicking Save in the modal box. The value is not updated in the form, and modifications to the input value on the form are found to affect the content of the modal box.
But the form added by the modal box can be responded to the page.
Original error code idea
After clicking edit, pass the clicked FormArray element to a temporary variable
this.selectedType = <formgroup>this.modelList.at(index);</formgroup>, and pass the value to the modal box form.Click to save the modal box and replace the original FormArray value again
this.modelList.removeAt(this.modelIndex) this.modelList.insert(this.modelIndex, this.selectedType)
- ##Click to add , create a new FormGroup object
- Save and add push to the FormArray of the original page
newModelType(): FormGroup {
return this.fb.group({
modelName: ['', Validators.required],
configList: this.fb.array([]),
});
}
// ...省略
// 模态框显示
show() {
this.isVisible = true
this.selectedType = this.newModelType();
}
// 保存
save() {
this.isVisible = false
// 原页面FormArray
this.modelList.push(this.selectedType);
}Finally found that this writing method can only be used in one direction Change, the modified value of the input outside the page will affect the modal box, but the value of the modal box is changed and saved, but the outside is not updated. Checking the internal parameters of the FormArray of the page through the console method found that there were actually changes, but Angular did not detect it. At this time, it is judged that the reason why there is no response is generally that the angular detection mechanism is not triggered. After carefully checking the document, I found that there is a very important line angular document at the bottom that says
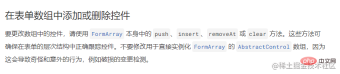

So what is the correct approach? ?
Don't be lazy when assigning values. You still have to re-create a new object and then get the assigned value of the original object. [Equivalent to deep copy] this.selectedType = this.newModelType();
const old = this.modelList.at(index);
this.selectedType.setValue({
'modelName': old.get('modelName').value
})You can update normally at this time.
Summary
In fact, in the end, it was essentially a return to the document. There are also many pitfalls in troubleshooting errors, and there are basically no angular articles in China, so we have to rely on external forums to find problems. For more programming-related knowledge, please visit:Programming Teaching! !
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of how to use FormArray and modal boxes in Angular. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools







