Home >Common Problem >What is a high-performance computer called?
What is a high-performance computer called?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2022-08-22 16:12:2017453browse
High-performance computers can also be called "supercomputers" and "supercomputers". They are mainly used to solve challenging problems that cannot be solved by other computers. They usually refer to extremely fast computing speeds, huge storage capacity, A type of computer with extremely high communication bandwidth. The main characteristics of high-performance computers include two aspects: huge data storage capacity and extremely fast data processing speed, so it can perform tasks in a variety of fields that cannot be performed by humans or ordinary computers.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
High-performance computers, also known as supercomputers and supercomputers, are the world's recognized high-tech commanding heights and one of the most important scientific fields in the 21st century.
High-performance computers (HPC, also known as supercomputers) are mainly used to solve challenging problems that cannot be solved by other computers. They usually refer to computers with extremely fast computing speed, huge storage capacity, and extremely high communication bandwidth. Computer-like.
The main features include two aspects: huge data storage capacity and extremely fast data processing speed, so it can perform work in a variety of fields that people or ordinary computers cannot perform.
High-performance computing is regarded as the "crown" of computer science and engineering, and countries have frequently launched research and development plans at the national level in recent years.
1. High-performance computing is an important scientific and technological direction
High-performance computers (HPC, High Performance Computer, also known as supercomputers) are important tools for the country. From nuclear explosion simulations, oil reservoir simulations, to extreme weather forecasts, high-performance computing protects national security and tranquility. Therefore, high-performance computing has also become one of the benchmarks for measuring the comprehensive strength between countries and is regarded as a symbol of national strength. Since 2020, the 14th Five-Year Plan and new infrastructure have driven the construction of high-performance computing centers in my country into a period of rapid growth. Local governments, enterprises and institutions in many places are actively building and preparing for the establishment of high-performance computing centers.
1.1. What is high performance computing?
High-performance computing refers to organizing multiple computing nodes, connecting them together through the network, and working together to form a more powerful computer, usually with extremely fast computing capabilities. A type of computer with high speed, extremely large storage capacity, and extremely high communication bandwidth. High-performance computing enables an entire computer cluster to work on the same task, solving a complex problem faster. A high-performance computer often performs one task (or a limited number of tasks). All computer resources are devoted to the same task. In order to solve the same problem, different computers in the cluster must have very good communication capabilities.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of high-performance computing node interconnection
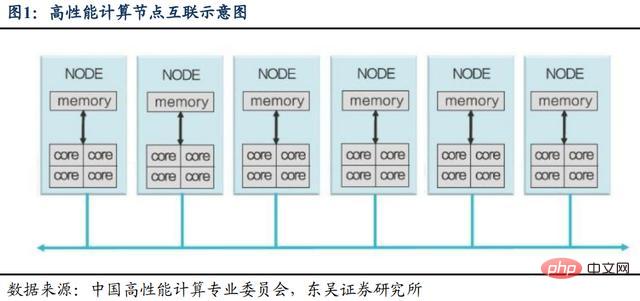
High-performance computers are a combination of computers and networks. Assuming that the Internet connects separate computers from the outside, then the cluster internalizes the network and makes the network a communication bridge for different computers within the system. The first person to creatively invent the cluster was Seymour Cray, known as the "Father of High-Performance Computing". In the 1960s, high-performance computing was only possible on specially designed, expensive mainframe computers. These mainframes require complex circuits to achieve high operating frequencies, so their design and production cycles are very long.
Seymour Cray proposed that parallelism is an effective way to improve computer performance. In 1964, the CDC 6600 developed by Seymour Cray came out. He connected multiple ordinary processors and made these processors work together. Government and scientific research departments began to purchase such new high-performance computers to replace the original mainframes. High-performance computers have made indelible contributions to large-scale scientific research projects such as the moon landing program, ushering in many years of sustained development and prosperity of high-performance computing technology and industry.
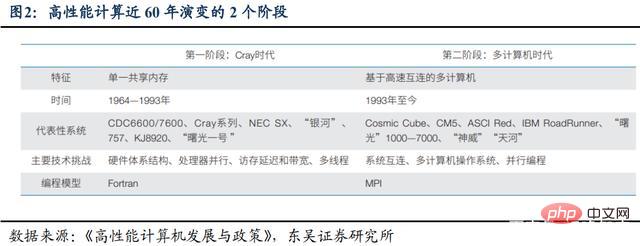
The evolution of high-performance computing in the past 60 years can be simply divided into two stages: the Cray era and the multi-computer era.
(1) Cray era. The 30 years from the 1960s to the early 1990s are called the "Cray Era". Led by the technological innovation of a single memory vector machine, Cray defined and led the high-performance computing market in the first 30 years. The first 30 years of development focused on "Dingtian" and only served national strategic departments.
(2) Multi-computer era. The last 30 years from the 1990s to the present are called the "multicomputer era". Due to the emergence of microprocessors and the popularization of a large number of industry-standard hardware, large-scale interconnection of multiple general-purpose and even commercial computing components has become scalable. Technical innovations in system architecture have dominated the development of high-performance computing to date. In the next 30 years, high-performance computers will meet the peak performance requirements of national strategic applications. At the same time, "location" has become the main goal of development. Market-driven and popularization of high-performance computing applications have become the salient features of the second stage.
1.2. Why is high performance computing important?
High-performance computing is the "crown" of computer science and engineering. High performance computing is one of the sources of computer technology. The core technologies of data centers that the Internet industry relies on, such as parallel programming tools such as Hadoop and remote communication technologies such as RDMA, are mostly derived from this. Therefore, high-performance computers are regarded as the "crown" of computer science and engineering. Countries frequently launch research and development plans at the national level. After China has repeatedly been listed in the global TOP500 of high-performance computing, the United States has included a number of Chinese high-performance computing-related institutions or enterprises on the entity list since 2015, including the National University of Defense Technology, Wuxi Jiangnan Computing Technology Research Institute, Sugon, Shenwei, etc. . However, there is still a large gap between my country's overall high-performance computing strength and that of the United States.
Therefore, the development of autonomous and controllable high-performance computing is crucial.


#2. High technical barriers to high-performance computing
High performance The core capability of computing is 64-bit double-precision floating point computing capability. High-performance computing is a general-purpose computing power, and its design goal is to provide complete and complex computing capabilities, with stronger high-precision computing capabilities. The Linpack test, which is widely used in the industry to measure high-performance computing performance, tests the "double-precision floating-point computing capability" of high-performance computing, that is, the calculation of 64-bit floating-point numbers (FP64), which is a high-precision numerical calculation . Among the numerical precision represented by binary, there are single precision (32 bits, FP32), half precision (16 bits, FP16) and integer types (such as INT8, INT4), etc. A higher number of digits means that people can reflect changes in two values within a wider range of values, thereby achieving more accurate calculations.
High-performance computing has higher underlying chip performance requirements than ordinary data centers and intelligent computing centers. There are many kinds of computing centers, which can be roughly divided into data centers, high-performance computing centers, intelligent computing centers, etc., and they can all provide services in the form of cloud. Taking the realization of artificial intelligence requirements as an example, reasoning, training and simulation are the three main tasks of AI.
In this dimension, the upper limit of the chip's application is determined by its underlying structure, and it cannot be improved even with software optimization. From the chip level, if the underlying chip uses a CPU-specific AI chip, it can only complete AI reasoning and training tasks, but cannot complete simulation. Because AI chips cannot implement double-precision floating-point operations, double-precision floating-point operations largely involve solving linear algebraic equations, and many problems in nature, including scientific issues, social issues, etc., can ultimately be transformed into linear algebraic equation-solving problems.
#The architecture design and software of high-performance computing are equally important. Chip is an important part of high-performance computing, but it is not the entire high-performance computing technology. High-performance computing is not simply stacking CPUs. If there are deficiencies in architectural design, high-speed Internet, parallel file systems, storage arrays, etc., high-performance computing performance cannot be improved no matter how many CPUs are stacked. With the enhancement of computing power and the increase in the scale and complexity of application projects, high-performance computers have increasingly higher performance requirements for parallel file systems. The technological spillover benefits of high-performance computing are very obvious. Since servers can smoothly adopt high-performance computing interconnect technology, CPU technology, operating system technology, and parallel software design technologies, the accumulation of high-performance computing can naturally overflow to the server industry.
3. The high-performance computing market is highly prosperous
3.1. In what scenarios is high-performance computing mainly used?
High-performance computing is suitable for tasks that require parallel computing, and application scenarios continue to expand. The main application scenarios of high-performance computing are divided into two categories. One is numerical simulation scenarios such as aircraft design, nuclear simulation experiments, nebula simulation, and code decryption. The other is data analysis scenarios such as big data analysis, statistics, and artificial intelligence.
Since many conditions in the engineering design of aircraft and other aircraft cannot be measured and can only be calculated and simulated, the United States is very cautious about exporting high-performance computing. High-performance computing applications are developing in a wider and wider direction from the high-precision in the past. With the development of high-performance computing, especially the continuous decline in usage costs, its application fields have also rapidly expanded from scientific computing fields such as nuclear weapons development, information security, and oil exploration with national strategic significance to the broader main battlefields of the national economy, such as Pharmaceuticals, gene sequencing, animation rendering, data mining, financial analysis, Internet services, etc.
Judging from the Linpack performance share of industry application fields in China's TOP100 high-performance computers in November 2021, computing power services, high-performance computing centers, artificial intelligence, scientific computing and other fields are the main users of high-performance computing , Internet big data, especially the field of AI, is growing strongly.
Figure 6: Share of application fields in China’s TOP100 industries (2021.11)
#3.2. How big is the market space for high-performance computing?
The 14th Five-Year Plan and the new infrastructure drive high-performance computing into a period of rapid growth. The construction of high-performance computing centers in our country mainly establishes the construction plan of high-performance computing centers through cooperation agreements between ministries and provinces (municipalities). The Ministry of Science and Technology sets goals for host performance on behalf of the national science and technology strategy. The local government hopes that the high-performance computing center can become a functional carrier for regional science and technology development, gathering talents, innovating science and technology, and promoting economic development. In March 2021, my country's "14th Five-Year Plan" clearly stated that it is necessary to "accelerate the construction of a national integrated big data center system, strengthen the overall intelligent dispatch of computing power, build a number of national hub nodes and big data center clusters, and build E-level and 10E-level supercomputing center." According to the plan, high-performance computing centers will be established in Hefei, Lanzhou, Xiamen, Taiyuan and other places.
The implementation of the "Eastern Digital and Western Counting" project is expected to further promote the development of high-performance computing centers in the western region. In February 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission approved the launch of the construction of national computing power hub nodes in 8 places including Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, Chengdu-Chongqing, Inner Mongolia, Guizhou, Gansu, and Ningxia, and planned 10 countries Data center cluster. At this point, the overall layout design of the national integrated big data center system has been completed, which represents the official launch of the "Eastern Data and Western Counting" project. The west has wind power generation and photovoltaic power generation, abundant energy, and relatively low annual average temperature, which is very suitable for the survival of computing centers. However, high-performance computing business does not have high demand for real-time communication. In the future, high-performance computing centers are expected to become the basis for optimizing the layout of computing power. important carrier.
We estimate that the investment in a single large-scale high-performance computing center will be more than 2 billion yuan. Based on the average number of new high-performance computing centers built every year, the market size of the high-performance computing center planned by the government will reach 10 billion yuan per year.
#China’s overall high-performance computing market will exceed 40 billion yuan in 2022. In addition to government planning, many Internet giants such as Alibaba and Tencent are actively deploying high-performance computing construction. Take Tencent as an example. Its Yangtze River Delta Artificial Intelligence High-Performance Computing Center, which officially started construction in June 2020, has invested more than 45 billion yuan. After completion, it will undertake various large-scale AI algorithm calculations, machine learning, image processing, scientific computing and engineering. Computational tasks. In addition, financial institutions, operators, etc. are actively deploying their own high-performance computing. According to Guanyan Tianxia's forecast, the overall market size of China's high-performance computing industry will exceed 40 billion yuan in 2022, with a CAGR of about 13% from 2021 to 2025.
4. The competitive landscape of the high-performance computing market is stable
Lenovo, Sugon, and Inspur rank the top three in terms of market share. Judging from the statistics of the number of systems of major companies in China's high-performance computing TOP100, before 2002, the TOP100 were mainly foreign HP and IBM, and later China's Lenovo, Sugon and Inspur were the main ones.
Zhongke Sugon completed the 863 project "Sugon 2000" super server with scalable cluster architecture in 1998. After completing the "Sugon 3000" super server in 2001, starting from 2005, market competition began to show outstanding performance , Sugon ranked first in market share in terms of installed units for 10 consecutive years from 2010 to 2019, accounting for nearly 40% in 2019.
After Inspur completed the "863 Plan" fault-tolerant server project in 2012, it began to show significant improvement in 2014.
Through the acquisition of IBM's X86 HPC product line in 2014, Lenovo's market share has suddenly increased. By 2021, it has achieved the first place in the TOP100 installed units.
Among Lenovo, Inspur, and Sugon, only Sugon has domestically produced independent intellectual property rights from hardware such as chips to software systems.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What is a high-performance computer called?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- 64-bit microcomputer system refers to
- Office automation is an application of computers. What does it belong to according to the classification of computer applications?
- What were the main logic components used in the world's first electronic digital computer?
- The development process of computer networks can be roughly divided into several stages
- What is usually referred to as a computer host?
- What does a microcomputer hardware system consist of?





