What are the three conveying methods of pneumatic conveyors?
Three pneumatic conveying methods: 1. Dilute phase conveying, the solid content is lower than "1-10kg" per cubic meter, the operating air speed is high, and the conveying distance is basically within 300 meters; 2. Dense phase Transportation, the solid content is "10-30kg" without cubic meters or the solid-gas ratio is greater than 25; 3. Negative pressure transportation, the pressure in the pipeline is lower than atmospheric pressure, self-priming feeding, but must be discharged under negative pressure, it can The conveying distance is shorter.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, DELL G3 computer.
What are the three conveying methods of pneumatic conveyor?
Pneumatic conveying is divided into:
1. Dilute phase conveying: the solid content is lower than 1-10kg/m3, operation The air speed is high (about 18~30m/s), and the conveying distance is basically within 300m. For the now mature equipment material seal pump, the conveying operation is simple, there are no mechanical rotating parts, the conveying pressure is low, no maintenance, and maintenance-free.
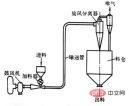
2. Dense phase transportation: a transportation process with a solid content of 10-30kg/m3 or a solid-gas ratio greater than 25. The operating air speed is lower and the air pressure is higher. Nowadays, the mature equipment warehouse pump has a transportation distance of more than 500m, which is suitable for long-distance transportation. However, this equipment has many valves, pneumatic and electric equipment. The conveying pressure is high and all pipelines need to be made of wear-resistant materials. Intermittent gas tank type dense phase conveying. The method is to add the particles into the pressure tank in batches, and then ventilate and blow them loose. After the pressure in the tank reaches a certain pressure, the discharge valve is opened and the granular materials are blown into the delivery pipe for transportation. Pulse conveying is to pass a stream of compressed air into the lower tank to blow the material loose; another stream of pulse compressed air with a frequency of 20 to 40 min-1 is blown into the entrance of the feeding pipe to form small segments of material columns that are alternately arranged in the pipe. and a small section of air column, which is propelled forward by air pressure.
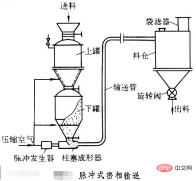
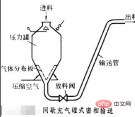
3. Negative pressure transportation: The pressure in the pipeline is lower than atmospheric pressure, and the material is self-primed, but must be discharged under negative pressure. , the distance that can be transported is shorter; advantages: smaller equipment investment and load. Disadvantages: high operating flow rate, severe pipe wear, and leaks due to wear that cannot be detected.
Expand knowledge
Pneumatic conveying, also known as air flow conveying, uses the energy of air flow to transport granular materials along the direction of air flow in a closed pipe. , is a specific application of fluidization technology. The pneumatic conveying device has a simple structure and is easy to operate. It can be conveyed horizontally, vertically or in an inclined direction. During the conveying process, it can also perform physical operations such as heating, cooling, drying and air flow classification of materials or some chemical operations at the same time. Compared with mechanical transportation, this method consumes more energy, the particles are easily damaged, and the equipment is also susceptible to abrasion. Materials that contain a lot of water, are sticky, or easily generate static electricity when moving at high speeds are not suitable for pneumatic conveying.
The main features of pneumatic conveying are large conveying volume, long conveying distance and high conveying speed; it can load materials in one place and then unload materials in multiple places.
When carrying out dilute phase transportation in horizontal pipelines, the gas velocity should be high to make the particles dispersed and suspended in the air flow. When the gas velocity decreases to a certain critical value, particles will begin to deposit on the lower part of the tube wall. This critical gas velocity is called the deposition velocity. This is the lower limit of the gas velocity when the dilute phase is transported horizontally. When the operating gas speed is lower than this value, a sedimentation layer appears in the tube, the flow channel cross-section is reduced, and the airflow above the sedimentation layer still runs at the sedimentation speed.
It is used for upward pneumatic transportation in vertical pipes. When the air speed is high, the particles are dispersed and suspended in the air flow. When the particle transport volume is constant, the solid content in the pipeline increases as the gas velocity is reduced. When the air velocity decreases to a certain critical value, the air flow can no longer disperse the dense particles evenly, and the particles converge into a plunger shape, causing a surge phenomenon and a sharp increase in pressure drop. This critical speed is called the choking speed, which is the lower limit of the gas speed when the dilute phase is transported vertically upward. For particles of uniform size, the deposition velocity and choking velocity are approximately equal. However, for materials with a certain particle size distribution, the deposition speed will be 2 to 6 times the choking speed
Suction characteristics
1. Suitable for transporting from many places Convey to one place. There can be one or several feeding points, and the feeding pipe can be equipped with one or more branch pipes. Not only can materials from multiple feeding points be transported to the unloading point in sequence, but materials from multiple feeding points can also be transported to the unloading point at the same time.
2. Under the action of negative pressure, the material is easily inhaled, so the material supply at the throat is simple. The hopper can be opened for continuous feeding and conveying.
3. Materials are transported under negative pressure, and moisture is easy to evaporate. Therefore, materials with higher moisture content are easier to transport than pressure-feeding. Materials supplied under heating can be cooled through transportation.
4. Components must be kept sealed. The structures of international separators, dust collectors, air locks and other components are relatively complex.
5. The fan is located at the end of the system, requiring a high degree of air purification.
Press feeding features
1. Suitable for dispersed transportation from one place to several places. That is, there is one feeding point, and there can be one or several unloading points.
2. Compared with the suction type, the concentration and conveying distance can be greatly increased.
3. Under positive pressure, materials are easily discharged from the discharge port, so the structure of the separator and dust collector is simple, and generally no air lock is needed.
4. The blower or air compressor is at the head end of the system and has low requirements for air purification.
5. Under the action of positive pressure, it is difficult for materials to enter the conveying pipe, so the structure of the feeding device is relatively complex.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What are the three conveying methods of pneumatic conveyors?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor





