Home >Web Front-end >Vue.js >Summarize and organize VUE instance parameters and MVVM mode knowledge points
Summarize and organize VUE instance parameters and MVVM mode knowledge points
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-08-09 17:37:382197browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about vue, which mainly introduces issues related to vue instance parameters and MVVM mode. Instantiate a Vue object, and the parameter is an option object. Let’s take a look at it together, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
Configuration parameters
Instantiate a Vue object. The parameter is an options object. The options contained in it will be briefly explained below.
new Vue({
options})
In the Vue instance, you can view the configuration items of the instance through this.$options

Data related options
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Declare the data object that requires reactive binding | |
| Receive data from the parent component | |
| Manually pass props when creating an instance to facilitate testing props | |
| is used to declare calculated properties | |
| Methods used to define Vue instances | |
| Listen to properties, monitor data changes on the Vue instance, and call its callback function |
DOM related options
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Declare the mount point of the Vue root component (unique to the root component) | |
| String template for mounting elements | |
| Rendering function, used to create virtual DOM, is an alternative to string templates | |
| It is only used in the development environment. When an error occurs in render(), additional rendering output is provided |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Occurs after the Vue instance is initialized, before the data observer and event/watcher events are configured | |
| Occurs after the Vue instance is initialized And after the data observer and event/watcher events are configured | |
| are called before the mount starts, at which time render() is called for the first time | |
| el is replaced by the newly created vm.$el and is mounted to the instance before calling | |
| Called when the data is updated, which occurs before the virtual DOM is re-rendered and patched | |
| Called after data changes cause the virtual DOM to be re-rendered and patched | |
| Called when the keep-alive component is activated | |
| When the keep-alive component is deactivated Call | |
| Call before the instance is destroyed, the Vue instance is still available | ##destroyed |
| filters | |
| components | |
Options
| ##parent | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mixins | Mix the attributes into the Vue instance object, and use it in the Vue The properties of the own instance object are executed before being called (multiple inheritance of components) | |||||||||||||
| extends | is used to declare inheritance of another component, eliminating the need to use Vue.extend. Convenient for extending single file components (single inheritance of components) | |||||||||||||
| provide&inject | 2 properties need to be used together to inject dependencies into all sub-components | |||||||||||||
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Allows the component to call itself recursively to display more friendly warning messages during debugging |
| delimiters | Change the style of the template string, The default is {{}} |
| functional | Make the component stateless (no data) and instanceless (no this context) |
| model | Allow custom components to customize props and events when using v-model |
| By default, the parent Scoped non-props property bindings will be applied to the root element of the child component. When writing components that are nested within other components or elements, you can turn off these default behaviors by setting this property to false | |
| When set to true, it will be retained and HTML comments in the rendering template |
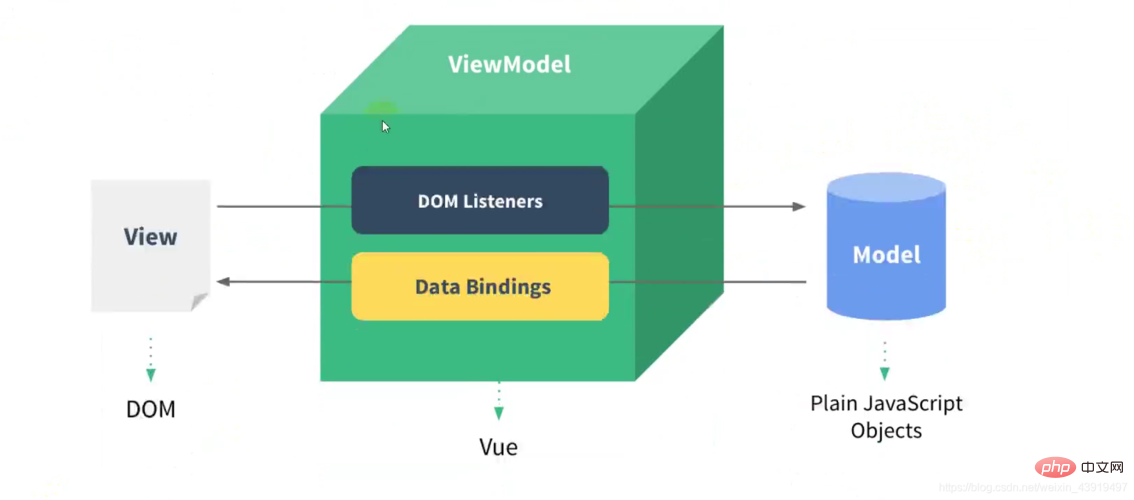 Simply put, when the view changes, the model will also change, and when the model changes, the view will also change. Changes occur, this is Vue's two-way data binding
Simply put, when the view changes, the model will also change, and when the model changes, the view will also change. Changes occur, this is Vue's two-way data binding
The key point is how the data updates the view, because the view updates the data can actually be monitored through events. For example, the input tag can monitor the input event.
- Implement a listener Observer to hijack and monitor all properties, and notify subscribers if there is any change.
- Implement a subscriber Watcher that can receive property change notifications and execute corresponding functions to update the view.
- Implement a parser Compile that can scan and parse the relevant instructions of each node, and initialize the template data and initialize the corresponding subscriber according to it.
Vue’s two-way binding principle:
The two-way binding of Vue data is to combine publisher-subscriber through data hijacking implemented through patterns. Its core is to set the set and get functions through the Object.defineProperty() method to achieve data hijacking. When the data changes, messages are published to subscribers and the corresponding monitoring callbacks are triggered. That is to say, the data and the view are synchronized. When the data changes, the view changes, and when the view changes, the data also changes;
[Related recommendations:The above is the detailed content of Summarize and organize VUE instance parameters and MVVM mode knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Let's talk about the return value of the setup function in vue3
- Detailed explanation of the parameters of the setup function in vue3 - props and context
- Example: What are the setup parameters attrs, slots, and emit in vue3?
- Summary Vue creates responsive data objects (reactive, ref, toRef, toRefs)
- In-depth analysis of Vue's computed property API (computed)

