Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >What is dd in linux
What is dd in linux
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2022-07-14 15:50:014365browse
In Linux, dd is a command used to read, convert and output data; the function of this command is to copy a file using blocks of a specified size, and perform specified conversions while copying. This command Data can be read from standard input or files, converted according to the specified format, and then output to a file, device, or standard output.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is dd in Linux
DD is a very useful command under Linux/UNIX system. Its function is to copy a file with blocks of a specified size, and perform specified operations while copying. Convert.
Linux dd command is used to read, convert and output data.
dd can read data from standard input or files, convert the data according to the specified format, and then output it to a file, device, or standard output.
Parameter description:
if=File name: Enter the file name, the default is standard input. That is, specify the source file.
of=File name: output file name, default is standard output. That is, specify the destination file.
ibs=bytes: Read bytes bytes at a time, that is, specify a block size of bytes bytes.
obs=bytes: Output bytes bytes at a time, that is, specify a block size of bytes bytes.
bs=bytes: Also set the read/output block size to bytes bytes.
cbs=bytes: Convert bytes bytes at a time, that is, specify the conversion buffer size.
skip=blocks: Skip blocks blocks from the beginning of the input file before starting copying.
seek=blocks: Skip blocks blocks from the beginning of the output file before starting copying.
count=blocks: Only copies blocks blocks, and the block size is equal to the number of bytes specified by ibs.
conv=
conversion: Convert the file with the specified parameters.
ascii: Convert ebcdic to ascii
ebcdic: Convert ascii to ebcdic
ibm: Convert ascii to alternate ebcdic
block: Convert each line to length cbs, fill the missing parts with spaces
unblock: Make each line The length is cbs, and the missing part is filled with spaces
lcase: Convert uppercase characters to lowercase characters
ucase: Convert lowercase characters For uppercase characters
swap: swap each pair of bytes entered
noerror: do not stop on error
notrunc: Do not truncate the output file
#sync: Fill each input block to ibs bytes, and fill in the missing parts with null (NUL) characters.
--help: Display help information
--version: Display version information
The example is as follows:
To make a boot disk under Linux, you can use the following command:
dd if=boot.img of=/dev/fd0 bs=1440k
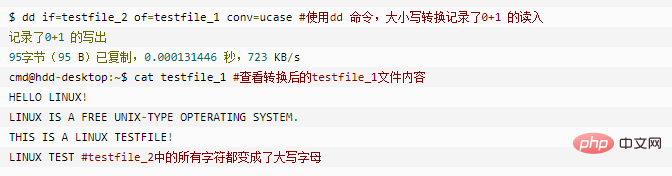
Convert all English letters in the testfile file to uppercase, and then convert it into the testfile_1 file. Use the following command in the command prompt:
dd if=testfile_2 of=testfile_1 conv=ucase
The content of testfile_2 is:
$ cat testfile_2 #testfile_2的内容 HELLO LINUX! Linux is a free unix-type opterating system. This is a linux testfile! Linux test
After the conversion is completed, the content of testfile_1 is as follows:
Recommended learning: Linux Video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What is dd in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

