Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Detailed explanation of explain usage for MySQL learning
Detailed explanation of explain usage for MySQL learning
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-03-07 16:56:132623browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces related issues about explain. The explain command is mainly used to view the execution plan of the SQL statement. Check the execution plan of the SQL statement. I didn't use indexes, did I do a full table scan, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql tutorial
The explain command is mainly used to view the execution plan of the SQL statement and check whether the SQL statement has been used. Index, whether there is a full table scan, etc. It can simulate the optimizer to execute SQL query statements to know how MySQL handles user SQL statements.
1. What explain can do
Through the explain statement, we can analyze the following results
| Reading order of the table | Operation type of data read operation |
|---|---|
| References between tables | Which indexes can be used |
| How many rows of each table are queried by the optimizer | Which indexes are actually used |
2. How to use explain
##Usage: explain SQL statement; type, possible_keys, key, key_len, ref, rows, Extra Summary description:
##Field
Description| id | |
|---|---|
| select_type | Query Type |
| table | The table that outputs the result set |
| type | The connection type of the table |
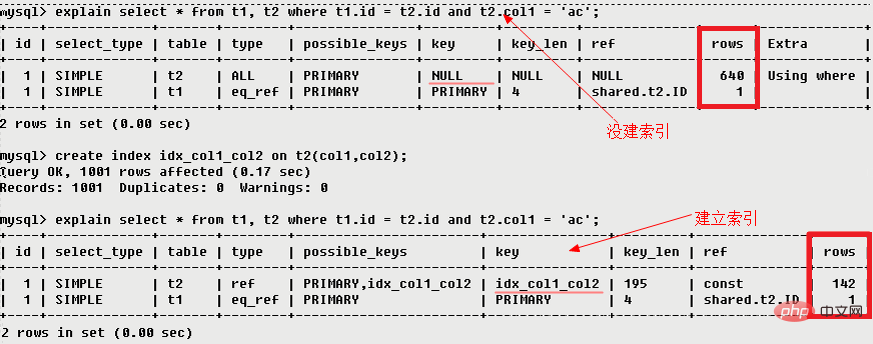
| possible_keys | Indices that may be used when querying |
| key | Index actually used |
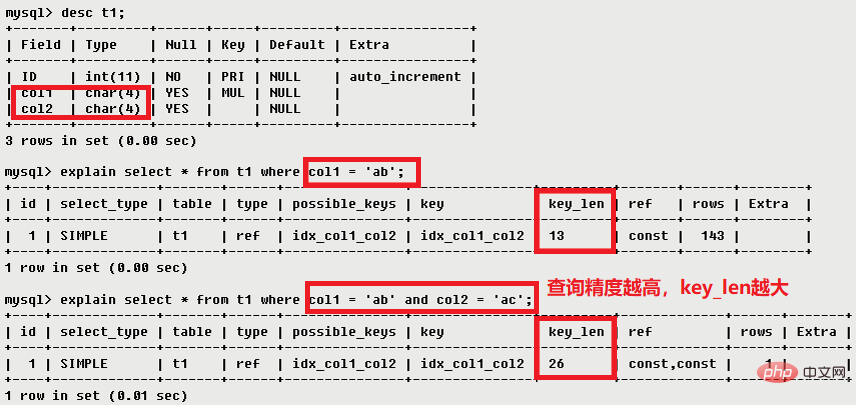
| key_len | The length of the index field |
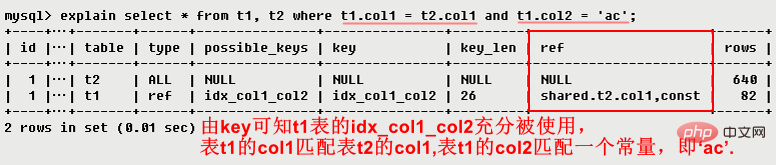
| ref | Comparison of columns and indexes |
| rows | The number of scanned rows (estimated number of rows) |
| Extra | Description and explanation of the execution |
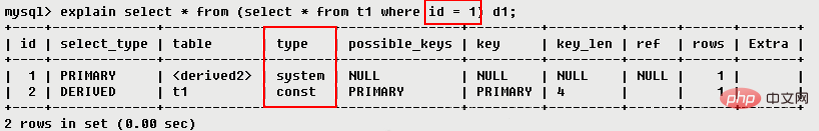
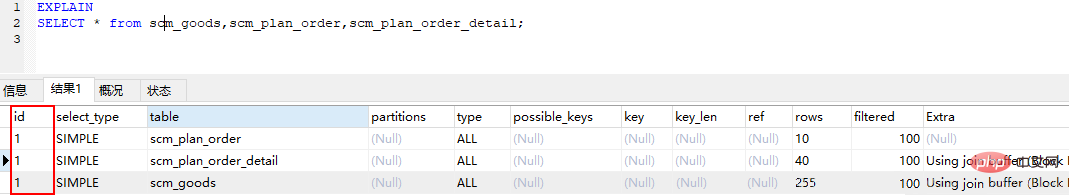
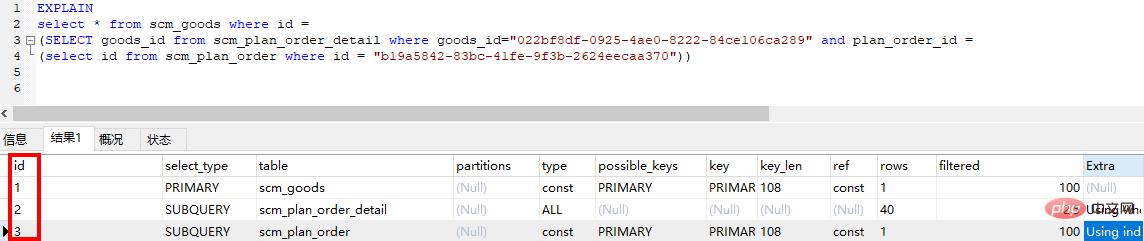
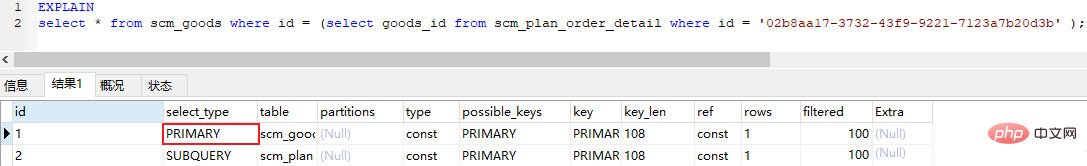
3. Explain the meaning of each field3.1 id ●● The id is the same, the execution order is from top to bottom, regardless of the order in sql
If it is a child For queries, the serial number of the id will increase. The larger the id, the higher the priority, and the earlier it will be executed
3.2 select_type select_type simple (Simple select, no complex queries such as union or subquery are used)
primary (The outermost query in the subquery, if the query contains any complex subparts, the outermost select is marked as primary)
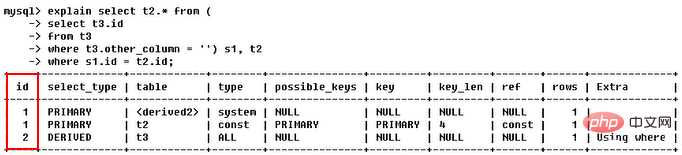
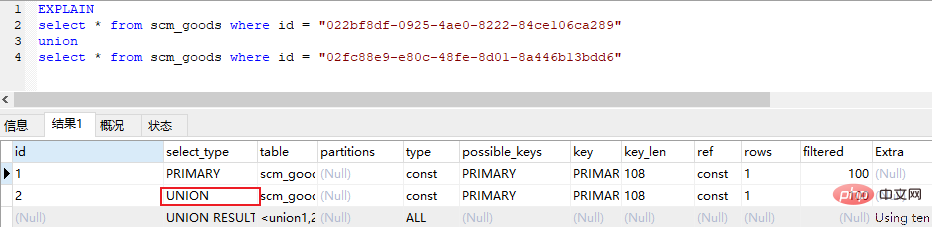
subquery (Subquery included in select or where list) Sync (4)derived (The subqueries contained in the from list are marked as derived (derived), MySQL will recursively execute these subqueries and put the results in a temporary table) (5)union (The second or subsequent select statement in the union)
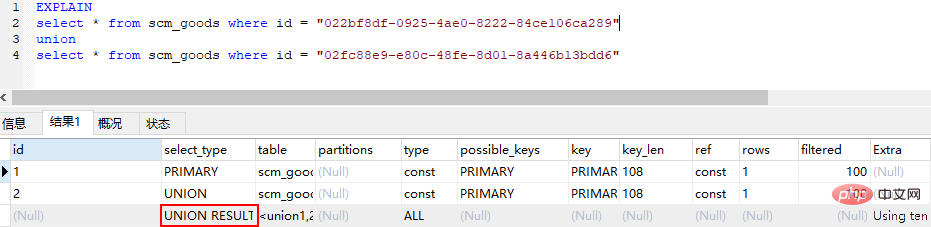
union result (The result of the union, the second select statement in the union statement All selects after select start)
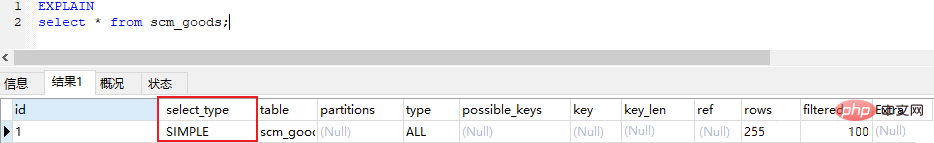
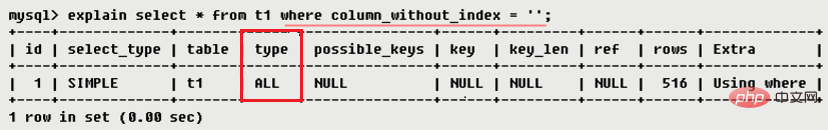
tableDisplay the name of the table in the database accessed in this step (display Which table does this row of data refer to?). type shows which type is used in the query. Type includes all, index, range, ref, eq_ref, const, system, NULL, its performance increases in order. : Full Table Scan, MySQL will traverse the entire table to find matching rows ## ● ●
·
·
● ## ● NULL : MySQL decomposes the statement during the optimization process, and does not even need to access the table or index during execution, such as selecting the minimum value from an index column This can be done via a separate index lookup. 3.5 possible_keys possible_keysDisplays one or more indexes that may be applied to this table. If an index exists on the field involved in the query, the index will be listed, but may not be actually used by the query . (The indexes that this query can utilize, if there are no indexes display null)3.6 key 3.7 key_len
The column that displays the index is used to indicate the connection matching conditions of the above table, that is Which columns or constants are used to find the value on the index column The number of rows indicates that MySQL estimates the number of rows that need to be read to find the required records based on table statistics and index selection.3.10 Extra Extra This column contains detailed information about MySQL resolving the query. There are the following situations: When the requested columns are all part of the same index, it means that the mysql server will filter the rows after the storage engine retrieves them. Indicates that MySQL needs to use Temporary tables are used to store result sets, which are commonly used in sorting and grouping queries. Common group by; order by Using filesort When the Query contains the order by operation, and the sorting completed by the index cannot be used The operation is called "file sorting" ● ● Impossible whereThis value emphasizes that the where statement will result in no rows that meet the condition (a result that cannot exist by collecting statistics). ● Select tables optimized awayThis value means that by using indexes only, the optimizer may return only one row from the aggregate function result ● No tables used Queryuses from dual or does not contain any from clause 4. Summary● explain will not tell you information about triggers, stored procedures or users The impact of custom functions on queries ● explain does not consider various Cache● explain cannot display the optimization work done by MySQL when executing queries ● explain can only Explain the select operation, other operations should be rewritten as select and then view the execution plan● Some statistical information is estimated, not precise values Recommended learning:mysql video tutorial |
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of explain usage for MySQL learning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!


 index
index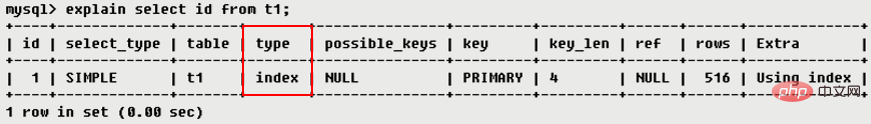 range
range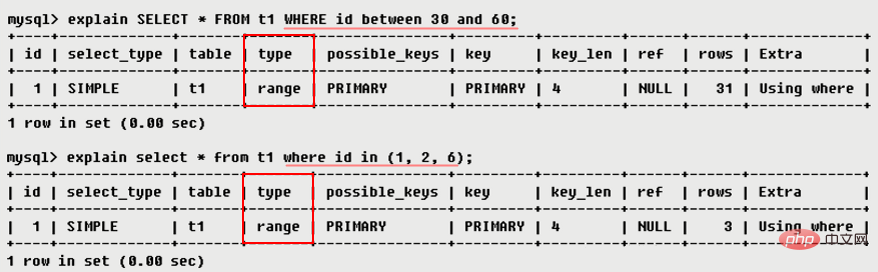 ref
ref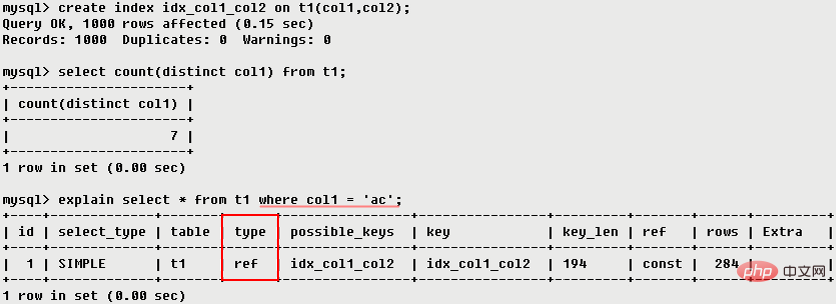 eq_ref
eq_ref