Home >Web Front-end >Front-end Q&A >Summary of strange button styles that appear frequently in CSS
Summary of strange button styles that appear frequently in CSS
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-01-06 17:54:091963browse
This article is based on some buttons that frequently appear in design drafts and are slightly difficult and tricky to implement using CSS. It explains how to implement them as much as possible using CSS. I hope everyone has to help.

First let’s take a look at these button shapes that often appear:
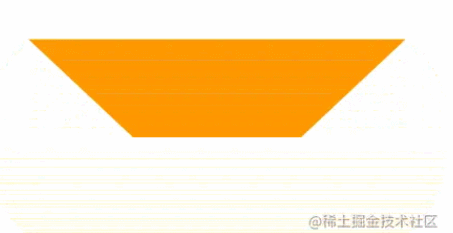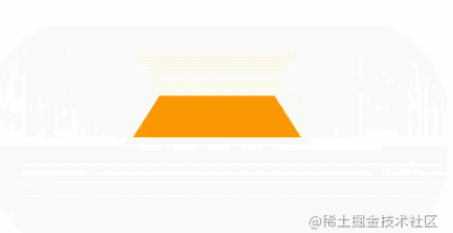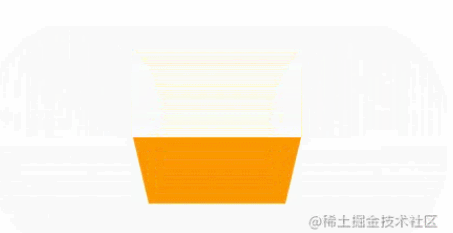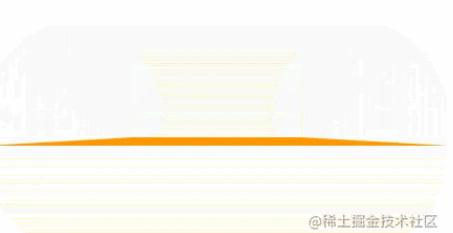
Rectangle and rounded corners buttons
Normally speaking, there are only two kinds of buttons we encounter-rectangular and rounded corners:

They are very simple, with width, height, rounded corners and background color.
<div class='btn rect'>rect</div>
<div class='btn circle'>circle</div>.btn {
margin: 8px auto;
flex-shrink: 0;
width: 160px;
height: 64px;
}
.rect {
background: #f6ed8d;
}
.circle {
border-radius: 64px;
background: #7de3c8;
}Trapezoid and Parallelogram
Next, based on the deformation of the rectangle, trapezoid and parallelogram buttons often appear.
To achieve them, you can mainly use transform, but please note that after using transform, the text in the label will also be deformed in the same way. Therefore, we usually use pseudo-elements of elements to achieve styling, so you can do It does not affect the text inside the button.
Parallelogram
Use transform: skewX(). Pay attention to what is said above. Use the pseudo-element of the element to implement the parallelogram. Do to not affect the internal text.
<div class='btn parallelogram'>Parallelogram</div>
.parallelogram {
position: relative;
width: 160px;
height: 64px;
&::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
background: #03f463;
transform: skewX(15deg);
}
}
If you don’t want to use pseudo-elements, in addition to transform: skewX(), parallelograms can also be implemented using gradients.
It’s probably like this:
{
background: linear-gradient(45deg, transparent 22%, #04e6fb 22%, #9006fb 78%, transparent 0);
}Trapezoid
The trapezoid is slightly more complicated than the parallelogram. It uses perspective. In fact, a certain 3D transformation is used. The principle is a rectangle rotating around the X axis, like this:

Use perspective and transform: rotateX(). Of course, they can be written together:
<div class='btn trapezoid'>Trapezoid</div>
.parallelogram {
position: relative;
width: 160px;
height: 64px;
&::after {
content:"";
position: absolute;
top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0;
transform: perspective(40px) rotateX(10deg);
transform-origin: bottom;
background: #ff9800;
}
}
Cut corners--solid color background and gradient background
The next step is the corner clipping graphics , the most common method is mainly implemented with the help of gradient linear-gradient. Looking at such a graph
<div></div>
notching {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, transparent 10px, #ff1493 0);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}The results are as follows,

Based on this, we only need Use multiple gradients to achieve 4 such graphics, and use background-position to position the four corners:
<div class="notching">notching</div>
.notching {
background:
linear-gradient(135deg, transparent 10px, #ff1493 0) top left,
linear-gradient(-135deg, transparent 10px, #ff1493 0) top right,
linear-gradient(-45deg, transparent 10px, #ff1493 0) bottom right,
linear-gradient(45deg, transparent 10px, #ff1493 0) bottom left;
background-size: 50% 50%;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
Use clip- path implements the corner-cut graphics of the gradient background
Of course, there is a problem with this technique. When the background color is required to be a gradient color, this method is clumsy.
Fortunately, we have another way to use clip-path to cut out a corner shape. In this way, the background color can be any customized color, whether it is a gradient or a solid color:
<div class="clip-notching">notching</div>
.clip-notching {
background: linear-gradient(
45deg,
#f9d9e7,
#ff1493
);
clip-path: polygon(
15px 0,
calc(100% - 15px) 0,
100% 15px,
100% calc(100% - 15px),
calc(100% - 15px) 100%,
15px 100%,
0 calc(100% - 15px),
0 15px
);
}Simply implement a gradient background, and then the core is to use clip-path: polygon() to cut out the shape we want (an 8-sided polygon) based on the gradient rectangular shape:

Of course, the above code is very easy to think of the following 6-sided shape, which can be easily obtained using gradient and clip-path:

Arrow button
Next is the arrow button, carefully observe the corner cut button above, when the corners on both sides have been cut off enough , it becomes an arrow shape.
We can use double gradients to implement a single arrow button:
<div class="arrow">arrow</div>
&.arrow {
background: linear-gradient(
-135deg,
transparent 22px,
#04e6fb 22px,
#65ff9a 100%
)
top right,
linear-gradient(
-45deg,
transparent 22px,
#04e6fb 22px,
#65ff9a 100%
)
bottom right;
background-size: 100% 50%;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}An arrow comes out:
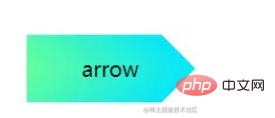


一样的,它也是两个渐变的叠加,渐变的颜色是透明 --> 颜色A --> 颜色B --> 透明。当然,同样在这里也可以使用 clip-path:
这里给出 clip-path 的解法:
{
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #04e6fb, #65ff9a);
clip-path: polygon(
0 0,
30px 50%,
0 100%,
calc(100% - 30px) 100%,
100% 50%,
calc(100% - 30px) 0
);
}内切圆角
下面这个按钮形状,多出现于优惠券,最常见的解法,也是使用渐变,当然,与切角不同,这里使用的径向渐变。
首先,看这样一个简单的例子:
<div></div>
div {
background-image: radial-gradient(circle at 100% 100%, transparent 0, transparent 12px, #2179f5 12px);
}可以得到这样一个图形:


所以,只需控制下 background-size,在 4 个角实现 4 个这样的图形即可:
<div class="inset-circle">inset-circle</div>
&.inset-circle {
background-size: 70% 70%;
background-image: radial-gradient(
circle at 100% 100%,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 0 0,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 100% 0,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 0 100%,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right bottom, left top, right top, left bottom;
}
借助 mask 实现渐变的内切圆角按钮
如果背景色要求渐变怎么办呢?
假设我们有一张矩形背景图案,我们只需要使用 mask 实现一层遮罩,利用 mask 的特性,把 4 个角给遮住即可。
mask 的代码和上述的圆角切角代码非常类似,简单改造下即可得到渐变的内切圆角按钮:
<div class="mask-inset-circle">inset-circle</div>
.mask-inset-circle {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #2179f5, #e91e63);
mask: radial-gradient(
circle at 100% 100%,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 0 0,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 100% 0,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
),
radial-gradient(
circle at 0 100%,
transparent 0,
transparent 12px,
#2179f5 13px
);
mask-repeat: no-repeat;
mask-position: right bottom, left top, right top, left bottom;
mask-size: 70% 70%;
}这样,我们就得到了这样一个图形:

当然,读懂上述代码,你需要首先弄清楚 CSS mask 属性的原理。
圆角不规则矩形
下面这个按钮形状,也是最近被问到最多的,先来看看它的造型:

不太好给它起名,一侧是规则的带圆角直角,另外一侧则是带圆角的斜边。
其实,它就是由圆角矩形 + 圆角平行四边形组成:

所以,借助两个伪元素,可以轻松的实现它们:
<div class="skew">Skew</div>
.skew {
position: relative;
width: 120px;
&::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
border-radius: 10px;
background: orange;
transform: skewX(15deg);
}
&::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: -13px;
width: 100px;
height: 64px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: orange;
}
}
由于一个伪元素叠加在另外一个之上,所以对其中一个使用渐变,一个则是纯色,其颜色是可以完美衔接在一起的,这样就实现了渐变色的该图形:

外圆角按钮
接下来这个按钮形状,常见于 Tab 页上,类似于 Chrome 的分页:

我们对这个按钮形状拆解一下,这里其实是 3 块的叠加:

只需要想清楚如何实现两侧的弧形三角即可。这里还是借助了渐变 -- 径向渐变,其实他是这样,如下图所示,我们只需要把黑色部分替换为透明即可,使用两个伪元素即可:

代码如下:
<div class="outside-circle">outside-circle</div>
.outside-circle {
position: relative;
background: #e91e63;
border-radius: 10px 10px 0 0;
&::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
left: -20px;
bottom: 0;
background: #000;
background:radial-gradient(circle at 0 0, transparent 20px, #e91e63 21px);
}
&::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
right: -20px;
bottom: 0;
background: #000;
background:radial-gradient(circle at 100% 0, transparent 20px, #e91e63 21px);
}
}即可得到:

上述的所有图形的完整代码,你可以在这里看到:CodePen Demo -- CSS Various Button Shapes | CSS 各种造型按钮
总结一下
基于上述的实现,我们不难发现,一些稍微特殊的按钮,无非都通过拼接、障眼法、遮罩等方式实现。
而在其中:
渐变(线性渐变 linear-gradient、径向渐变 radial-gradient、多重渐变)
遮罩 mask
裁剪 clip-path
变形 transform
发挥了重要的作用,熟练使用它们,我们对于这些图形就可以信手拈来,基于它们的变形也能从容面对。
上述的图形,再配合 filter: drop-shadow(),基本都能实现不规则阴影。
再者,更为复杂的图形,如下所示:

还是切图吧,CSS 虽好,实际使用中也需要考虑投入产出比。
(Learning video sharing: css video tutorial)
The above is the detailed content of Summary of strange button styles that appear frequently in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- What is the usage of content in css3
- Take a look at how to achieve the dynamic effect of the revolving door of pictures using CSS?
- How CSS implements absolute positioning and centering technology for horizontal and vertical centering
- 13 commonly used CSS font style attributes, which ones do you know?
- Use pure CSS to achieve the animation effect of rotating React icons

