Teach you step by step how to use Redis to implement billion-level data statistics (actual combat)
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-08-09 10:43:185856browse

In the business scenario of mobile applications, we need to save such information: a key is associated with a data collection, and at the same time, we also need to statistically sort the data in the collection. [Related recommendations: Redis Video Tutorial]
Common scenarios are as follows:
- Give a userId to determine the user’s login status;
- two The check-in status of 100 million users in the last 7 days, counting the total number of users who checked in continuously within 7 days;
- counts the number of new users added every day and the number of retained users the next day;
- counts the number of visitors to the website ( Unique Visitor, UV) volume
- Latest comment list
- Music list based on playback volume
Normally, the number of users and visits we face are Huge, such as millions or tens of millions of users, or tens of millions or even billions of access information.
So, we must choose a collection type that can count large amounts of data (such as billions) very efficiently.
How to choose an appropriate data set, we must first understand the commonly used statistical models and use reasonable data analysis to solve practical problems.
Four statistical types:
Binary status statistics;
Aggregation statistics;
Sorting statistics;
Cardinality statistics.
This article will use extended data types other than String, Set, Zset, List, hashBitmap, HyperLogLog to fulfill.
The instructions involved in the article can be run and debugged through the online Redis client, address: try.redis.io/, which is super convenient.
Message
Share more and give more, create more value for others in the early stage without considering returns, in the long run , these efforts will be rewarded to you exponentially.
Especially when you first start cooperating with others, don't worry about short-term returns. It doesn't make much sense. It's more about exercising your own vision, perspective and problem-solving abilities.
Binary status statistics
Brother Ma, what are binary status statistics?
That is, the values of the elements in the collection are only 0 and 1. In the scenario of check-in and check-in and whether the user is logged in, you only need to record check-in (1) or Not signed in (0) , Logged in (1) or Not logged in (0) .
Suppose we use the String type implementation of Redis in the scenario of determining whether the user is logged in (key -> userId, value -> 0 means offline, 1 - login), if To store the login status of 1 million users, if it is stored in the form of strings, 1 million strings will need to be stored, which consumes too much memory.
For binary state scenarios, we can use Bitmap to achieve it. For example, we use one bit to represent the login status, and 100 million users only occupy 100 million bits of memory ≈ (100000000 / 8/ 1024/1024) 12 MB.
大概的空间占用计算公式是:($offset/8/1024/1024) MB
What is Bitmap?
The underlying data structure of Bitmap uses the SDS data structure of String type to save the bit array. Redis utilizes the 8 bits of each byte array, and each bit represents an element. binary state (either 0 or 1).
Bitmap can be regarded as an array with bit units. Each unit of the array can only store 0 or 1. The subscript of the array is called offset in Bitmap.
For the purpose of visual display, we can understand that each byte of the buf array is represented by a row. Each row has 8 bits, and the 8 grids represent the 8 bits in this byte respectively, as shown below Shown:
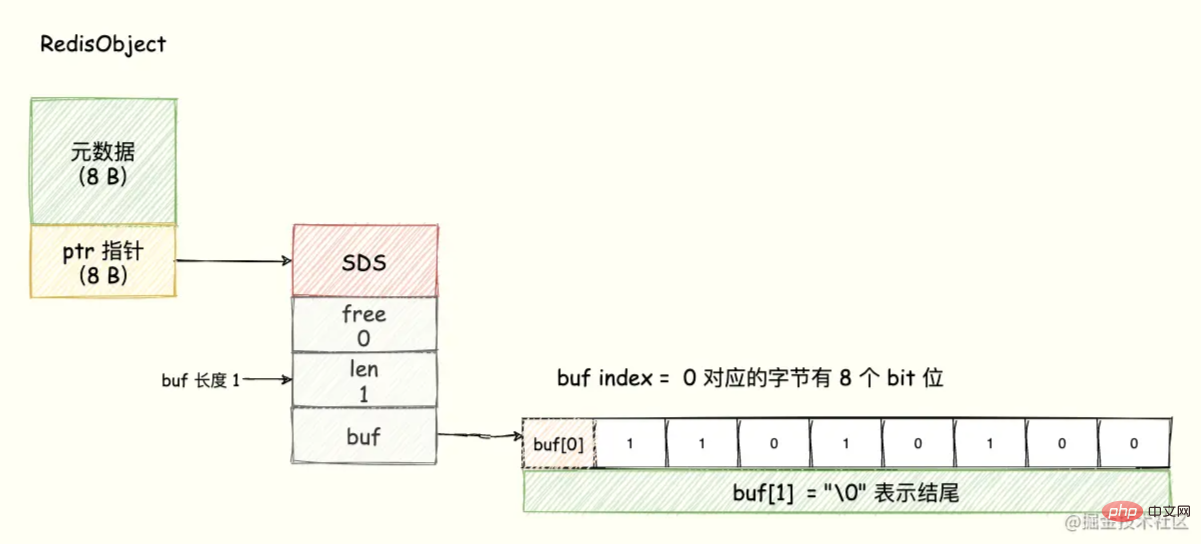
8 bits make up a Byte, so Bitmap will greatly save storage space. This is the advantage of Bitmap.
Determine user login status
How to use Bitmap to determine whether a user among a large number of users is online?
Bitmap provides GETBIT and SETBIT operations, which read and write the bit at the offset position of the bit array through an offset value offset. It should be noted that offset starts from 0 start.
Only one key = login_status is needed to store the user login status collection data. Use the user ID as the offset, which is set to 1 online and 0 offline. Use GETBIT to determine whether the corresponding user is online. 500 million users only require 6 MB of space.
SETBIT command
SETBIT <key> <offset> <value></value></offset></key>
Set or clear the bit value of the key value at offset (can only be 0 or 1).
GETBIT command
GETBIT <key> <offset></offset></key>
获取 key 的 value 在 offset 处的 bit 位的值,当 key 不存在时,返回 0。
假如我们要判断 ID = 10086 的用户的登陆情况:
第一步,执行以下指令,表示用户已登录。
SETBIT login_status 10086 1
第二步,检查该用户是否登陆,返回值 1 表示已登录。
GETBIT login_status 10086
第三步,登出,将 offset 对应的 value 设置成 0。
SETBIT login_status 10086 0
用户每个月的签到情况
在签到统计中,每个用户每天的签到用 1 个 bit 位表示,一年的签到只需要 365 个 bit 位。一个月最多只有 31 天,只需要 31 个 bit 位即可。
比如统计编号 89757 的用户在 2021 年 5 月份的打卡情况要如何进行?
key 可以设计成 uid:sign:{userId}:{yyyyMM},月份的每一天的值 - 1 可以作为 offset(因为 offset 从 0 开始,所以 offset = 日期 - 1)。
第一步,执行下面指令表示记录用户在 2021 年 5 月 16 号打卡。
SETBIT uid:sign:89757:202105 15 1
第二步,判断编号 89757 用户在 2021 年 5 月 16 号是否打卡。
GETBIT uid:sign:89757:202105 15
第三步,统计该用户在 5 月份的打卡次数,使用 BITCOUNT 指令。该指令用于统计给定的 bit 数组中,值 = 1 的 bit 位的数量。
BITCOUNT uid:sign:89757:202105
这样我们就可以实现用户每个月的打卡情况了,是不是很赞。
如何统计这个月首次打卡时间呢?
Redis 提供了 BITPOS key bitValue [start] [end]指令,返回数据表示 Bitmap 中第一个值为 bitValue 的 offset 位置。
在默认情况下, 命令将检测整个位图, 用户可以通过可选的 start 参数和 end 参数指定要检测的范围。
所以我们可以通过执行以下指令来获取 userID = 89757 在 2021 年 5 月份首次打卡日期:
BITPOS uid:sign:89757:202105 1
需要注意的是,我们需要将返回的 value + 1 表示首次打卡的天,因为 offset 从 0 开始。
连续签到用户总数
在记录了一个亿的用户连续 7 天的打卡数据,如何统计出这连续 7 天连续打卡用户总数呢?
我们把每天的日期作为 Bitmap 的 key,userId 作为 offset,若是打卡则将 offset 位置的 bit 设置成 1。
key 对应的集合的每个 bit 位的数据则是一个用户在该日期的打卡记录。
一共有 7 个这样的 Bitmap,如果我们能对这 7 个 Bitmap 的对应的 bit 位做 『与』运算。
同样的 UserID offset 都是一样的,当一个 userID 在 7 个 Bitmap 对应对应的 offset 位置的 bit = 1 就说明该用户 7 天连续打卡。
结果保存到一个新 Bitmap 中,我们再通过 BITCOUNT 统计 bit = 1 的个数便得到了连续打卡 7 天的用户总数了。
Redis 提供了 BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]这个指令用于对一个或者多个 键 = key 的 Bitmap 进行位元操作。
opration 可以是 and、OR、NOT、XOR。当 BITOP 处理不同长度的字符串时,较短的那个字符串所缺少的部分会被当做 0 。
空的 key 也被看作是包含 0 的字符串序列。
便于理解,如下图所示:
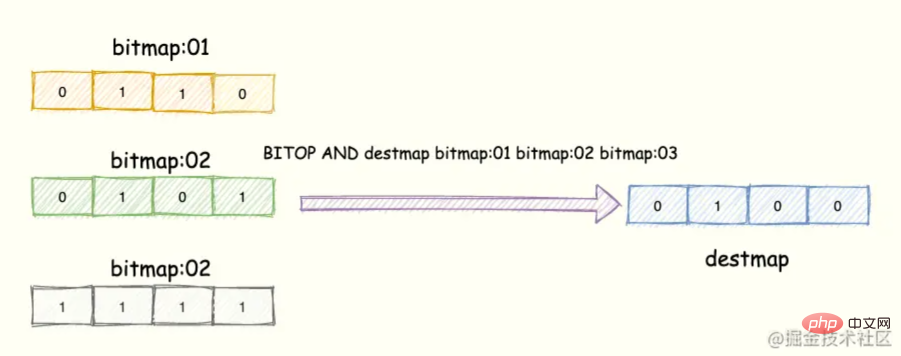
3 个 Bitmap,对应的 bit 位做「与」操作,结果保存到新的 Bitmap 中。
操作指令表示将 三个 bitmap 进行 AND 操作,并将结果保存到 destmap 中。接着对 destmap 执行 BITCOUNT 统计。
// 与操作 BITOP AND destmap bitmap:01 bitmap:02 bitmap:03 // 统计 bit 位 = 1 的个数 BITCOUNT destmap
简单计算下 一个一亿个位的 Bitmap占用的内存开销,大约占 12 MB 的内存(10^8/8/1024/1024),7 天的 Bitmap 的内存开销约为 84 MB。同时我们最好给 Bitmap 设置过期时间,让 Redis 删除过期的打卡数据,节省内存。
小结
思路才是最重要,当我们遇到的统计场景只需要统计数据的二值状态,比如用户是否存在、 ip 是否是黑名单、以及签到打卡统计等场景就可以考虑使用 Bitmap。
只需要一个 bit 位就能表示 0 和 1,在统计海量数据的时候将大大减少内存占用。
基数统计
基数统计:统计一个集合中不重复元素的个数,常见于计算独立用户数(UV)。
实现基数统计最直接的方法,就是采用集合(Set)这种数据结构,当一个元素从未出现过时,便在集合中增加一个元素;如果出现过,那么集合仍保持不变。
当页面访问量巨大,就需要一个超大的 Set 集合来统计,将会浪费大量空间。
另外,这样的数据也不需要很精确,到底有没有更好的方案呢?
这个问题问得好,Redis 提供了 HyperLogLog 数据结构就是用来解决种种场景的统计问题。
HyperLogLog 是一种不精确的去重基数方案,它的统计规则是基于概率实现的,标准误差 0.81%,这样的精度足以满足 UV 统计需求了。
关于 HyperLogLog 的原理过于复杂,如果想要了解的请移步:
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/53416615
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HyperLogLog
网站的 UV
通过 Set 实现
一个用户一天内多次访问一个网站只能算作一次,所以很容易就想到通过 Redis 的 Set 集合来实现。
用户编号 89757 访问 「Redis 为什么这么快 」时,我们将这个信息放到 Set 中。
SADD Redis为什么这么快:uv 89757
当用户编号 89757 多次访问「Redis 为什么这么快」页面,Set 的去重功能能保证不会重复记录同一个用户 ID。
通过 SCARD 命令,统计「Redis 为什么这么快」页面 UV。指令返回一个集合的元素个数(也就是用户 ID)。
SCARD Redis为什么这么快:uv
通过 Hash 实现
码老湿,还可以利用 Hash 类型实现,将用户 ID 作为 Hash 集合的 key,访问页面则执行 HSET 命令将 value 设置成 1。
即使用户重复访问,重复执行命令,也只会把这个 userId 的值设置成 “1"。
最后,利用 HLEN 命令统计 Hash 集合中的元素个数就是 UV。
如下:
HSET redis集群:uv userId:89757 1 // 统计 UV HLEN redis集群
HyperLogLog 王者方案
码老湿,Set 虽好,如果文章非常火爆达到千万级别,一个 Set 就保存了千万个用户的 ID,页面多了消耗的内存也太大了。同理,Hash数据类型也是如此。咋办呢?
利用 Redis 提供的 HyperLogLog 高级数据结构(不要只知道 Redis 的五种基础数据类型了)。这是一种用于基数统计的数据集合类型,即使数据量很大,计算基数需要的空间也是固定的。
每个 HyperLogLog 最多只需要花费 12KB 内存就可以计算 2 的 64 次方个元素的基数。
Redis 对 HyperLogLog 的存储进行了优化,在计数比较小的时候,存储空间采用系数矩阵,占用空间很小。
只有在计数很大,稀疏矩阵占用的空间超过了阈值才会转变成稠密矩阵,占用 12KB 空间。
PFADD
将访问页面的每个用户 ID 添加到 HyperLogLog 中。
PFADD Redis主从同步原理:uv userID1 userID 2 useID3
PFCOUNT
利用 PFCOUNT 获取 「Redis主从同步原理」页面的 UV值。
PFCOUNT Redis主从同步原理:uv
PFMERGE 使用场景
HyperLogLog 除了上面的 PFADD 和 PFCOIUNT 外,还提供了 PFMERGE ,将多个 HyperLogLog 合并在一起形成一个新的 HyperLogLog 值。
语法
PFMERGE destkey sourcekey [sourcekey ...]
使用场景
比如在网站中我们有两个内容差不多的页面,运营说需要这两个页面的数据进行合并。
其中页面的 UV 访问量也需要合并,那这个时候 PFMERGE 就可以派上用场了,也就是同样的用户访问这两个页面则只算做一次。
如下所示:Redis、MySQL 两个 Bitmap 集合分别保存了两个页面用户访问数据。
PFADD Redis数据 user1 user2 user3 PFADD MySQL数据 user1 user2 user4 PFMERGE 数据库 Redis数据 MySQL数据 PFCOUNT 数据库 // 返回值 = 4
将多个 HyperLogLog 合并(merge)为一个 HyperLogLog , 合并后的 HyperLogLog 的基数接近于所有输入 HyperLogLog 的可见集合(observed set)的并集。
user1、user2 都访问了 Redis 和 MySQL,只算访问了一次。
排序统计
Redis 的 4 个集合类型中(List、Set、Hash、Sorted Set),List 和 Sorted Set 就是有序的。
- List:按照元素插入 List 的顺序排序,使用场景通常可以作为 消息队列、最新列表、排行榜;
- Sorted Set:根据元素的 score 权重排序,我们可以自己决定每个元素的权重值。使用场景(排行榜,比如按照播放量、点赞数)。
最新评论列表
码老湿,我可以利用 List 插入的顺序排序实现评论列表
比如微信公众号的后台回复列表(不要杠,举例子),每一公众号对应一个 List,这个 List 保存该公众号的所有的用户评论。
每当一个用户评论,则利用 LPUSH key value [value ...] 插入到 List 队头。
LPUSH 码哥字节 1 2 3 4 5 6
接着再用 LRANGE key star stop 获取列表指定区间内的元素。
> LRANGE 码哥字节 0 4 1) "6" 2) "5" 3) "4" 4) "3" 5) "2"
注意,并不是所有最新列表都能用 List 实现,对于因为对于频繁更新的列表,list类型的分页可能导致列表元素重复或漏掉。
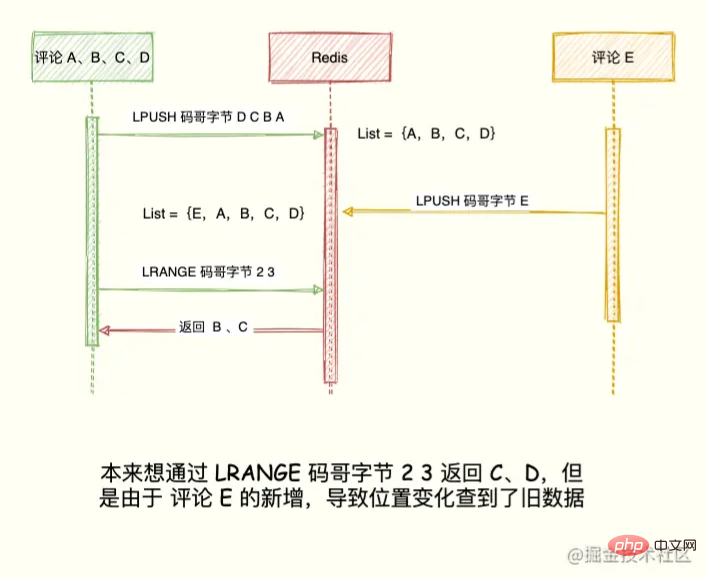
比如当前评论列表 List ={A, B, C, D},左边表示最新的评论,D 是最早的评论。
LPUSH 码哥字节 D C B A
展示第一页最新 2 个评论,获取到 A、B:
LRANGE 码哥字节 0 1 1) "A" 2) "B"
按照我们想要的逻辑来说,第二页可通过 LRANGE 码哥字节 2 3 获取 C,D。
如果在展示第二页之前,产生新评论 E,评论 E 通过 LPUSH 码哥字节 E 插入到 List 队头,List = {E, A, B, C, D }。
现在执行 LRANGE 码哥字节 2 3 获取第二页评论发现, B 又出现了。
LRANGE 码哥字节 2 3 1) "B" 2) "C"
出现这种情况的原因在于 List 是利用元素所在的位置排序,一旦有新元素插入,List = {E,A,B,C,D}。
原先的数据在 List 的位置都往后移动一位,导致读取都旧元素。
小结
只有不需要分页(比如每次都只取列表的前 5 个元素)或者更新频率低(比如每天凌晨统计更新一次)的列表才适合用 List 类型实现。
对于需要分页并且会频繁更新的列表,需用使用有序集合 Sorted Set 类型实现。
另外,需要通过时间范围查找的最新列表,List 类型也实现不了,需要通过有序集合 Sorted Set 类型实现,如以成交时间范围作为条件来查询的订单列表。
排行榜
码老湿,对于最新列表的场景,List 和 Sorted Set 都能实现,为啥还用 List 呢?直接使用 Sorted Set 不是更好,它还能设置 score 权重排序更加灵活。
原因是 Sorted Set 类型占用的内存容量是 List 类型的数倍之多,对于列表数量不多的情况,可以用 Sorted Set 类型来实现。
比如要一周音乐榜单,我们需要实时更新播放量,并且需要分页展示。
除此以外,排序是根据播放量来决定的,这个时候 List 就无法满足了。
我们可以将音乐 ID 保存到 Sorted Set 集合中,score 设置成每首歌的播放量,该音乐每播放一次则设置 score = score +1。
ZADD
比如我们将《青花瓷》和《花田错》播放量添加到 musicTop 集合中:
ZADD musicTop 100000000 青花瓷 8999999 花田错
ZINCRBY
《青花瓷》每播放一次就通过 ZINCRBY指令将 score + 1。
> ZINCRBY musicTop 1 青花瓷 100000001
ZRANGEBYSCORE
最后我们需要获取 musicTop 前十播放量音乐榜单,目前最大播放量是 N ,可通过如下指令获取:
ZRANGEBYSCORE musicTop N-9 N WITHSCORES
65哥:可是这个 N 我们怎么获取呀?
ZREVRANGE
可通过 ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]指令。
其中元素的排序按 score 值递减(从大到小)来排列。
具有相同 score 值的成员按字典序的逆序(reverse lexicographical order)排列。
> ZREVRANGE musicTop 0 0 WITHSCORES 1) "青花瓷" 2) 100000000
小结
即使集合中的元素频繁更新,Sorted Set 也能通过 ZRANGEBYSCORE 命令准确地获取到按序排列的数据。
在面对需要展示最新列表、排行榜等场景时,如果数据更新频繁或者需要分页显示,建议优先考虑使用 Sorted Set。
聚合统计
指的就是统计多个集合元素的聚合结果,比如说:
- 统计多个元素的共有数据(交集);
- 统计两个集合其中的一个独有元素(差集统计);
- 统计多个集合的所有元素(并集统计)。
码老湿,什么样的场景会用到交集、差集、并集呢?
Redis 的 Set 类型支持集合内的增删改查,底层使用了 Hash 数据结构,无论是 add、remove 都是 O(1) 时间复杂度。
并且支持多个集合间的交集、并集、差集操作,利用这些集合操作,解决上边提到的统计问题。
交集-共同好友
比如 QQ 中的共同好友正是聚合统计中的交集。我们将账号作为 Key,该账号的好友作为 Set 集合的 value。
模拟两个用户的好友集合:
SADD user:码哥字节 R大 Linux大神 PHP之父 SADD user:大佬 Linux大神 Python大神 C++菜鸡
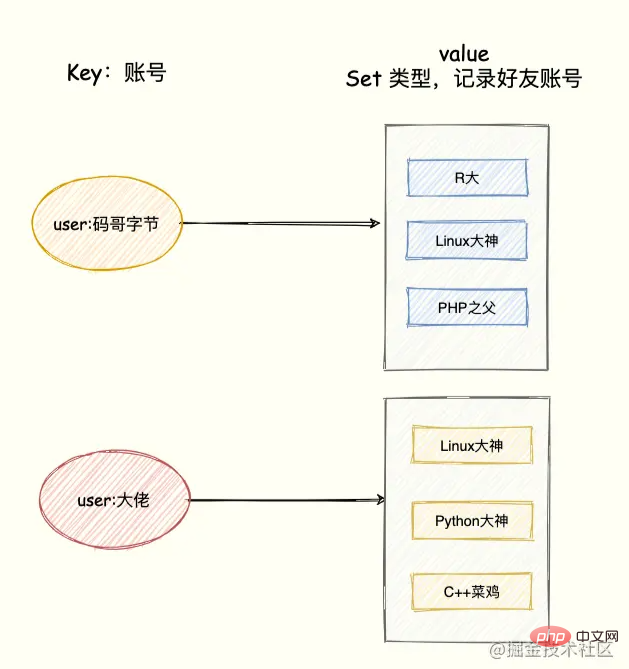
统计两个用户的共同好友只需要两个 Set 集合的交集,如下命令:
SINTERSTORE user:共同好友 user:码哥字节 user:大佬
命令的执行后,「user:码哥字节」、「user:大佬」两个集合的交集数据存储到 user:共同好友这个集合中。
差集-每日新增好友数
比如,统计某个 App 每日新增注册用户量,只需要对近两天的总注册用户量集合取差集即可。
比如,2021-06-01 的总注册用户量存放在 key = user:20210601 set 集合中,2021-06-02 的总用户量存放在 key = user:20210602 的集合中。
如下指令,执行差集计算并将结果存放到 user:new 集合中。
SDIFFSTORE user:new user:20210602 user:20210601
执行完毕,此时的 user:new 集合将是 2021/06/02 日新增用户量。
除此之外,QQ 上有个可能认识的人功能,也可以使用差集实现,就是把你朋友的好友集合减去你们共同的好友即是可能认识的人。
并集-总共新增好友
还是差集的例子,统计 2021/06/01 和 2021/06/02 两天总共新增的用户量,只需要对两个集合执行并集。
SUNIONSTORE userid:new user:20210602 user:20210601
此时新的集合 userid:new 则是两日新增的好友。
小结
Set 的差集、并集和交集的计算复杂度较高,在数据量较大的情况下,如果直接执行这些计算,会导致 Redis 实例阻塞。
所以,可以专门部署一个集群用于统计,让它专门负责聚合计算,或者是把数据读取到客户端,在客户端来完成聚合统计,这样就可以规避由于阻塞导致其他服务无法响应。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of Teach you step by step how to use Redis to implement billion-level data statistics (actual combat). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!


)