Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Quickly understand the usage of crypto module in Nodejs in one article
Quickly understand the usage of crypto module in Nodejs in one article
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-07-13 16:33:426264browse
crypto is a module that implements encryption and decryption in node.js. This article will take you through the crypto module and introduce the use of the crypto module for hashing (hash) algorithms, HMAC algorithms, Symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption methods.

1. crypto
crypto is the implementation of encryption in node.js and decryption module, in node.js, the OpenSSL class library is used as a means to internally implement encryption and decryption. OpenSSL is a reliable and rigorously tested Implementation tools for encryption and decryption algorithms. [Recommended learning: "nodejs Tutorial"]
windows version openSSL download
http://dl.pconline.com.cn/download/355862- 1.html
2. Hash (hash) algorithm
The hash algorithm is also called the hash algorithm and is used to transform input of any length into fixed-length output, common ones include md5, sha1, etc.
- The same input will produce the same output
- Different output will produce different output
- The output length is the same for any input length
- The input value cannot be deduced from the output
2.1 Get all hashes Algorithm
console.log(crypto.getHashes());
2.2 Syntax description
crypto.createHash(algorithm);//创建HASH对象 hash.update(data,[input_encoding]);//增加要添加摘要的数据,摘要输出前可以使用多次update hash.digest([encoding]);//输出摘要内容,输出后则不能再添加摘要内容
2.3 Hash algorithm example
var crypto = require('crypto'); var md5 = crypto.createHash('md5');//返回哈希算法 var md5Sum = md5.update('hello');//指定要摘要的原始内容,可以在摘要被输出之前使用多次update方法来添加摘要内容 var result = md5Sum.digest('hex');//摘要输出,在使用digest方法之后不能再向hash对象追加摘要内容。 console.log(result);
Multiple updates
var fs = require('fs');
var shasum = crypto.createHash('sha1');//返回sha1哈希算法
var rs = fs.createReadStream('./readme.txt');
rs.on('data', function (data) {
shasum.update(data);//指定要摘要的原始内容,可以在摘要被输出之前使用多次update方法来添加摘要内容
});
rs.on('end', function () {
var result = shasum.digest('hex');//摘要输出,在使用digest方法之后不能再向hash对象追加摘要内容。
console.log(result);
})3. HMAC algorithm
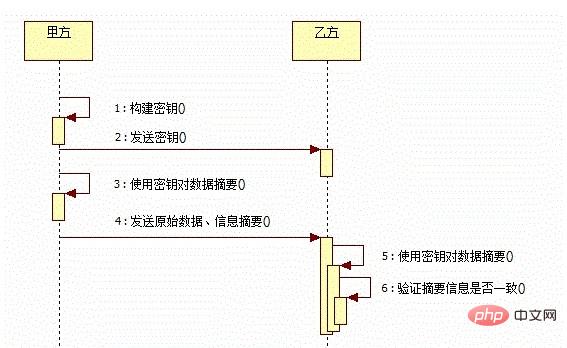
The HMAC algorithm combines a hashing algorithm with a key to prevent damage to the integrity of the signature

3.1 Syntax
let hmac crypto.createHmac(algorithm,key); hmac.update(data);
- algorithm is an available digest algorithm, such as sha1, md5, sha256
- key is one character String, used to specify a key in PEM format
3.2 Generate private key
PEM is the standard format of OpenSSL, and OpenSSL uses the PEM file format to store certificates and the key, which are based on the Base64 encoded certificate.
$ openssl genrsa -out rsa_private.key 1024
3.3 Example
let pem = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, './rsa_private.key'));
let key = pem.toString('ascii');
let hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha1', key);
let rs = fs.createReadStream(path.join(__dirname, './1.txt'));
rs.on('data', function (data) {
hmac.update(data);
});
rs.on('end', function () {
let result = hmac.digest('hex');
console.log(result);
});4. Symmetric encryption
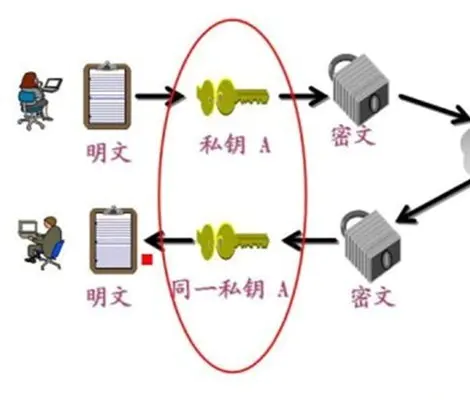
- blowfish algorithm is a symmetric encryption algorithm ,Symmetry means that the same key is used for ,encryption and decryption.
var crypto = require('crypto'); var fs = require('fs'); let str = 'hello'; let cipher = crypto.createCipher('blowfish', fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_private.key'))); let encry = cipher.update(str, 'utf8','hex'); encry += cipher.final('hex'); console.log(encry); let deciper = crypto.createDecipher('blowfish', fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_private.key'))); let deEncry = deciper.update(encry, 'hex','utf8'); deEncry += deciper.final('utf8'); console.log(deEncry);
5. Asymmetric encryption algorithm
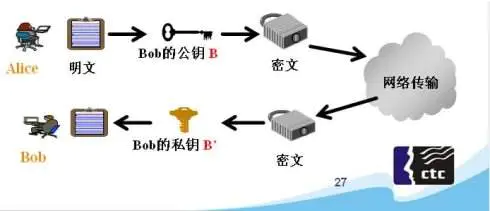
- The asymmetric encryption algorithm requires two keys: Public key (publickey) and private key (privatekey)
- The public key and the private key are a pair. If the public key is used to encrypt data, only the corresponding private key can be used to decrypt it. If the private key is encrypted , only public key decryption
- Because encryption and decryption use two different keys, this algorithm is called an asymmetric encryption algorithm
Create a public key for the private key
openssl rsa -in rsa_private.key -pubout -out rsa_public.key
var crypto = require('crypto'); var fs = require('fs'); let key = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_private.key')); let cert = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_public.key')); let secret = crypto.publicEncrypt(cert, buffer);//公钥加密 let result = crypto.privateDecrypt(key, secret);//私钥解密 console.log(result.toString());
6. Signature
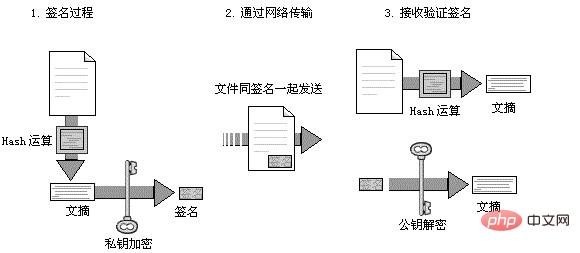
In the network, the owner of the private key can sign a piece of data before it is sent. After the data is signed and a signature is obtained and the data is sent to the data recipient through the network, the data recipient can verify the signature through the public key to ensure that this data It is the original data sent by the owner of the private key and has not been modified during transmission on the network.
let private = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_private.key'), 'ascii'); let public = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'rsa_public.key'), 'ascii'); let str = 'zhufengpeixun'; let sign = crypto.createSign('RSA-SHA256'); sign.update(str); let signed = sign.sign(private, 'hex'); let verify = crypto.createVerify('RSA-SHA256'); verify.update(str); let verifyResult = verify.verify(public,signed,'hex'); //true
Original address: https://juejin.cn/post/6844903800491376653
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit : Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of Quickly understand the usage of crypto module in Nodejs in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

