Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >An in-depth analysis of the built-in modules in Node.js
An in-depth analysis of the built-in modules in Node.js
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-07-01 10:46:042079browse
This article will take you to understand the built-in modules in Node.js, take a look at the operating mechanism of Node.js built-in modules, and briefly introduce EventEmitter (observer mode) through examples.
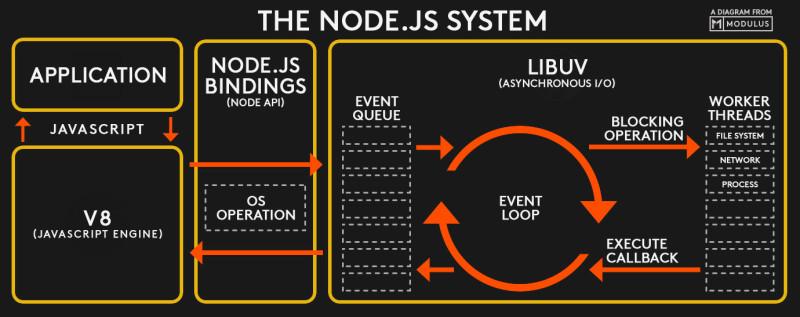
Node.js architecture diagram
Built-in modules
Some chestnuts
- File System API for operating files
- Process Record some information about the Node.js process
-
OS Operating system related API
- os.arch() Gets the architecture information of the operating system
- os.cpus() Gets the operating system CPU and kernel related information
[Recommended learning: "nodejs Tutorial"]
Node.js built-in module operating mechanism
Through Node.js source code analysis
The application layer code calls the Node.js module
-
The Node.js module calls the underlying C module through
internalBindingThe built-in modules of Node are stored in the lib folder
The built-in modules call the
internalBindingV8 level methodinternalBindingIn the C code in the src directory, the
C code defines some The underlying method is exported through the interface of V8 for the Node layer to call
Finally, the Node layer returns to the application layer
EventEmitter (Observer mode)
In some cases, the data is not called through the Node.js source code, but directly notified to the Node.js code to do something through the underlying operating system, such as: EventEmitter
Chestnut
process.stdin.on("data", (e) => {
const playerAction = e.toString().trim();
});on The principle of the event is to use Class: EventEmitter
EventEmitter can pass some changes that occur at the bottom layer, such as receiving a mouse event, to the application layer, so that developers can perform corresponding operations
Event listener application scenarios
Use Observer pattern to solve the problem of communication between multiple module objects
// index.js
const EventEmitter = require("events").EventEmitter;
class GeekTime extends EventEmitter {
constructor() {
super();
setInterval(() => {
this.emit("newLesson", { price: Math.random() * 100 });
}, 3000);
}
}
const geekTime = new GeekTime();
module.exports = geekTime;// buy.js
const geekTime = require("./index.js");
geekTime.addListener("newLesson", (res) => {
console.log("有新课了!!", res.price);
if (res.price < 80) {
console.log("价格小于80,买买买!");
}
});- Node.js Chestnut:
EventEmitter - Browser Chestnut - addEventListener - removeEventListener
The difference between observer mode and publish-subscribe mode
Publish-subscribe mode, the registration and triggering of events occur on a third-party platform independent of both parties. JS implementation - callback function Observer pattern: Publishers will directly reach subscribers. JS implementation method - throwing events
You can refer to This design pattern article-Nuggets booklet
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Programming video! !
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of the built-in modules in Node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- A brief discussion on readable streams in Nodejs. How to implement readable streams?
- How to import module in nodejs? Introduction to the execution process of require
- A brief discussion on the writable stream write and implementation methods in Nodejs
- A brief discussion on fs.mkdir and fs.rmdir in Nodejs file module
- A brief discussion on multi-threaded operations in Nodejs

