Home >Web Front-end >Vue.js >An in-depth analysis of key values in Vuejs
An in-depth analysis of key values in Vuejs
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-06-02 14:14:492793browse
This article will introduce you to the relevant knowledge of key values in Vuejs. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Starting from the previous article
I wrote an article a few days ago, sortable.js - Vue data update problem At that time, I only analyzed the data from the perspective of forced refresh, and did not find the real "culprit".
Thank you very much for someone helping me point out that it may be the key value of Vue that causes the data to be rendered incorrectly. From this, I made further attempts. [Related recommendation: "vue.js Tutorial"] An incorrect use of
key - use index as key
I don’t know if you will directly use index as its key value when you write v-for, yes, I admit that I will , I have to say, this is really not a good habit.
Based on the previous article, we still use sortable.js as an example to discuss. The following is the core code, in which the value of arrData is [1,2,3,4]
<div id="sort">
<div v-for="(item,index) in arrData" :key="index" >
<div>{{item}}</div>
</div>
</div> mounted () {
let el = document.getElementById('sort')
var sortable = new Sortable(el, {
onEnd: (e) => {
const tempItem = this.arrData.splice(e.oldIndex, 1)[0]
this.arrData.splice(e.newIndex, 0, tempItem)
}
})
}Of course, at the beginning, there must be no problem with data rendering
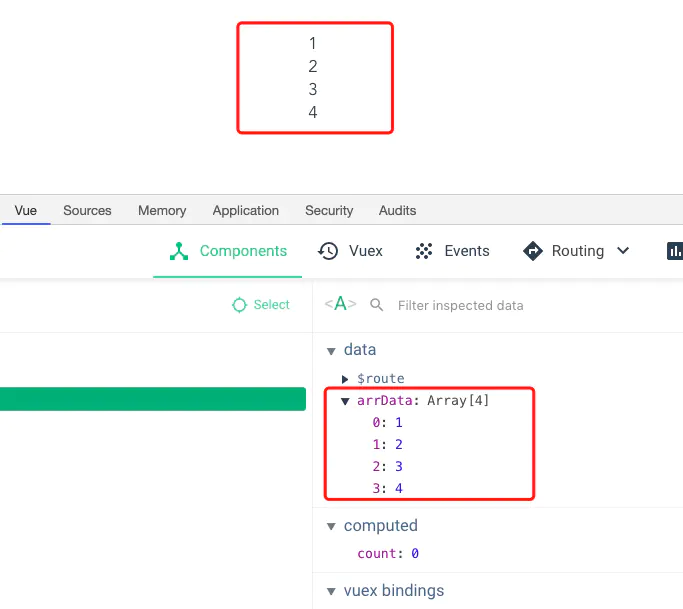
Okay, let’s take a look at the following operations:
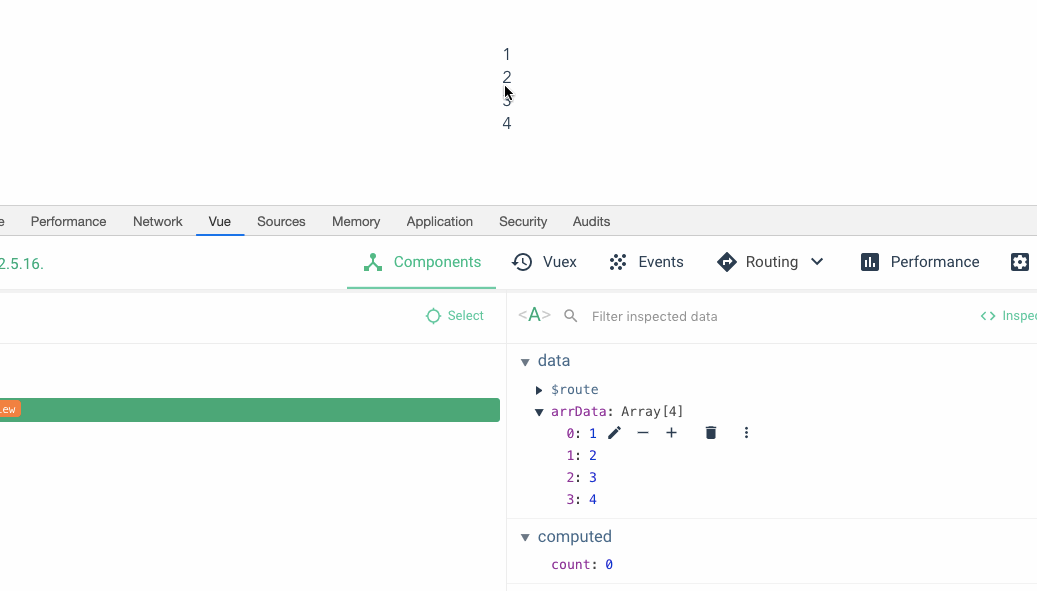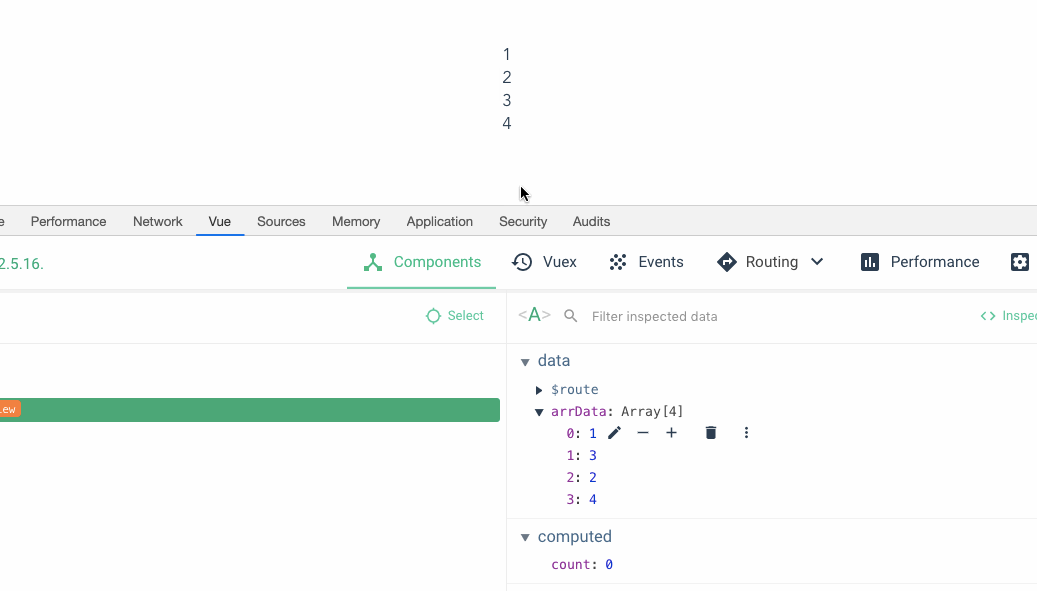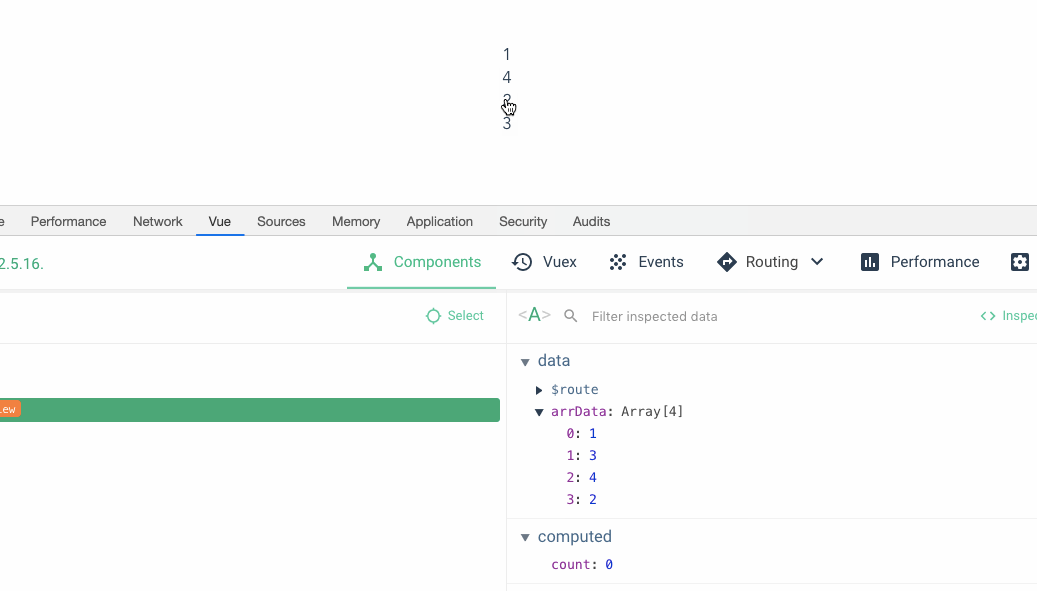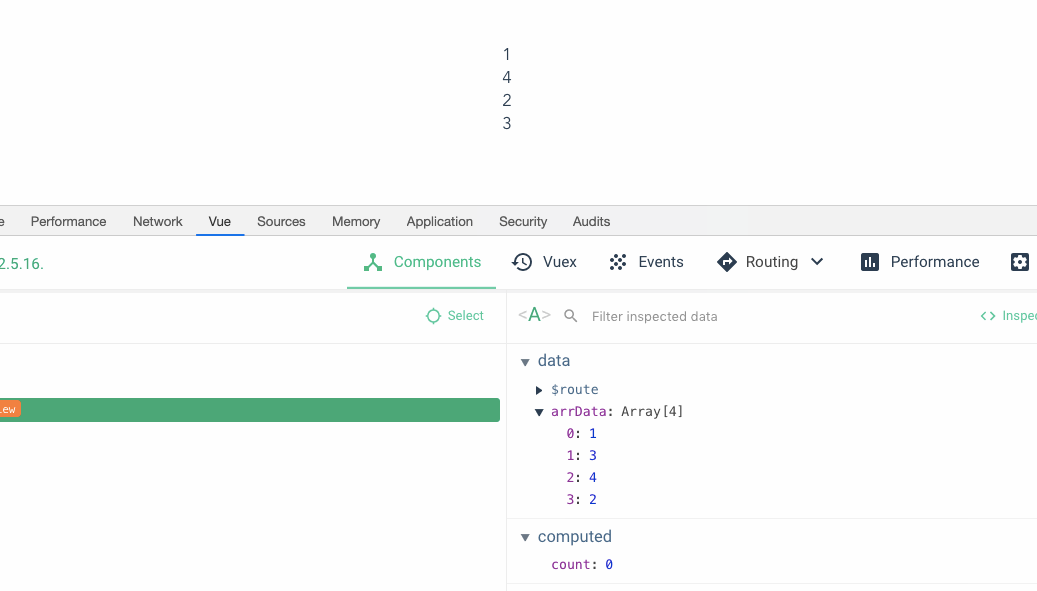
You can see Yes, when I drag 3 on top of 2, the data below becomes 1342, but the view above is still 1234. Then when I dragged the fourth position to the third position, the data below also took effect, but the data above seemed all messed up. Great, we recreated the crime scene.
Then I changed the bound key value. Because the example here is quite special, we think that the values of item are different
<div id="sort">
<div v-for="(item,index) in arrData" :key="item" >
<div>{{item}}</div>
</div>
</div>Look at the effect again:

Yes, at this time the data is completely synchronized with the view.
Why?
First look at the introduction of key in the official document
Child elements with the same parent element must have a unique key. Duplicate keys will cause rendering errors.
The reason why the above rendering error occurs is because our key value is not unique. For example, the above key value is adjusted when the array is After the order, the original key value of each item has changed, resulting in a rendering error.
Let us first draw a conclusion, There are hidden dangers in using index as the key value, unless you can ensure that index is always Can it be used as a unique identifier
What is the use of key value
After vue2.0, we do not writekey If so, warning will be reported, which means that the official wants us to write the value of key, so key is in vue What role did it play?
Can performance be improved without using key?The answer is, yes! Can!
Let’s look at the official explanation first:
If key is not used, Vue will use an algorithm that minimizes dynamic elements and tries to repair/reuse elements of the same type as much as possible. Using key, it rearranges the order of elements based on key changes and removes elements where key does not exist.
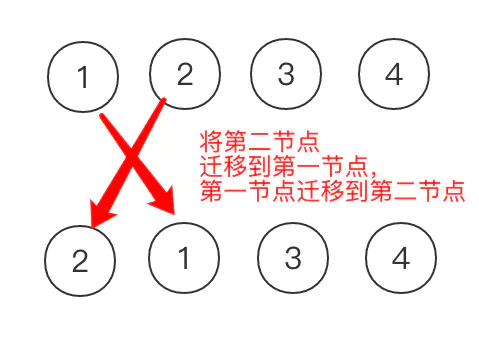
For example, if an array [1,2,3,4] becomes [2,1,3,4], then the value without key will take the form of An "in-place update strategy", see the figure below. It does not move the position of the element node, but directly modifies the element itself, thus saving some performance

And for elements with key values , its update method is shown in the figure below. As you can see, here it is a removal/add operation to the DOM, which is relatively performance-consuming.
The performance is better without key. Why do we need to bring key Let’s first look at an example. The core code is as follows: This imitates a function of switching tab, that is, the switched tab1 is 1,2,3,4. tab2 is 5,6,7,8. There is a function to set the font color of the first item to red by clicking on it.
那么当我们点击tab1将字体色设置成红色之后,再切换到 tab2,我们预期的结果是我们第一项字体的初始颜色而不是红色,但是结果却还是红色。
<div id="sort">
<button @click="trunToTab1">tab1</button>
<button @click="trunToTab2">tab2</button>
<div v-for="(item, index) in arrData">
<div @click="clickItem(index)" class="item">{{item}}</div>
</div>
</div> trunToTab1 () {
this.arrData = [1,2,3,4]
},
trunToTab2 () {
this.arrData = [5,6,7,8]
},
clickItem () {
document.getElementsByClassName('item')[0].style.color = 'red'
}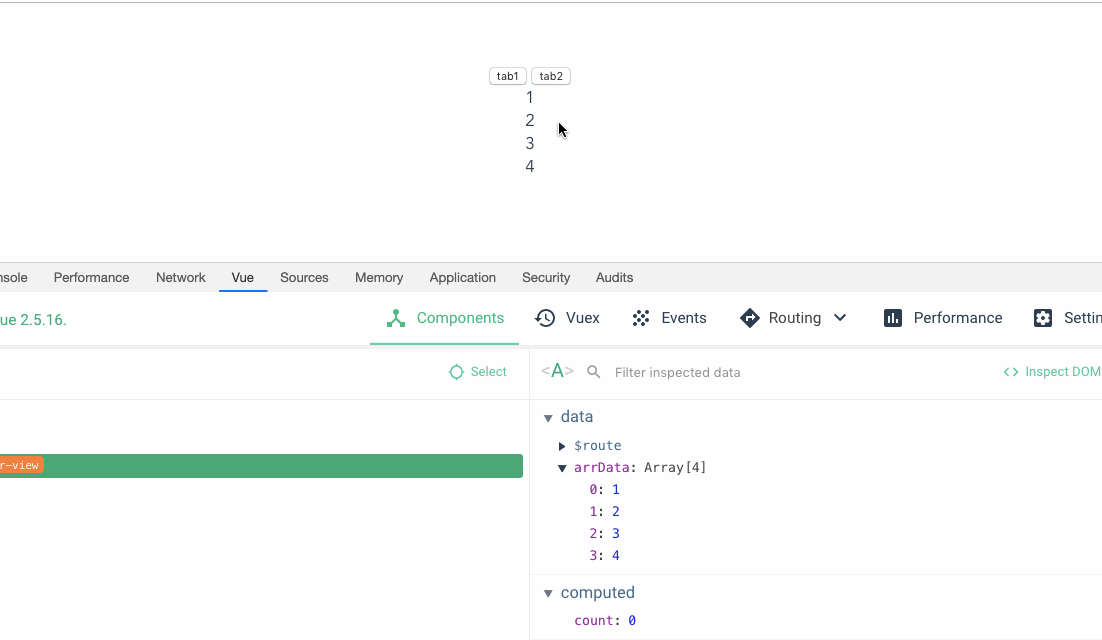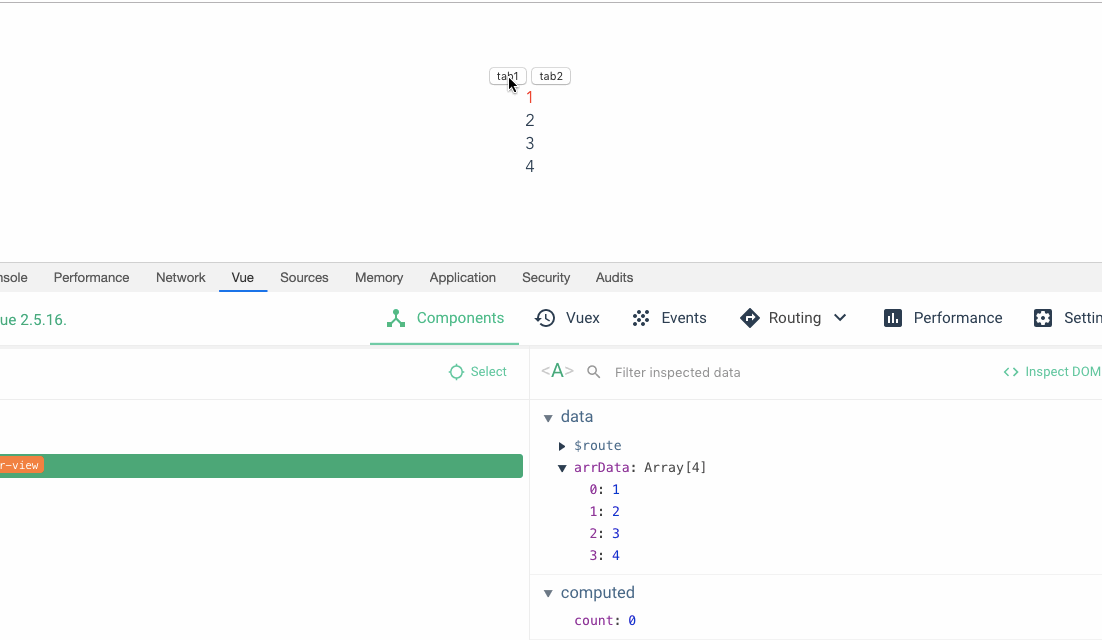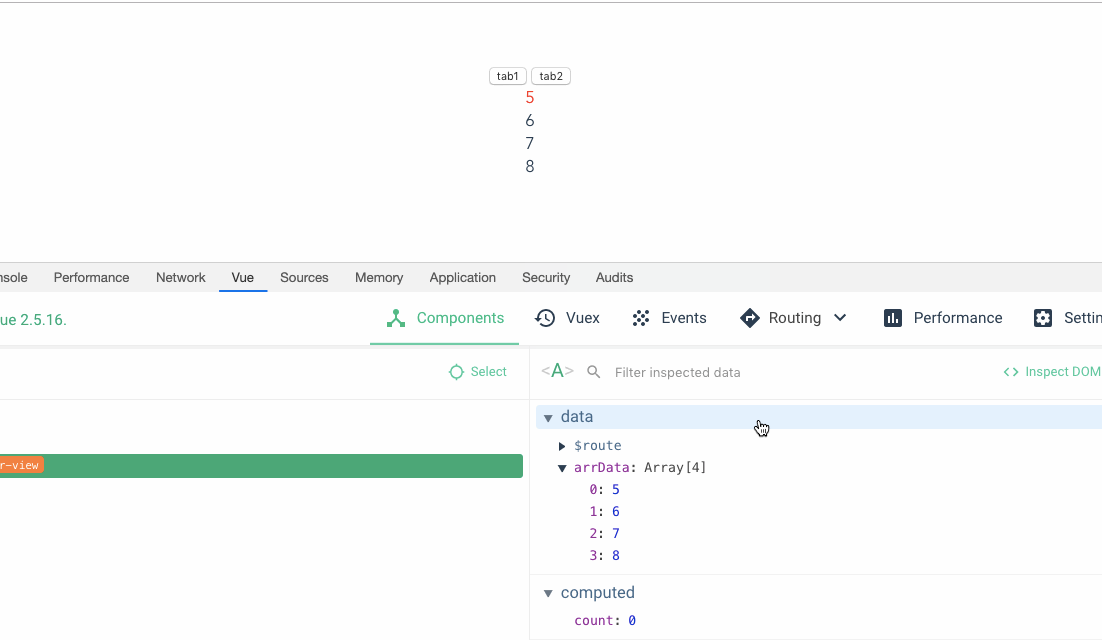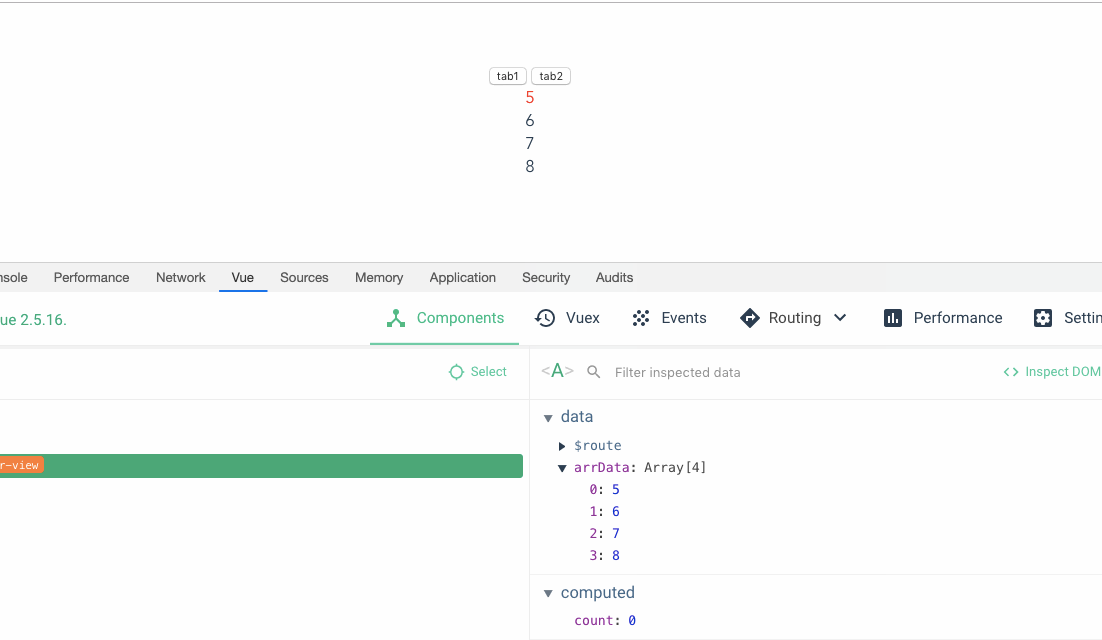
这就超出了我们的预期了,也就是官方文档所说的,默认模式指的就是不带 key 的状态,对于依赖于子组件状态或者临时 DOM 状态的,这种模式是不适用的。
这个默认的模式是高效的,但是只适用于不依赖子组件状态或临时 DOM 状态 (例如:表单输入值) 的列表渲染输出。
我们来看带上 key 之后的效果
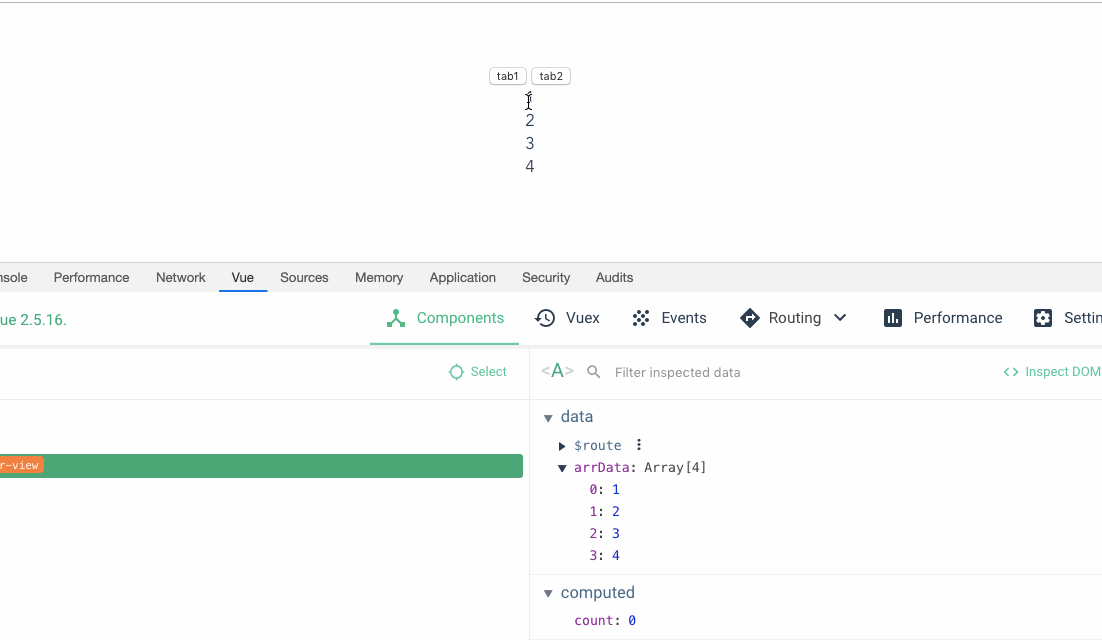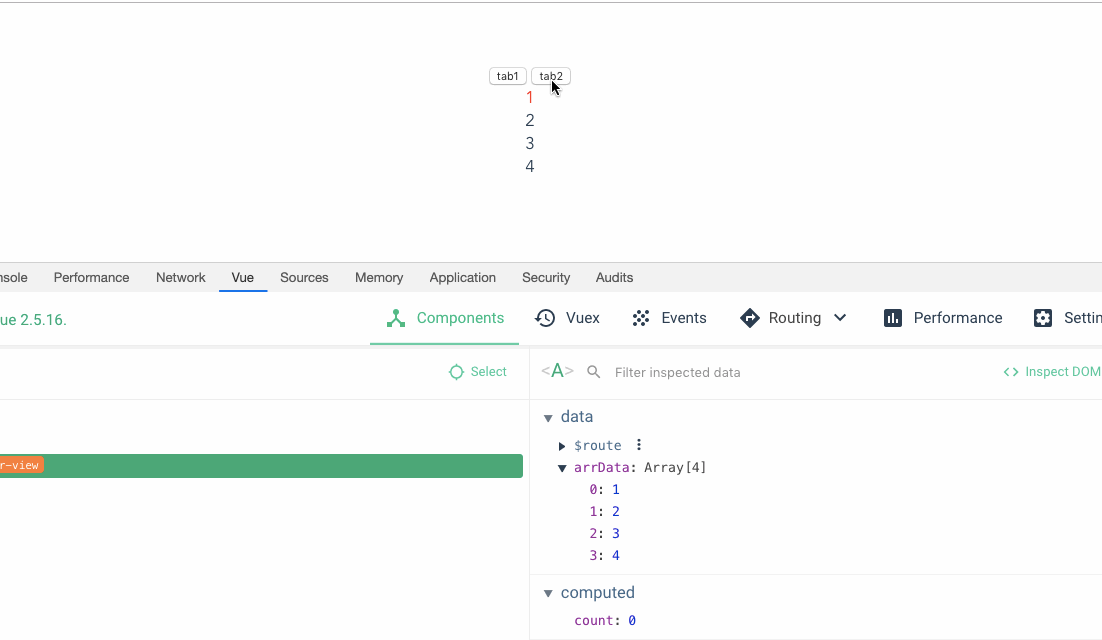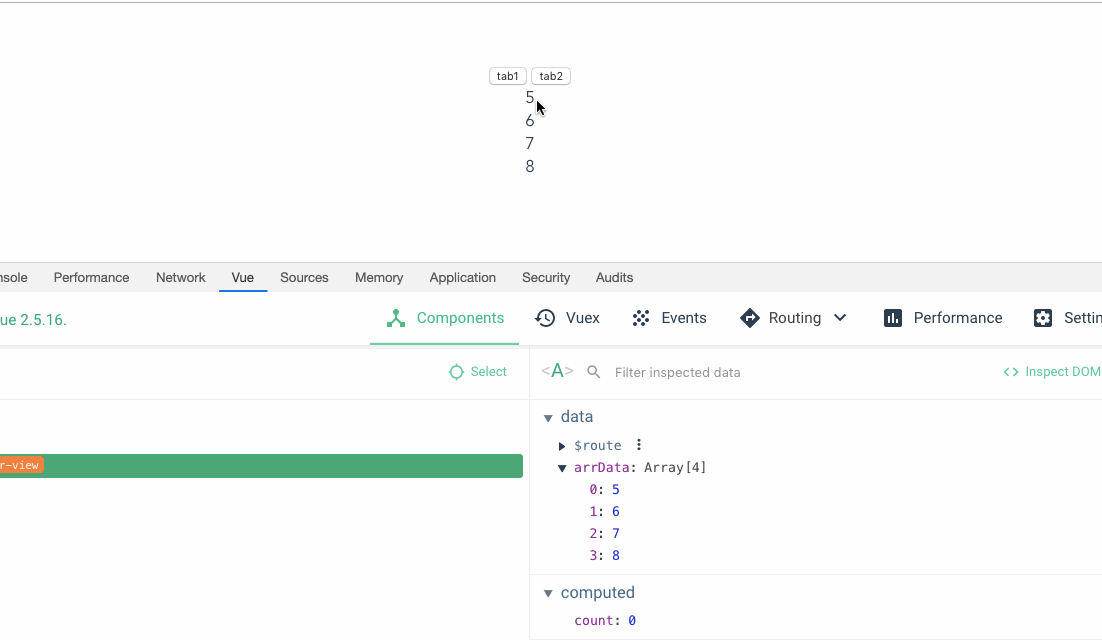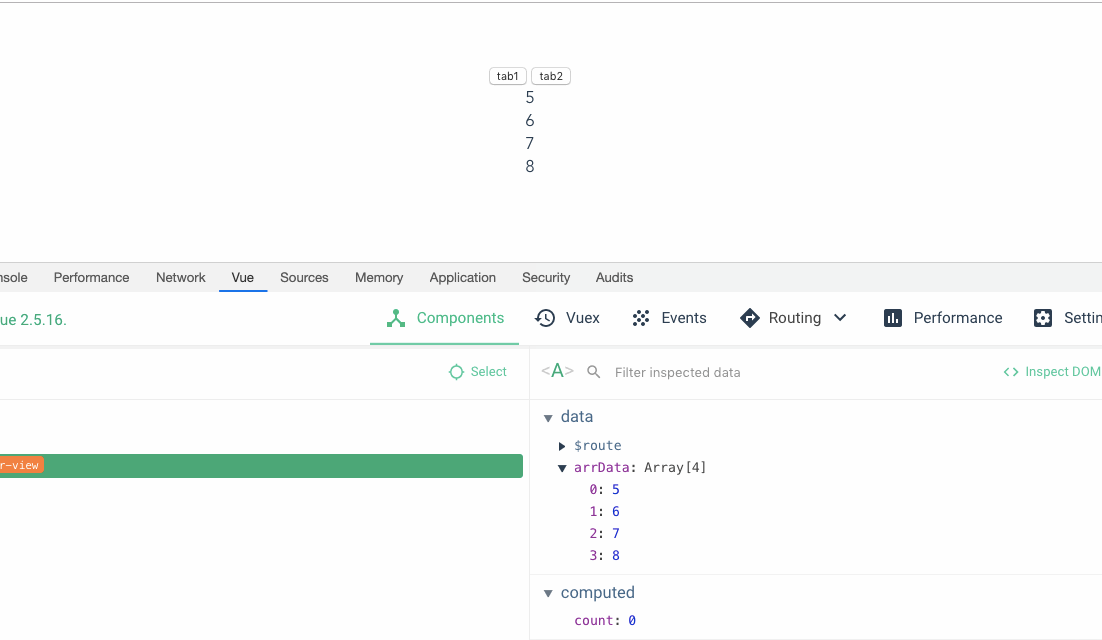
这就是官方文档之所以推荐我们写 key 的原因,根据文档的介绍,如下:
使用
key,它会基于key的变化重新排列元素顺序,并且会移除key不存在的元素。 它也可以用于强制替换元素/组件而不是重复使用它。当你遇到如下场景的时候它可能会很有用:
- 完整地触发组件的生命周期钩子
- 触发过渡
那么 Vue 底层 key 值到底是怎么去做到以上的功能?我们就得聊聊 diff 算法以及虚拟 DOM 了。
key 在 diff 算法中的作用
这里我们不谈 diff 算法的具体,只看 key 值在其中的作用。(diff 算法有机会我们再聊)
看 vue 源码中 src/core/vdom/patch.js
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)我们整理一下代码块:
// 如果有带 key
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) {
// 创建 index 表
oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}
if (isDef(newStartVnode.key)) {
// 有 key ,直接从上面创建中获取
idxInOld = oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
} else {
// 没有key, 调用 findIdxInOld
idxInOld = findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx);
}那么最主要还是 createKeyToOldIdx 和 findIdxInOld 两个函数的比较,那么他们做了什么呢?
function createKeyToOldIdx (children, beginIdx, endIdx) {
let i, key
const map = {}
for (i = beginIdx; i <= endIdx; ++i) {
key = children[i].key
if (isDef(key)) map[key] = i
}
return map
} function findIdxInOld (node, oldCh, start, end) {
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
const c = oldCh[i]
if (isDef(c) && sameVnode(node, c)) return i
}
}我们可以看到,如果我们有 key 值,我们就可以直接在 createKeyToOldIdx 方法中创建的 map 对象中根据我们的 key 值,直接找到相应的值。没有 key 值,则需要遍历才能拿到。相比于遍历,映射的速度会更快。
key 值是每一个 vnode 的唯一标识,依靠 key,我们可以更快的拿到 oldVnode 中相对应的节点。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of key values in Vuejs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

