There are only three steps to use Compose. Of course, the prerequisite is that Compose must be installed first.
Command:
docker infoor
docker --versionIf it is not installed, please refer to the Docker official website The installation instructions are very detailed. There are various system installation methods under the Install menu on the left. Such as the installation method of ubuntu system.
Compose installation command:
curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.7.1/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` > /usr/local/bin/docker-compose chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composeIf the download always fails or the connection times out, you can click here to download various versions of Compose.
Then upload the downloaded file to the host where Compose is to be installed, using the upload method of your choice.
Here is to upload the file "docker-compose-Linux-x86_64" to /opt, then copy the file to the /usr/local/bin/ folder, name it docker-compose, and then give it to docker-compose Grant executable permissions. Then check the version information of compose to verify whether compose can be used normally.
Command:
cp /opt/docker-compose-Linux-x86_64 /usr/local/bin/docker-compose chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose docker-compose --versionNow compose can be used normally. We can also see from this that this is not a real installation. We just downloaded a file, placed it in the specified location, renamed it, and then gave it executable permissions. Use Compose to deploy WordPress1. Define the environment in which the application runs through the Dockerfile file so that the environment can be reproduced anywhere.
Command:
mkdir -p /opt/compose-wordpress cd /opt/compose-wordpress nano DockerfileThe editing content is (no changes are made to the image here, it is just a demonstration of how to operate if you need to build an image):
FROM mysql MAINTAINER AuthorName <email></email>Save and exit.
2. Define each service in the docker-compose.yml file to form an application so that the application can run in each independent environment.
Command:
vim docker-compose.ymlThe editing content is:
version: '2' services: db: build: . volumes: "./.data/db:/var/lib/mysql" restart: always environment: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: wordpress MYSQL_DATABASE: wordpress MYSQL_USER: wordpress MYSQL_PASSWORD: wordpress wordpress: depends_on: db image: wordpress:latest links: db ports: "9527:80" restart: always environment: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306 WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: wordpressSave and exit.
3. Finally, run the following command in the /opt/compose-wordpress folder to start Compose to run the entire application.
Command:
docker-compose up -dIf you do not add the parameter -d, you will see a partial screenshot of the running log as follows:
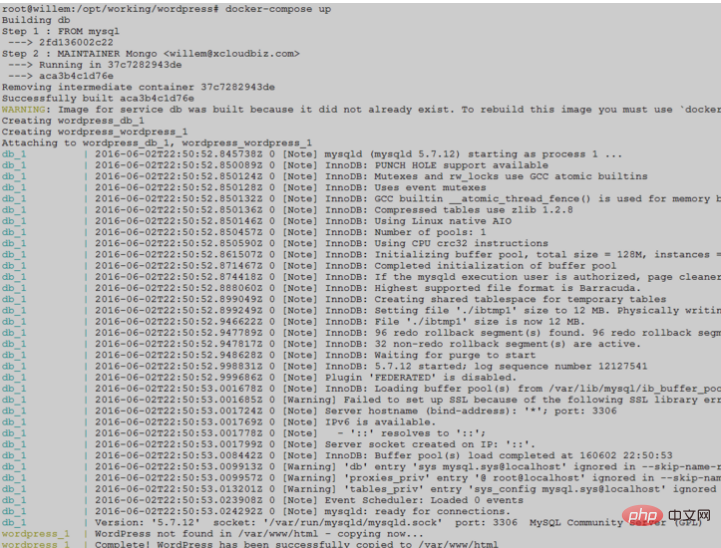
The port number of the container mapping host here is 9527, and its domain name is also resolved to the host IP. The effect of the first visit is as follows:
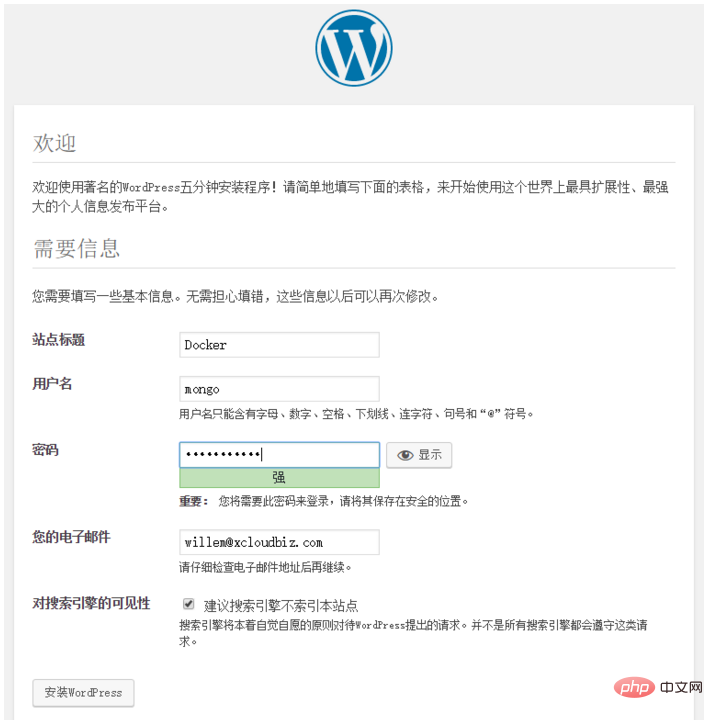 The successful installation prompt is as follows:
The successful installation prompt is as follows:
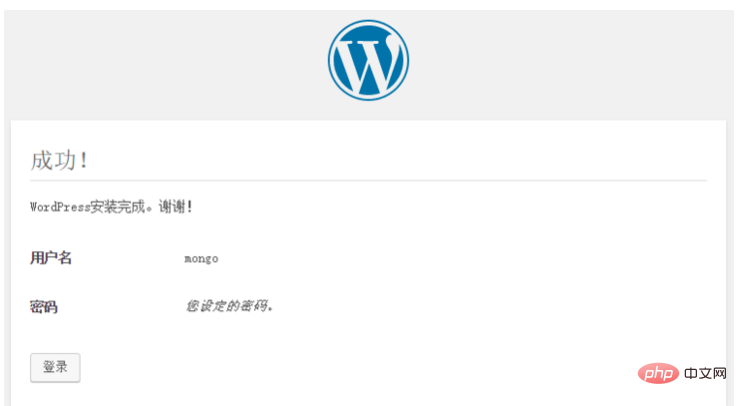 The login account and password here are the account and password set during installation:
The login account and password here are the account and password set during installation: