Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Front-end interview: Implementation of 6 classic sorting algorithms, how many do you know? (Attached animation + video)
Front-end interview: Implementation of 6 classic sorting algorithms, how many do you know? (Attached animation + video)
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2021-04-06 10:28:051957browse
This article will share with you the implementation methods of 6 classic sorting algorithms. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

#The sorting algorithm is a high-frequency inspection point in interviews, and we need to be proficient in it. This article has compiled the most classic and commonly used sorting algorithms and paired them with animations and videos, hoping to help you win them more easily.
First of all, according to the characteristics of the sorting algorithm, it can be divided into the following two categories:
- Comparative sorting
- Non- Comparison sorting
As the name suggests, Comparison sorting is sorted through comparison between elements, while non-comparison sorting does not involve comparison operations between elements.
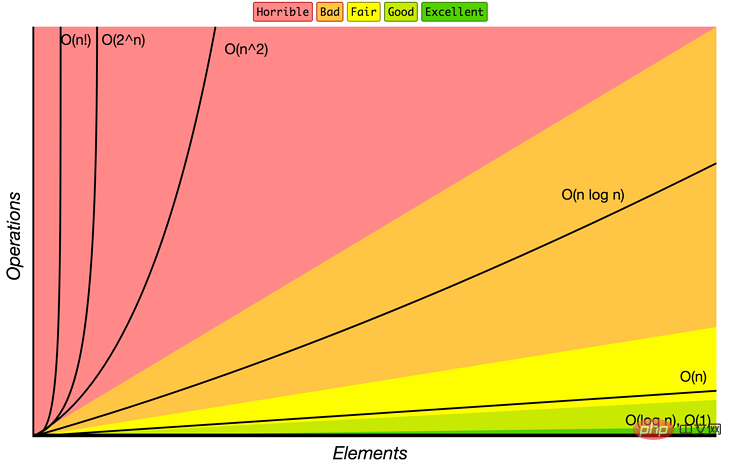
The time complexity of comparison sorting cannot exceed O(nlogn), which is also called nonlinear sorting.
The time complexity of non-comparative sorting can exceed O(nlogn) and can run in linear time, also known as linear sorting.

If you don’t understand time complexity yet, you can move to my column JavaScript algorithm time and space complexity analysis.
01 Bubble Sort Bubble Sort
Bubble sort visualization video:
https://www.reddit.com/r /programming/comments/e55j0i/bubble_sort_visualization/
Bubble sorting, simple and crude, one sentence explanation:
Bubble sorting will compare in each bubble operation For two adjacent elements , see if they meet the size relationship requirements. If not, swap them. Iterate until no more exchanges are needed, that is, the sorting is completed.
const bubbleSort = function(arr) {
const len = arr.length
if (len < 2) return arr
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
const temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]
arr[j + 1] = temp
}
}
}
return arr
}- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1)
- Stable
Note: The stability here means that bubble sort is a stable sorting algorithm.
What is a stable sorting algorithm?
Stability of sorting algorithm
Only use execution efficiency and memory consumption to judge the quality of the sorting algorithm. If it's not enough, there is another important metric for sorting algorithms, stability.
It means, If there are elements with equal values in the sequence to be sorted, after sorting, the original order between the equal elements will not change.
For example:
For example, we have a set of data: 1, 9, 2, 5, 8, 9. After sorting by size, it is 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 9.
There are two 9s in this set of data. After sorting by a certain sorting algorithm, if the order of the two 9s does not change, we will call this sorting algorithm a stable sorting algorithm.
Otherwise, it is an unstable sorting algorithm.
Bubble sort optimization
The above code can also be optimized. When a certain bubble operation has no data exchange, it means that it has been To achieve complete order, there is no need to continue to perform subsequent bubbling operations.
const bubbleSort = function(arr) {
const len = arr.length
let flag = false
if (len < 2) return arr
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
flag = false // 提前退出冒泡循环的标志
for (let j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
const temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[j + 1]
arr[j + 1] = temp
flag = true // 表示有数据交换
}
}
if (!flag) break // 没有数据交换,提前退出
}
return arr
}02 Insertion Sort
Insertion Sort As the name suggests, for unsorted data, in Scan the sorted sequence from back to front, find the corresponding position and insert it, keeping the elements in the sorted sequence in order.
Start traversing from i equal to 1, get the current element curr, and compare it with the previous element.
If the previous element is greater than the current element, exchange the previous element with the current element, and continue looping until the elements in the unsorted sequence are empty and the sorting is completed.
const insertSort = function(arr) {
const len = arr.length
let curr, prev
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
curr = arr[i]
prev = i - 1
while (prev >= 0 && arr[prev] > curr) {
arr[prev + 1] = arr[prev]
prev--
}
arr[prev + 1] = curr
}
return arr
}- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1)
- Stable
03 Selection Sort
Selection Sort Visualization Video:
https://www.reddit.com/r/programming/comments/e5md13/selection_sort_visualization /
Selection sorting is somewhat similar to insertion sorting, and is also divided into sorted sequences and unsorted sequences.
But selection sorting isstore the smallest element at the beginning of the array, then find the smallest element from the remaining unsorted sequence, and then put it after the sorted sequence. And so on until the sorting is completed.
const selectSort = function(arr) {
const len = arr.length
let temp, minIndex
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j
}
}
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[minIndex]
arr[minIndex] = temp
}
return arr
}- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1)
- Unstable
04 Merge Sort

A typical application of the divide-and-conquer method. The idea of the divide-and-conquer algorithm is largely based on recursion. , and is more suitable to be implemented using recursion.
The processing process is from bottom to top, dealing with sub-problems first and then merging them.
如果感觉自己对递归掌握的还不是很透彻的同学,可以移步我的这篇专栏你真的懂递归吗?。
顾名思义,分而治之。一般分为以下三个过程:
分解:将原问题分解成一系列子问题。
解决:递归求解各个子问题,若子问题足够小,则直接求解。
合并:将子问题的结果合并成原问题。
归并排序就是将待排序数组不断二分为规模更小的子问题处理,再将处理好的子问题合并起来,这样整个数组就都有序了。
const mergeSort = function(arr) {
const merge = (right, left) => {
const result = []
let i = 0, j = 0
while (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
if (left[i] < right[j]) {
result.push(left[i++])
} else {
result.push(right[j++])
}
}
while (i < left.length) {
result.push(left[i++])
}
while (j < right.length) {
result.push(right[j++])
}
return result
}
const sort = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) { return arr }
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2)
const left = arr.slice(0, mid)
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length)
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right))
}
return sort(arr)
}- 时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
- 稳定
05 快速排序 Quick Sort
快速排序可视化视频:
https://www.reddit.com/r/dataisbeautiful/comments/e9fb2k/oc_quicksort_visualization/
快速排序也是分治法的应用,处理过程是由上到下的,先分区,然后再处理子问题。
快速排序通过遍历数组,将待排序元素分隔成独立的两部分,一部分记录的元素均比另一部分的元素小,则可以分别对这两部分记录的元素继续进行排序,直到排序完成。
这就需要从数组中挑选出一个元素作为 基准(pivot),然后重新排序数列,将元素比基准值小的放到基准前面,比基准值大的放到基准后面。
然后将小于基准值的子数组(left)和大于基准值的子数组(right)递归地调用 quick 方法,直到排序完成。
const quickSort = function(arr) {
const quick = function(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) return arr
const len = arr.length
const index = Math.floor(len >> 1)
const pivot = arr.splice(index, 1)[0]
const left = []
const right = []
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (arr[i] > pivot) {
right.push(arr[i])
} else if (arr[i] <= pivot) {
left.push(arr[i])
}
}
return quick(left).concat([pivot], quick(right))
}
const result = quick(arr)
return result
}- 时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度: O(nlogn)
- 不稳定
06 堆排序 Heap Sort
堆排序相比其他几种排序代码会有些复杂,不过没关系,我们先来看一些前置知识,可以帮助我们更好的理解堆排序。
堆排序顾名思义就是要利用堆这种数据结构进行排序。堆是一种特殊的树,满足以下两点就是堆:
堆是一个完全二叉树
堆中每一个节点的值都必须大于等于(或小于等于)其子树中的每个节点的值
每个节点的值都大于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,叫做大顶堆,每个节点的值都小于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,叫做小顶堆。
也就是说,大顶堆中,根节点是堆中最大的元素。小顶堆中,根节点是堆中最小的元素。
如果你对树这种数据结构还不是很了解,可以移步我的这篇专栏“树”业有专攻
堆如果用一个数组表示的话,给定一个节点的下标 i (i从1开始),那么它的父节点一定为 A[i / 2],左子节点为 A[2i],右子节点为 A[2i + 1]。
堆排序包含两个过程,建堆和排序。首先构建一个大顶堆,也就是将最大值存储在根节点(i = 1),每次取大顶堆的根节点与堆的最后一个节点进行交换,此时最大值放入了有效序列的最后一位,并且有效序列减 1,有效堆依然保持完全二叉树的结构,然后进行堆化成为新的大顶堆。重复此操作,直到有效堆的长度为 0,排序完成。
const heapSort = function(arr) {
buildHeap(arr, arr.length - 1)
let heapSize = arr.length - 1 // 初始化堆的有效序列长度
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i > 1; i--) {
swap(arr, 1, i) // 交换堆顶元素与最后一个有效子元素
heapSize-- // 有效序列长度减 1
heapify(arr, heapSize, 1) // 堆化有效序列
}
return arr
}
// 构建大顶堆
const buildHeap = function(items, heapSize) {
// 从后往前并不是从序列的最后一个元素开始,而是从最后一个非叶子节点开始,这是因为,叶子节点没有子节点,不需要自上而下式堆化。
// 最后一个子节点的父节点为 n/2 ,所以从 n/2 位置节点开始堆化
for (let i = Math.floor(heapSize / 2); i >= 1; i--) {
heapify(items, heapSize, i)
}
}
// 堆化
const heapify = function(arr, heapSize, i) {
while (true) {
let maxIndex = i
if (2 * i <= heapSize && arr[i] < arr[i * 2]) {
maxIndex = i * 2
}
if (2 * i + 1 <= heapSize && arr[maxIndex] < arr[i * 2 + 1]) {
maxIndex = i * 2 + 1
}
if (maxIndex === i) break
swap(arr, i, maxIndex)
i = maxIndex
}
}
// 交换工具函数
const swap = function(arr, i, j) {
let temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
}- 时间复杂度: O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
- 不稳定
为了方便你理解和记忆,我将这 6 种排序算法的复杂度和稳定性汇总成表格如下:
本文讲解了十大经典排序算法中的 6 种排序算法,这 6 种排序算法是平时开发中比较常见的,大家务必要熟练掌握。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of Front-end interview: Implementation of 6 classic sorting algorithms, how many do you know? (Attached animation + video). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!


)
)