Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >47 pictures to guide you through MySQL advancement
47 pictures to guide you through MySQL advancement
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2020-10-14 17:27:202633browse
MySQL Tutorial column takes you through 47 pictures to understand the advanced MySQL.

In the MySQL introductory chapter, we mainly introduce the basic SQL commands, data types and functions. With the above knowledge, you can develop MySQL. , but if you want to become a qualified developer, you also need to possess some more advanced skills. Let’s discuss what advanced skills MySQL requires
MySQL Storage Engine
Storage engine overview
The core point of the database is to store data, and data storage cannot avoid dealing with disks. So how and how data is stored is the key to storage. Therefore, the storage engine is equivalent to the engine of data storage, driving data to be stored at the disk level.
The architecture of MySQL can be understood according to the three-tier model

The storage engine is also a component of MySQL. It is a kind of software. The main functions it can do and support are
- Concurrency
- Support transactions
- Integrity constraints
- Physical storage
- Support Index
- Performance Help
MySQL supports multiple storage engines by default to suit different database applications. Users can choose the appropriate storage engine according to their needs. The following are supported by MySQL Storage Engine
- MyISAM
- InnoDB
- BDB
- MEMORY
- MERGE
- EXAMPLE
- NDB Cluster
- ARCHIVE
- CSV
- BLACKHOLE
- FEDERATED
By default, if the table is created without Specifying the storage engine will use the default storage engine. If you want to modify the default storage engine, you can set default-table-type in the parameter file to view the current storage engine
show variables like 'table_type';复制代码

Strange, why is it gone? I checked online and found that this parameter was canceled in 5.5.3
You can query the storage engines supported by the current database through the following two methods
show engines \g复制代码

When creating a new table, you can set the storage engine of the new table by adding the ENGINE keyword.
create table cxuan002(id int(10),name varchar(20)) engine = MyISAM;复制代码

In the above picture we specified the storage engine of MyISAM.
What if you don’t know the storage engine of the table? You can view it by show create table

If the storage engine is not specified, from MySQL 5.1 version onwards, MySQL The default built-in storage engine is already InnoDB. Create a table and take a look

As shown in the figure above, we have not specified a default storage engine. Let’s take a look at the table

As you can see, the default storage engine is InnoDB.
If you want to replace the storage engine, you can use
alter table cxuan003 engine = myisam;复制代码
to replace it. After the replacement is completed, 0 rows affected will be displayed, but in fact the operation has been successful
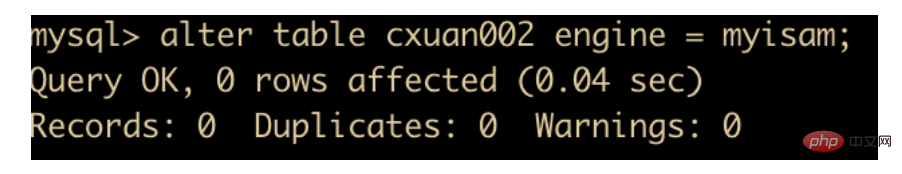
We use show create table to check the sql of the table and we will know

MyISAM
Before version 5.1, MyISAM was the default storage engine of MySQL. MyISAM had poor concurrency and was used in fewer scenarios. Its main features are
If
transactionoperations are not supported, ACID features will not exist. This design is for performance and efficiency considerations.Does not support
foreign keyoperations. If you forcibly add a foreign key, MySQL will not report an error, but the foreign key will not work.MyISAM's default lock granularity is
table-level lock, so the concurrency performance is relatively poor, locking is faster, there are fewer lock conflicts, and deadlocks are less likely to occur. Case.MyISAM will store three files on the disk. The file names are the same as the table names, and the extensions are
.frm (storage table definition),. MYD(MYData,storage data),MYI(MyIndex,storage index). What needs special attention here is that MyISAM only cachesindex filesand does not cache data files.-
The index types supported by MyISAM are
global index (Full-Text),B-Tree index,R-Tree indexFull-Text index: It appears to solve the problem of low efficiency of fuzzy query for text.
B-Tree index: All index nodes are stored according to the data structure of the balanced tree, and all index data nodes are in leaf nodes
R-Tree index: Its storage method is the same as B-Tree indexes have some differences. They are mainly designed to index fields that store spatial and multidimensional data. The current MySQL version only supports geometry type fields for indexing. Compared with BTREE, the advantage of RTREE is range search.
If the host where the database is located goes down, MyISAM data files are easily damaged and difficult to recover.
In terms of performance of add, delete, modify and query: SELECT has higher performance and is suitable for situations where there are many queries
InnoDB
Since After MySQL 5.1, the default storage engine became the InnoDB storage engine. Compared with MyISAM, the InnoDB storage engine has undergone major changes. Its main feature is that it
- supports transaction operations and has transaction ACID Isolation feature, the default isolation level is
repetable-read(repetable-read), implemented throughMVCC (Concurrent Version Control). It can solve the problems ofdirty readingandnon-repeatable reading. - InnoDB supports foreign key operations.
- InnoDB’s default lock granularity
row-level lockhas better concurrency performance, but deadlock may occur. - Like MyISAM, the InnoDB storage engine also has a
.frm file storage table structuredefinition, but the difference is that InnoDB's table data and index data are stored together, both in On the leaf nodes of the B number, the table data and index data of MyISAM are separated. - InnoDB has a secure log file. This log file is used to recover data loss caused by database crash or other situations and ensure data consistency.
- InnoDB and MyISAM support the same index types, but the specific implementations vary greatly due to different file structures.
- In terms of performance of add, delete, modify, and query, if a large number of add, delete, and modify operations are performed, it is recommended to use the InnoDB storage engine. It deletes rows during deletion operations and does not rebuild the table.
MEMORY
The MEMORY storage engine creates tables using content that exists in memory. Each MEMORY table actually corresponds to only one disk file, and the format is .frm. MEMORY type tables are accessed very quickly because their data is stored in memory. The HASH index is used by default.
MERGE
The MERGE storage engine is a combination of a set of MyISAM tables. The MERGE table itself has no data. Querying, updating, and deleting operations on MERGE type tables are actually internal MyISAM table. The MERGE table retains two files on the disk, one is the .frm file that stores the table definition, and the other is the .MRG file that stores the composition of the MERGE table, etc.
Choose the appropriate storage engine
In the actual development process, we often choose the appropriate storage engine based on the application characteristics.
- MyISAM: If the application is usually retrieval-oriented, with only a small number of insert, update, and delete operations, and the integrity and concurrency of things are not very high, it is usually recommended to choose the MyISAM storage engine.
- InnoDB: If foreign keys are used, a high degree of concurrency is required, and data consistency requirements are high, then the InnoDB engine is usually selected. Generally, major Internet companies have higher requirements for concurrency and data integrity, so they generally use Use the InnoDB storage engine.
- MEMORY: The MEMORY storage engine stores all data in memory and can provide extremely fast access when quick location is required. MEMORY is typically used for small tables that are updated less frequently and for quick access to results.
- MERGE: MERGE uses MyISAM tables internally. The advantage of the MERGE table is that it can break through the limit on the size of a single MyISAM table, and by distributing different tables on multiple disks, the MERGE table can be effectively improved. access efficiency.
Choose the appropriate data type
A problem we often encounter is how to choose the appropriate data type when building a table. Usually choosing the appropriate data type can improve performance, To reduce unnecessary trouble, let’s discuss how to choose the appropriate data type.
Selection of CHAR and VARCHAR
char and varchar are two data types that we often use to store strings. char generally stores fixed-length strings and is of fixed length. Character type, such as the following
| value | char(5) | storage bytes |
|---|---|---|
| '' | ' ' | 5 bytes |
| 'cx' | ' cx ' | 5 bytes |
| 'cxuan' | 'cxuan' | 5 bytes |
| 'cxuan007' | 'cxuan' | 5 bytes |
can be seen, no matter What is your value written? Once you specify the length of char characters, if the length of your string is not enough to specify the length of the characters, then fill it with spaces. If it exceeds the length of the string, only the characters of the specified character length will be stored. .
Note here: If MySQL uses non-
strict mode, the last row of the above table can be stored. If MySQL usesstrict mode, then an error will be reported when storing the last row in the table.
If the varchar character type is used, let’s look at an example
| Value | varchar(5) | Storage bytes |
|---|---|---|
| '' | '' | 1 byte |
| 'cx' | 'cx ' | 3 bytes |
| 'cxuan' | ' cxuan' | 6 bytes |
| 'cxuan007' | 'cxuan' | 6 bytes |
You can see that if varchar is used, the stored bytes will be stored according to the actual value. You may wonder why the length of varchar is 5, but it needs to store 3 bytes or 6 bytes. This is because when using the varchar data type for storage, a string length is added to the end by default, occupying 1 word. section (two bytes are used if the column declaration is longer than 255). varchar does not fill empty strings.
Generally use char to store fixed-length strings, such as ID number, mobile phone number, email, etc.; use varchar to store variable-length strings. Since the length of char is fixed, its processing speed is much faster than VARCHAR, but the disadvantage is that it wastes storage space. However, with the continuous evolution of MySQL versions, the performance of the varchar data type is also constantly improving and improving, so it is used in many applications , the VARCHAR type is more commonly used.
In MySQL, different storage engines have different principles for using CHAR and VARCHAR
- MyISAM: It is recommended to use fixed-length data columns instead of variable-length data columns. It is CHAR
- MEMORY: Use fixed length for processing, CHAR and VARCHAR will be treated as CHAR
- InnoDB: It is recommended to use VARCHAR type
TEXT and BLOB
Generally when saving a small amount of text, we will choose CHAR and VARCHAR. When saving a large amount of text, we often choose TEXT and BLOB; the main difference between TEXT and BLOB is that BLOB can save Binary data; while TEXT can only save character data, TEXT is subdivided into
- TEXT
- MEDIUMTEXT
- LONGTEXT
BLOB is subdivided down into
- BLOB
- MEDIUMBLOB
- LONGBLOB
three The main difference between them is the different length of stored text and different storage bytes. Users should choose the smallest storage type that meets their needs according to the actual situation. The following mainly introduces some problems with BLOB and TEXT
TEXT and BLOB will have some performance problems after deleting data. In order to improve performance, it is recommended to use the OPTIMIZE TABLE function to defragment the table.
You can also use synthetic indexes to improve query performance for text fields (BLOB and TEXT). The synthetic index is to create a hash value based on the content of the large text (BLOB and TEXT) field, and store this value in the corresponding column, so that the corresponding data row can be found based on the hash value. Generally, hashing algorithms such as md5() and SHA1() are used. If the strings generated by the hashing algorithm have trailing spaces, do not store them in CHAR and VARCHAR. Let's take a look at this usage
First create a table that records blob fields and hash values

Insert data into cxuan005, where the hash value is used as info Hash value.

Then insert two more pieces of data

Insert one Info is the data of cxuan005

If you want to query the data where info is cxuan005, you can query it by querying the hash column

This is an example of a synthetic index. If you want to perform fuzzy query on BLOB, you must use a prefix index.
Other ways to optimize BLOB and TEXT:
- Do not retrieve BLOB and TEXT indexes unless necessary
- Separate BLOB or TEXT columns into separate tables .
Selection of floating point numbers and fixed point numbers
Floating point numbers refer to values containing decimals. After floating point numbers are inserted into the specified column and exceed the specified precision, the floating point numbers will be rounded. MySQL The floating-point numbers refer to float and double, and the fixed-point numbers refer to decimal. Fixed-point numbers can save and display data more accurately. Let's use an example to explain the accuracy of floating point numbers
First create a table cxuan006, just to test the floating point number problem, so the data type we choose here is float

Then insert two pieces of data respectively

Then execute the query, you can see that the two queried data are rounded differently

In order to clearly see the precision issue between floating point numbers and fixed point numbers, let’s look at an example again

First modify cxuan006 The two fields have the same length and number of decimal places
Then insert two pieces of data

Execute the query operation, you can find that, Compared with fixed-point numbers, floating-point numbers will produce errors

Date type selection
In MySQL, used to represent Date types include DATE, TIME, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP. In
138 pictures to show you how to get started with MySQL
, we have introduced the differences between date types. It will not be elaborated here again. The following mainly introduces the selection of
- TIMESTAMP is related to the time zone and can better reflect the current time. If the recorded date needs to be used by people in different time zones, it is best to use TIMESTAMP.
- DATE is used to represent the year, month and day. If the actual application value needs to save the year, month and day, you can use DATE.
- TIME is used to represent hours, minutes and seconds. If the actual application value needs to save hours, minutes and seconds, you can use TIME.
- YEAR is used to represent the year. YEAR has 2-digit (preferably 4-digit) and 4-digit year formats. The default is 4 digits. If the actual application only saves the year, then it is perfectly fine to use 1 bytes to save the YEAR type. Not only can it save storage space, but it can also improve table operation efficiency.
MySQL Character Set
Let’s get to know the MySQL character set. Simply put, a character set is a set of text symbols, encoding, and comparison rules. In 1960, the American Standards Organization ANSI released the first computer character set, which is the famous ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange). Since ASCII encoding, each country and international organization has developed its own character set, such as ISO-8859-1, GBK, etc.
But each country uses its own character set, which brings great difficulties to portability. Therefore, in order to unify character encoding, International Organization for Standardization (ISO) specified a unified character standard - Unicode encoding, which accommodates almost all character encodings. The following are some common character encodings
| Character set | Is it a negative length | Encoding method |
|---|---|---|
| ASCII | is a | single-byte 7-bit encoding |
| ISO-8859-1 | is | Single-byte 8-bit encoding |
| GBK | is | Double-byte encoding |
| UTF-8 | No | 1 - 4-byte encoding |
| UTF-16 | No | 2 byte or 4 byte encoding |
| UTF-32 | Yes | 4 byte encoding |
对数据库来说,字符集是很重要的,因为数据库存储的数据大多数都是各种文字,字符集对数据库的存储、性能、系统的移植来说都非常重要。
MySQL 支持多种字符集,可以使用 show character set; 来查看所有可用的字符集

或者使用
select character_set_name, default_collate_name, description, maxlen from information_schema.character_sets;复制代码
来查看。
使用 information_schema.character_set 来查看字符集和校对规则。
索引的设计和使用
我们上面介绍到了索引的几种类型并对不同的索引类型做了阐述,阐明了优缺点等等,下面我们从设计角度来聊一下索引,关于索引,你必须要知道的一点就是:索引是数据库用来提高性能的最常用工具。
索引概述
所有的 MySQL 类型都可以进行索引,对相关列使用索引是提高 SELECT 查询性能的最佳途径。MyISAM 和 InnoDB 都是使用 BTREE 作为索引,MySQL 5 不支持函数索引,但是支持 前缀索引。
前缀索引顾名思义就是对列字段的前缀做索引,前缀索引的长度和存储引擎有关系。MyISAM 前缀索引的长度支持到 1000 字节,InnoDB 前缀索引的长度支持到 767 字节,索引值重复性越低,查询效率也就越高。
在 MySQL 中,主要有下面这几种索引
-
全局索引(FULLTEXT):全局索引,目前只有 MyISAM 引擎支持全局索引,它的出现是为了解决针对文本的模糊查询效率较低的问题,并且只限于 CHAR、VARCHAR 和 TEXT 列。 -
哈希索引(HASH):哈希索引是 MySQL 中用到的唯一 key-value 键值对的数据结构,很适合作为索引。HASH 索引具有一次定位的好处,不需要像树那样逐个节点查找,但是这种查找适合应用于查找单个键的情况,对于范围查找,HASH 索引的性能就会很低。默认情况下,MEMORY 存储引擎使用 HASH 索引,但也支持 BTREE 索引。 -
B-Tree 索引:B 就是 Balance 的意思,BTree 是一种平衡树,它有很多变种,最常见的就是 B+ Tree,它被 MySQL 广泛使用。 -
R-Tree 索引:R-Tree 在 MySQL 很少使用,仅支持 geometry 数据类型,支持该类型的存储引擎只有MyISAM、BDb、InnoDb、NDb、Archive几种,相对于 B-Tree 来说,R-Tree 的优势在于范围查找。
索引可以在创建表的时候进行创建,也可以单独创建,下面我们采用单独创建的方式,我们在 cxuan004 上创建前缀索引

我们使用 explain 进行分析,可以看到 cxuan004 使用索引的情况

如果不想使用索引,可以删除索引,索引的删除语法是

索引设计原则
创建索引的时候,要尽量考虑以下原则,便于提升索引的使用效率。
- 选择
索引位置,选择索引最合适的位置是出现在where语句中的列,而不是select关键字后的选择列表中的列。 - 选择使用
唯一索引,顾名思义,唯一索引的值是唯一的,可以更快速的确定某条记录,例如学生的学号就适合使用唯一性索引,而学生的性别则不适合使用,因为不管搜索哪个值,都差不多有一半的行。 - 为经常使用的字段建立索引,如果某个字段经常用作查询条件,那么这个字段的查询速度在极大程度上影响整个表的查询速度,因此为这样的字段建立索引,可以提高整个表的查询速度。
- 不要过度索引,限制索引数目,索引的数目不是越多越好,每个索引都会占据磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。
- 尽量使用
前缀索引,如果索引的值很长,那么查询速度会受到影响,这个时候应该使用前缀索引,对列的某几个字符进行索引,可以提高检索效率。 - 利用最左前缀,在创建一个 n 列的索引时,实际上是创建了 MySQL 可利用的 n 个索引。多列索引可以起到几个索引的作用,利用索引最左边的列来匹配行,这样的列称为最左前缀。
- 对于使用 InnoDB 存储引擎的表来说,记录会按照一定的顺序保存。如果有明确的主键定义,那么会按照主键的顺序进行保存;如果没有主键,但是有唯一索引,那么就按照唯一索引的顺序进行保存。如果既没有主键又没有唯一索引,那么表中会自动生成一个内部列,按照这个列的顺序进行保存。一般来说,使用主键的顺序是最快的
- 删除不再使用或者很少使用的索引
视图
MySQL 从 5.0 开始就提供了视图功能,下面我们对视图功能进行介绍。
什么是视图
视图的英文名称是 view,它是一种虚拟存在的表。视图对于用户来说是透明的,它并不在数据库中实际存在,视图是使用数据库行和列动态组成的表,那么视图相对于数据库表来说,优势体现在哪里?
视图相对于普通的表来说,优势包含下面这几项
- 使用视图可以简化操作:使用视图我们不用关注表结构的定义,我们可以把经常使用的数据集合定义成视图,这样能够简化操作。
- 安全性:用户对视图不可以随意的更改和删除,可以保证数据的安全性。
- 数据独立性:一旦视图的结构 确定了, 可以屏蔽表结构变化对用户的影响, 数据库表增加列对视图没有影响;具有一定的独立性
对视图的操作
视图的操作包括创建或者修改视图、删除视图以及查看视图定义。
创建或修改视图
使用 create view 来创建视图
为了演示功能,我们先创建一张表 product 表,有三个字段,id,name,price,下面是建表语句
create table product(id int(11),name varchar(20),price float(10,2));复制代码
然后我们向其中插入几条数据
insert into product values(1, "apple","3.5"),(2,"banana","4.2"),(3,"melon","1.2");复制代码
插入完成后的表结构如下

然后我们创建视图
create view v1 as select * from product;复制代码
然后我们查看一下 v1 视图的结构
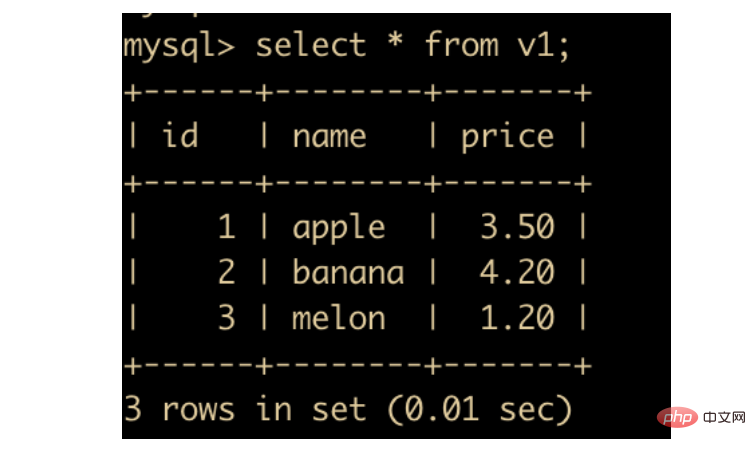
可以看到我们把 product 中的数据放在了视图中,也相当于是创建了一个 product 的副本,只不过这个副本跟表无关。
视图使用
show tables;复制代码
也能看到所有的视图。
删除视图的语法是
drop view v1;复制代码

能够直接进行删除。
视图还有其他操作,比如查询操作
你还可以使用
describe v1;复制代码

查看表结构
更新视图
update v1 set name = "grape" where id = 1;复制代码

存储过程
MySQL 从 5.0 开始起就支持存储过程和函数了。
那么什么是存储过程呢?
存储过程是在数据库系统中完成一组特定功能的 SQL 语句集,它存储在数据库系统中,一次编译后永久有效。那么使用存储过程有什么优点呢?
- 使用存储过程具有可封装性,能够隐藏复杂的 SQL 逻辑。
- 存储过程可以接收参数,并返回结果
- 存储过程性能非常高,一般用于批量执行语句
使用存储过程有什么缺点?
- 存储过程编写复杂
- 存储过程对数据库的依赖性比较强,可移植性比较差
存储过程使用
存储过程创建
在认识到存储过程是什么之后,我们就来使用一下存储过程,这里需要先了解一个小技巧,也就是 delimiter 的用法,delimiter 用于自定义结束符,什么意思呢,如果你使用
delimiter ?复制代码
的话,那么你在 sql 语句末使用 ; 是不能使 SQL 语句执行的,不信?我们可以看下

可以看到,我们在 SQL 语句的行末使用了 ; 但是我们却没有看到执行结果。下面我们使用
delimiter ;复制代码
恢复默认的执行条件再来看下

我们创建存储过程首先要把 ; 替换为 ?,下面是一个存储过程的创建语句
mysql> delimiter ? mysql> create procedure sp_product() -> begin -> select * from product; -> end ?复制代码

存储过程实际上是一种函数,所以创建完毕后,我们可以使用 call 方法来调用这个存储过程

因为我们上面定义了使用 delimiter ? 来结尾,所以这里也应该使用。
存储过程也可以接受参数,比如我们定义一种接收参数的情况

然后我们使用 call 调用这个存储过程

可以看到,当我们调用 id = 2 的时候,存储过程的 SQL 语句相当于是
select * from product where id = 2;复制代码
所以只查询出 id = 2 的结果。
存储过程删除
一次只能删除一个存储过程,删除存储过程的语法如下
drop procedure sp_product ;复制代码
直接使用 sp_product 就可以了,不用加 ()。
存储过程查看
存储过程创建后,用户可能需要需要查看存储过程的状态等信息,便于了解存储过程的基本情况
我们可以使用
show create procedure proc_name;复制代码
变量的使用
在 MySQL 中,变量可分为两大类,即系统变量和用户变量,这是一种粗略的分法。但是根据实际应用又被细化为四种类型,即局部变量、用户变量、会话变量和全局变量。
用户变量
用户变量是基于会话变量实现的,可以暂存,用户变量与连接有关,也就是说一个客户端定义的变量不能被其他客户端使用看到。当客户端退出时,链接会自动释放。我们可以使用 set 语句设置一个变量
set @myId = "cxuan";复制代码
然后使用 select 查询条件可以查询出我们刚刚设置的用户变量

用户变量是和客户端有关系,当我们退出后,这个变量会自动消失,现在我们退出客户端
exit复制代码
现在我们重新登陆客户端,再次使用 select 条件查询

发现已经没有这个 @myId 了。
局部变量
MySQL 中的局部变量与 Java 很类似 ,Java 中的局部变量是 Java 所在的方法或者代码块,而 MySQL 中的局部变量作用域是所在的存储过程。MySQL 局部变量使用 declare 来声明。
会话变量
服务器会为每个连接的客户端维护一个会话变量。可以使用
show session variables;复制代码
显示所有的会话变量。
我们可以手动设置会话变量
set session auto_increment_increment=1; 或者使用 set @@session.auto_increment_increment=2;复制代码
然后进行查询,查询会话变量使用

或者使用

全局变量
当服务启动时,它将所有全局变量初始化为默认值。其作用域为 server 的整个生命周期。
可以使用
show global variables;复制代码
查看全局变量
可以使用下面这两种方式设置全局变量
set global sql_warnings=ON; -- global不能省略 /** 或者 **/ set @@global.sql_warnings=OFF;复制代码
查询全局变量时,可以使用

或者是

MySQL 流程语句介绍
MySQL 支持下面这些控制语句
- IF
IF 用于实现逻辑判断,满足不同条件执行不同的 SQL 语句
IF ... THEN ...复制代码
- CASE
CASE 实现比 IF 稍微复杂,语法如下
CASE ... WHEN ... THEN... ... END CASE复制代码
CASE 语句也可以使用 IF 来完成
- LOOP
LOOP 用于实现简单的循环
label:LOOP ... END LOOP label;复制代码
如果 ... 中不写 SQL 语句的话,那么就是一个简单的死循环语句
- LEAVE
用来表示从标注的流程构造中退出,通常和 BEGIN...END 或者循环一起使用
- ITERATE
ITERATE 语句必须用在循环中,作用是跳过当前循环的剩下的语句,直接进入下一轮循环。
- REPEAT
带有条件的循环控制语句,当满足条件的时候退出循环。
REPEAT ... UNTIL END REPEAT;复制代码
- WHILE
WHILE 语句表示的含义和 REPEAT 相差无几,WHILE 循环和 REPEAT 循环的区别在于:WHILE 是满足条件才执行循环,REPEAT 是满足条件退出循环;
触发器
MySQL 从 5.0 开始支持触发器,触发器一般作用在表上,在满足定义条件时触发,并执行触发器中定义的语句集合,下面我们就来一起认识一下触发器。
举个例子来认识一下触发器:比如你有一个日志表和金额表,你每录入一笔金额就要进行日志表的记录,你会怎么样?同时在金额表和日志表插入数据吗?如果有了触发器,你可以直接在金额表录入数据,日志表会自动插入一条日志记录,当然,触发器不仅只有新增操作,还有更新和删除操作。
创建触发器
我们可以用如下的方式创建触发器
create trigger triggername triggertime triggerevent on tbname for each row triggerstmt复制代码
上面涉及到几个参数,我知道你有点懵逼,解释一下。
-
triggername:这个指的就是触发器的名字 -
triggertime:这个指的就是触发器触发时机,是BEFORE还是AFTER -
triggerevent: 这个指的就是触发器触发事件,一共有三种事件:INSERT、UPDATE 或者 DELETE。 -
tbname:这个参数指的是触发器创建的表名,在哪个表上创建 -
triggerstmt: 触发器的程序体,也就是 SQL 语句
所以,可以创建六种触发器
BEFORE INSERT、AFTER INSERT、BEFORE UPDATE、AFTER UPDATE、BEFORE DELETE、AFTER DELETE
上面的 for each now 表示任何一条记录上的操作都会触发触发器。
下面我们通过一个例子来演示一下触发器的操作
我们还是用上面的 procuct 表做例子,我们创建一个 product_info 产品信息表。
create table product_info(p_info varchar(20)); 复制代码
然后我们创建一个 trigger

我们在 product 表中插入一条数据
insert into product values(4,"pineapple",15.3);复制代码
我们进行 select 查询,可以看到现在 product 表中有四条数据

我们没有向 product_info 表中插入数据,现在我们来看一下 product_info 表中,我们预想到是有数据的,具体来看下

这条数据是什么时候插入的呢?我们在创建触发器 tg_pinfo 的时候插入了的这条数据。
删除触发器
触发器可以使用 drop 进行删除,具体删除语法如下
drop trigger tg_pinfo;复制代码
和删除表的语法是一样的
查看触发器
我们经常会查看触发器,可以通过执行 show triggers 命令查看触发器的状态、语法等信息。
另一种查询方式是查询表中的 information_schema.triggers 表,这个可以查询指定触发器的指定信息,操作起来方便很多
触发器的作用
- 在添加一条数据前,检查数据是否合理,例如检查邮件格式是否正确
- 删除数据后,相当于数据备份的作用
- 可以记录数据库的操作日志,也可以作为表的执行轨迹
注意:触发器的使用有两个限制
- 触发程序不能调用将数据返回客户端的存储程序。也不能使用 CALL 语句的动态 SQL 语句。
- 不能在触发器中开始和结束语句,例如 START TRANSACTION

更多相关免费学习推荐:mysql教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of 47 pictures to guide you through MySQL advancement. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- What should I do if mysql prompts that the startup password is incorrect?
- How to delete user permissions in mysql under linux?
- How to retrieve accidentally deleted data in mysql
- How to check the current number of connections in mysql
- How to delete a field in the table in mysql
- Mysql query the table structure under the database?

