Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >When using nested if statements, C language stipulates that else is always what?
When using nested if statements, C language stipulates that else is always what?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2020-08-31 12:05:5921027browse
When using if statements in nests, C language stipulates that else is always paired with the previous if that is closest to it without else, regardless of the writing format. if means "if", else means "else", the structure of "if else" is: "if (judgment condition) {statement block 1} else {statement block 2}".

The syntax of C language stipulates that the else clause is always combined with the previous if without else clause, regardless of the writing format.
In C language, use the if and else keywords to judge conditions. Please look at the following code first:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age;
printf("请输入你的年龄:");
scanf("%d", &age);
if(age>=18){
printf("恭喜,你已经成年,可以使用该软件!\n");
}else{
printf("抱歉,你还未成年,不宜使用该软件!\n");
}
return 0;
}Possible running results:
请输入你的年龄:23↙ 恭喜,你已经成年,可以使用该软件!
or:
请输入你的年龄:16 抱歉,你还未成年,不宜使用该软件!
In this code, age>=18 It is a condition that needs to be judged. >= means "greater than or equal to", which is equivalent to ≥ in mathematics.
If the condition is true, that is, age is greater than or equal to 18, then execute the statement following if (line 8); if the condition is not true, that is, age is less than 18, then execute ## The statement after #else (line 10).
if else is:
if(判断条件){
语句块1
}else{
语句块2
} means that if the judgment condition is true, then execute statement block 1, otherwise execute statement block 2. The execution process can be represented as the following figure:
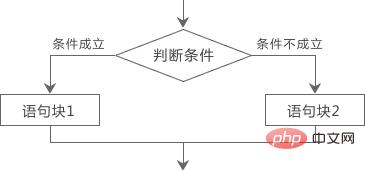 ##The so-called statement block is one or more statements surrounded by
##The so-called statement block is one or more statements surrounded by
gather. If there is only one statement in the statement block, you can also omit { }, for example: <pre class="brush:js;toolbar:false">if(age>=18) printf("恭喜,你已经成年,可以使用该软件!\n");
else printf("抱歉,你还未成年,不宜使用该软件!\n");</pre>Since the if else statement can execute different codes according to different situations, it is also called a branch structure or selection. Structure, in the above code, there are two branches.
Find the larger value of the two numbers:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, max;
printf("输入两个整数:");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
if(a>b) max=a;
else max=b;
printf("%d和%d的较大值是:%d\n", a, b, max);
return 0;
}Running result:
输入两个整数:34 28↙ 34和28的较大值是:34
In this example, with the help of the variable max, max is used to save the larger value, and finally Output max.
Nesting of if statementsif statements can also be nested, for example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a,b;
printf("Input two numbers:");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
if(a!=b){ //!=表示不等于
if(a>b) printf("a>b\n");
else printf("a<b\n");
}else{
printf("a=b\n");
}
return 0;
}Running result:
Input two numbers:12 68 a<b
When nesting if statements, pay attention to the pairing of if and else. C language stipulates that else is always paired with the nearest if before it
, for example:
if(a!=b) // ①
if(a>b) printf("a>b\n"); // ②
else printf("a<b\n"); // ③③ is paired with ②, not with ①.
Related recommendations:
c language tutorial videoThe above is the detailed content of When using nested if statements, C language stipulates that else is always what?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- How to find the greatest common divisor of two numbers in C language
- What should I do if fopen in C language fails to open a file?
- What software can I use to learn C language?
- What are the requirements for legal identifiers in C language?
- How to use the system() function in C language?
- What is the remainder symbol in C language?
- What are your understanding and thoughts about C language?
- What are the legal data type keywords provided by C language?

