Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Deep understanding of webpack
Deep understanding of webpack
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2020-07-11 16:46:372290browse

Webpack is currently one of the most popular packaging tools. It has simple configuration, powerful functions, and a rich loader and plug-in system, providing many conveniences for front-end developers. The author assumes that readers have some experience in using webpack before reading this chapter, so I will not go into details about how to use webpack.
Reading this chapter, you can learn the following:
- Webpack packaged code structure
- Webpack core architecture——Tapable
- Webpack event Flow
- Webpack plug-in implementation mechanism
- Webpack loader implementation mechanism
Webpack packaged code structure
Simple packaging
We first write the simplest method, and then use webpack for packaging:
// /webpack/bundles/simple/moduleA.js
window.printA = function printA() {
console.log(`This is module A!`);
}
A relatively basic webpack configuration file:
// /webpack/bundles/simple/webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: {
main: './moduleA.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'simple.bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './index.html'
})
]
}
Create an HTML file for testing in a browser environment:
nbsp;html> <meta> <meta> <meta> <title>Webpack - Simple Bundle</title>
After executing the packaging command webpack we get a dist directory, we open simple.bundle.js File:
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
window.printA = function printA() {
console.log(`This is module A!`);
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);
Mainly look at this paragraph:
// ......
var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
// ......
webpack internally defines a webpack_require method. The essence of this method is very Simple:
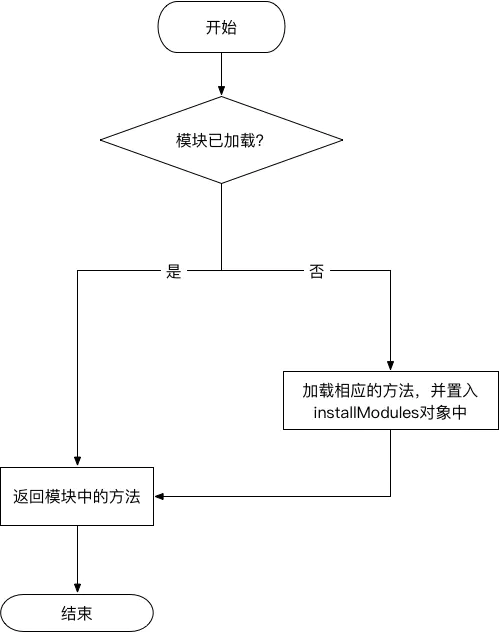
#There are simple dependencies between multiple modules
For example, moduleB.js depends on the moduleA.js file.
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/moduleA.js
module.exports = window.printA = function printA() {
console.log(`This is module A!`);
}
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/moduleB.js
const printA = require('./moduleA');
module.exports = window.printB = function printB() {
printA();
console.log('This is module B!');
}
Change the entry in the configuration file to
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/webpack.config.js // ... main: './moduleB.js' // ...
Package again, we get the following code:
// /webpack/bundles/simpleDependencies/dist/bundle.js
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const printA = __webpack_require__(1);
module.exports = window.printB = function printB() {
printA();
console.log('This is module B!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = window.printA = function printA() {
console.log(`This is module A!`);
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);
We can find some changes in this piece:
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const printA = __webpack_require__(1);
module.exports = window.printB = function printB() {
printA();
console.log('This is module B!');
}
In moduleB.js, you need to depend on moduleA, so you need to execute __webpack_require(1) first to get module A before proceeding to the next step.
Multiple entries
It should be noted that the moduleId in the packaged file will not be repeated. If there are two entry files, the entry module id will be 0, and other dependencies Module ids are not repeated. We create the following files, among which index0.js depends on common.js and dependency.js, while index1.js depends on the two files index0.js and common.js.
// /webpack/bundles/multi/common.js
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is common module!');
}
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dependency .js
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is dependency module!');
}
// /webpack/bundles/multi/index0.js
const common = require('./common');
const dependency = require('./dependency');
module.exports = window.print0 = function() {
common();
dependency();
console.log('This is module 0!');
}
// /webpack/bundles/multi/index1.js
const common = require('./common');
const index0 = require('./index0');
module.exports = window.print1 = function() {
common();
console.log('This is module 1!');
}
Modify the file entry in webpack.config.js:
// /webpack/bundles/multi/webpack.config.js
// ...
entry: {
index0: './index0.js',
index1: './index1.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
// ...
Packaged file:
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dist/index0.bundle.js
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 1);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is common module!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const common = __webpack_require__(0);
const dependency = __webpack_require__(2);
module.exports = window.print0 = function() {
common();
dependency();
console.log('This is module 0!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 2 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is dependency module!');
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);
// /webpack/bundles/multi/dist/index1.bundle.js
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 3);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is common module!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const common = __webpack_require__(0);
const dependency = __webpack_require__(2);
module.exports = window.print0 = function() {
common();
dependency();
console.log('This is module 0!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 2 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
module.exports = function() {
console.log('This is dependency module!');
}
/***/ }),
/* 3 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const common = __webpack_require__(0);
const index0 = __webpack_require__(1);
module.exports = window.print1 = function() {
common();
console.log('This is module 1!');
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);
Obviously, before using the CommonsChunkPlugin plugin, these two There are duplicate codes in the files. That is to say, each entrance will be packaged independently.
Let’s look at the situation after adding the CommonsChunkPlugin plug-in (modifying webpack.config.js):
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/webpack.config.js
plugins: [
// ...
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'common',
filename: 'common.js'
})
]
In this way, three files will be generated, index0.bundle.js, index1.bundel.js And common.js:
// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/common.js
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // install a JSONP callback for chunk loading
/******/ var parentJsonpFunction = window["webpackJsonp"];
/******/ window["webpackJsonp"] = function webpackJsonpCallback(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules) {
/******/ // add "moreModules" to the modules object,
/******/ // then flag all "chunkIds" as loaded and fire callback
/******/ var moduleId, chunkId, i = 0, resolves = [], result;
/******/ for(;i <p>common.js has included all the public methods and created a method named webpackJsonp in the browser window object. </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/common.js
// ...
/******/ var parentJsonpFunction = window["webpackJsonp"];
/******/ window["webpackJsonp"] = function webpackJsonpCallback(chunkIds, moreModules, executeModules) {
/******/ // add "moreModules" to the modules object,
/******/ // then flag all "chunkIds" as loaded and fire callback
/******/ var moduleId, chunkId, i = 0, resolves = [], result;
/******/ for(;i <p>This method is similar to __webpack_require__, which also caches modules. It's just that webpack will pre-extract public modules and cache them first, and then you can use the webpackJsonp method in other bundle.js to load the module. </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/index0.bundle.js
webpackJsonp([1],[],[1]);// /webpack/bundles/CommonsChunkPlugin/dist/index1.bundle.js
webpackJsonp([0],{
/***/ 3:
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const common = __webpack_require__(0);
const index0 = __webpack_require__(1);
module.exports = window.print1 = function() {
common();
console.log('This is module 1!');
}
/***/ })
},[3]);Webpack core architecture——Tapable
Clone the webpack source code from github to local, we can first Understand the overall process of webpack:
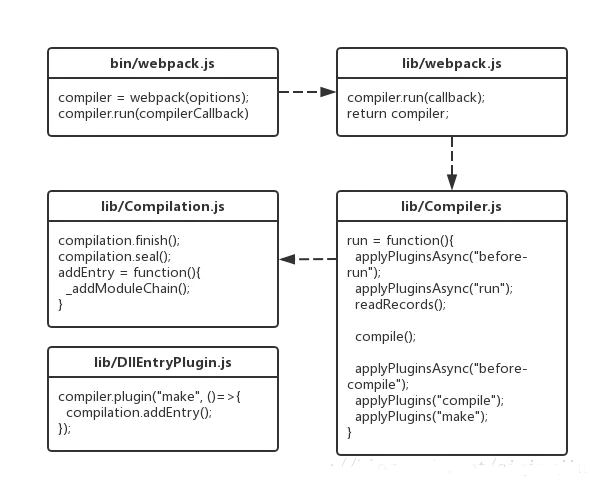
- lib/webpack.js returns a compiler object and calls compiler.run() ## In #lib/Compiler.js, the run method triggers two events, before-run and run, and then reads the file through readRecords, packages it through compile, and triggers before-compile, compile, make and other events after packaging; compile is the main process , a Compilation class is instantiated in this method, and its finish and seal methods are called.
- lib/Compilation.js defines the finish and seal methods, as well as an important method addEntry. This method accomplishes two things by calling its private method _addModuleChain: getting the corresponding module factory according to the module type and creating the module; building the module.
- lib/Compiler.js does not explicitly call addEntry, but triggers the make event. lib/DllEntryPlugin.js is a plug-in that listens to the make event and calls addEntry in the callback function.
- Calling the loader to handle the dependencies between modules.
- Abstract the file processed by the loader into an abstract syntax tree AST through acorn.
- Traverse the AST and build all dependencies of the module.
lib/webpack.js, which is the entry file for webpack.
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
const webpackOptionsValidationErrors = validateSchema(
webpackOptionsSchema,
options
);
if (webpackOptionsValidationErrors.length) {
throw new WebpackOptionsValidationError(webpackOptionsValidationErrors);
}
let compiler;
if (Array.isArray(options)) {
compiler = new MultiCompiler(options.map(options => webpack(options)));
} else if (typeof options === "object") {
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options);
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler);
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
compiler.hooks.environment.call();
compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call();
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler);
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid argument: options");
}
if (callback) {
if (typeof callback !== "function")
throw new Error("Invalid argument: callback");
if (
options.watch === true ||
(Array.isArray(options) && options.some(o => o.watch))
) {
const watchOptions = Array.isArray(options)
? options.map(o => o.watchOptions || {})
: options.watchOptions || {};
return compiler.watch(watchOptions, callback);
}
compiler.run(callback);
}
return compiler;
};
lib/webpack.js The process is roughly as follows:
- 参数验证
- 创建
Compiler(编译器)对象 - 注册并执行
NodeEnvironmentPlugin - 执行钩子
environment里的方法 - 执行钩子
afterEnvironment里的方法 - 注册并执行各种插件
- 将
compiler向外导出
显然,Compiler是我们需要深究的一个部分,因为 webpack 最终向外部返回也就是这个 Compiler 实例。大致了解下 Compiler 的实现:
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.hooks = {
// ...
};
this._pluginCompat.tap("Compiler", options => {
// ...
});
// ...
this.resolvers = {
normal: {
// ...
},
loader: {
// ...
},
context: {
// ...
}
};
// ...
}
watch(watchOptions, handler) {
// ...
}
run(callback) {
// ...
}
runAsChild(callback) {
// ...
}
purgeInputFileSystem() {
// ...
}
emitAssets(compilation, callback) {
// ...
}
emitRecords(callback) {
// ...
}
readRecords(callback) {
// ...
}
createChildCompiler(
compilation,
compilerName,
compilerIndex,
outputOptions,
plugins
) {
// ...
}
isChild() {
// ...
}
createCompilation() {
// ...
}
newCompilation(params) {
// ...
}
createNormalModuleFactory() {
// ...
}
createContextModuleFactory() {
// ...
}
newCompilationParams() {
// ...
}
compile(callback) {
// ...
}
}
Compiler 继承自 Tapable,在其构造方法中,定义了一些事件钩子(hooks)、一些变量以及一些方法。这些变量以及方法目前看来还是非常抽象的,所以我们有必要去了解下 Tapable 的实现。
Tapable的Github主页 对 Tapable 的介绍如下:
- The tapable packages exposes many Hook classes, which can be used to create hooks for plugins.
实际上,webpack基于事件流机制,它的工作流程就是将各个插件串联起来,而实现这一切的核心就是Tapable,webpack中最核心的负责编译的Compiler和负责创建bundles的Compilation都是Tapable的实例。Tapable 向外暴露许多的钩子类,这些类可以很方便地为插件创建事件钩子。 Tapable 中定义了如下几种钩子类:
- SyncHook
- SyncBailHook
- SyncWaterfallHook
- SyncLoopHook
- AsyncParallelHook
- AsyncParallelBailHook
- AsyncSeriesHook
- AsyncSeriesBailHook
- AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
所有钩子类的构造函数都接收一个可选的参数,这个参数是一个由字符串参数组成的数组,如下:
const hook = new SyncHook(["arg1", "arg2", "arg3"]);
钩子概览
Tapable的钩子分为两类,同步和异步,其中异步又分为并行和串行:
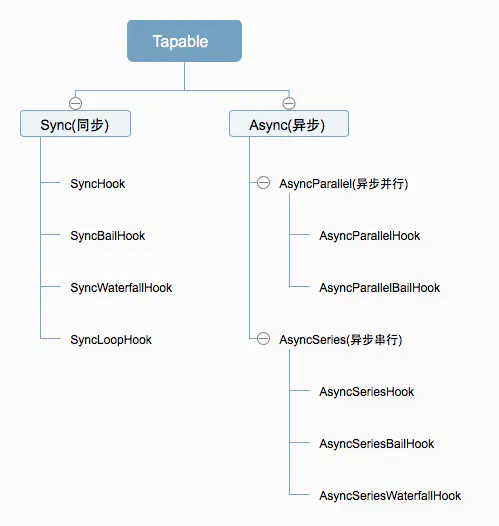
每种钩子都有各自的使用方式,如下表:
| 序号 | 钩子名 | 执行方式 | 使用要点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SyncHook | 同步串行 | 不关心监听函数的返回值 |
| 2 | SyncBailHook | 同步串行 | 只要监听函数中有一个函数的返回值不为 null,则跳过剩下所有的逻辑 |
| 3 | SyncWaterfallHook | 同步串行 | 上一个监听函数的返回值可以传给下一个监听函数 |
| 4 | SyncLoopHook | 同步循环 | 当监听函数被触发的时候,如果该监听函数返回true时则这个监听函数会反复执行,如果返回 undefined 则表示退出循环 |
| 5 | AsyncParallelHook | 异步并发 | 不关心监听函数的返回值 |
| 6 | AsyncParallelBailHook | 异步并发 | 只要监听函数的返回值不为 null,就会忽略后面的监听函数执行,直接跳跃到callAsync等触发函数绑定的回调函数,然后执行这个被绑定的回调函数 |
| 7 | AsyncSeriesHook | 异步串行 | 不关系callback()的参数 |
| 8 | AsyncSeriesBailHook | 异步串行 | callback()的参数不为null,就会直接执行callAsync等触发函数绑定的回调函数 |
| 9 | AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook | 异步串行 | 上一个监听函数的中的callback(err, data)的第二个参数,可以作为下一个监听函数的参数 |
Sync钩子
同步串行
(1) SyncHook
不关心监听函数的返回值
- 使用
const { SyncHook } = require("tapable");
let queue = new SyncHook(['name']); //所有的构造函数都接收一个可选的参数,这个参数是一个字符串的数组。
// 订阅
queue.tap('1', function (name, name2) {// tap 的第一个参数是用来标识订阅的函数的
console.log(name, name2, 1);
return '1'
});
queue.tap('2', function (name) {
console.log(name, 2);
});
queue.tap('3', function (name) {
console.log(name, 3);
});
// 发布
queue.call('webpack', 'webpack-cli');// 发布的时候触发订阅的函数 同时传入参数
// 执行结果:
/*
webpack undefined 1 // 传入的参数需要和new实例的时候保持一致,否则获取不到多传的参数
webpack 2
webpack 3
*/
- 原理
class SyncHook_MY{
constructor(){
this.hooks = [];
}
// 订阅
tap(name, fn){
this.hooks.push(fn);
}
// 发布
call(){
this.hooks.forEach(hook => hook(...arguments));
}
}
(2) SyncBailHook
只要监听函数中有一个函数的返回值不为 null,则跳过剩下所有的逻辑
- 使用
const {
SyncBailHook
} = require("tapable");
let queue = new SyncBailHook(['name']);
queue.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(name, 1);
});
queue.tap('2', function (name) {
console.log(name, 2);
return 'wrong'
});
queue.tap('3', function (name) {
console.log(name, 3);
});
queue.call('webpack');
// 执行结果:
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
*/
- 原理
class SyncBailHook_MY {
constructor() {
this.hooks = [];
}
// 订阅
tap(name, fn) {
this.hooks.push(fn);
}
// 发布
call() {
for (let i = 0, l = this.hooks.length; i <p>(3) SyncWaterfallHook<br>上一个监听函数的返回值可以传给下一个监听函数</p>
- 使用
const {
SyncWaterfallHook
} = require("tapable");
let queue = new SyncWaterfallHook(['name']);
// 上一个函数的返回值可以传给下一个函数
queue.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(name, 1);
return 1;
});
queue.tap('2', function (data) {
console.log(data, 2);
return 2;
});
queue.tap('3', function (data) {
console.log(data, 3);
});
queue.call('webpack');
// 执行结果:
/*
webpack 1
1 2
2 3
*/
- 原理
class SyncWaterfallHook_MY{
constructor(){
this.hooks = [];
}
// 订阅
tap(name, fn){
this.hooks.push(fn);
}
// 发布
call(){
let result = null;
for(let i = 0, l = this.hooks.length; i <p>(4) SyncLoopHook<br>当监听函数被触发的时候,如果该监听函数返回true时则这个监听函数会反复执行,如果返回 undefined 则表示退出循环。</p>
- 使用
const {
SyncLoopHook
} = require("tapable");
let queue = new SyncLoopHook(['name']);
let count = 3;
queue.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log('count: ', count--);
if (count > 0) {
return true;
}
return;
});
queue.call('webpack');
// 执行结果:
/*
count: 3
count: 2
count: 1
*/
- 原理
class SyncLoopHook_MY {
constructor() {
this.hook = null;
}
// 订阅
tap(name, fn) {
this.hook = fn;
}
// 发布
call() {
let result;
do {
result = this.hook(...arguments);
} while (result)
}
}
Async钩子
异步并行
(1) AsyncParallelHook
不关心监听函数的返回值。有三种注册/发布的模式,如下:
| 异步订阅 | 调用方法 |
|---|---|
| tap | callAsync |
| tapAsync | callAsync |
| tapPromise | promise |
- usage - tap
const {
AsyncParallelHook
} = require("tapable");
let queue1 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']);
console.time('cost');
queue1.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(name, 1);
});
queue1.tap('2', function (name) {
console.log(name, 2);
});
queue1.tap('3', function (name) {
console.log(name, 3);
});
queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => {
console.timeEnd('cost');
});
// 执行结果
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
webpack 3
cost: 4.520ms
*/
- usage - tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']);
console.time('cost1');
queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 1);
cb();
}, 1000);
});
queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 2);
cb();
}, 2000);
});
queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 3);
cb();
}, 3000);
});
queue2.callAsync('webpack', () => {
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost1');
});
// 执行结果
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
webpack 3
over
time: 3004.411ms
*/
- usage - promise
let queue3 = new AsyncParallelHook(['name']);
console.time('cost3');
queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 1);
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 2);
resolve();
}, 2000);
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name, cb) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 3);
resolve();
}, 3000);
});
});
queue3.promise('webpack')
.then(() => {
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost3');
}, () => {
console.log('error');
console.timeEnd('cost3');
});
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
webpack 3
over
cost3: 3007.925ms
*/
异步串行
(1) AsyncSeriesHook
不关心callback()的参数。
- usage - tap
const {
AsyncSeriesHook
} = require("tapable");
// tap
let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']);
console.time('cost1');
queue1.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(1);
return "Wrong";
});
queue1.tap('2', function (name) {
console.log(2);
});
queue1.tap('3', function (name) {
console.log(3);
});
queue1.callAsync('zfpx', err => {
console.log(err);
console.timeEnd('cost1');
});
// 执行结果
/*
1
2
3
undefined
cost1: 3.933ms
*/
- usage - tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']);
console.time('cost2');
queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 1);
cb();
}, 1000);
});
queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 2);
cb();
}, 2000);
});
queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, cb) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name, 3);
cb();
}, 3000);
});
queue2.callAsync('webpack', (err) => {
console.log(err);
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost2');
});
// 执行结果
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
webpack 3
undefined
over
cost2: 6019.621ms
*/
- usage - promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesHook(['name']);
console.time('cost3');
queue3.tapPromise('1',function(name){
return new Promise(function(resolve){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(name, 1);
resolve();
},1000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('2',function(name,callback){
return new Promise(function(resolve){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(name, 2);
resolve();
},2000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('3',function(name,callback){
return new Promise(function(resolve){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(name, 3);
resolve();
},3000)
});
});
queue3.promise('webapck').then(err=>{
console.log(err);
console.timeEnd('cost3');
});
// 执行结果
/*
webapck 1
webapck 2
webapck 3
undefined
cost3: 6021.817ms
*/
- 原理
class AsyncSeriesHook_MY {
constructor() {
this.hooks = [];
}
tapAsync(name, fn) {
this.hooks.push(fn);
}
callAsync() {
var slef = this;
var args = Array.from(arguments);
let done = args.pop();
let idx = 0;
function next(err) {
// 如果next的参数有值,就直接跳跃到 执行callAsync的回调函数
if (err) return done(err);
let fn = slef.hooks[idx++];
fn ? fn(...args, next) : done();
}
next();
}
}
(2) AsyncSeriesBailHook
callback()的参数不为null,就会直接执行callAsync等触发函数绑定的回调函数。
- usage - tap
const {
AsyncSeriesBailHook
} = require("tapable");
// tap
let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']);
console.time('cost1');
queue1.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(1);
return "Wrong";
});
queue1.tap('2', function (name) {
console.log(2);
});
queue1.tap('3', function (name) {
console.log(3);
});
queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => {
console.log(err);
console.timeEnd('cost1');
});
// 执行结果:
/*
1
null
cost1: 3.979ms
*/
- usage - tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']);
console.time('cost2');
queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 1);
callback();
}, 1000)
});
queue2.tapAsync('2', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 2);
callback('wrong');
}, 2000)
});
queue2.tapAsync('3', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 3);
callback();
}, 3000)
});
queue2.callAsync('webpack', err => {
console.log(err);
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost2');
});
// 执行结果
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
wrong
over
cost2: 3014.616ms
*/
- usage - promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesBailHook(['name']);
console.time('cost3');
queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 1);
resolve();
}, 1000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('2', function (name, callback) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 2);
reject();
}, 2000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('3', function (name, callback) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(name, 3);
resolve();
}, 3000)
});
});
queue3.promise('webpack').then(err => {
console.log(err);
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost3');
}, err => {
console.log(err);
console.log('error');
console.timeEnd('cost3');
});
// 执行结果:
/*
webpack 1
webpack 2
undefined
error
cost3: 3017.608ms
*/
(3) AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
上一个监听函数的中的callback(err, data)的第二个参数,可以作为下一个监听函数的参数
- usage - tap
const {
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
} = require("tapable");
// tap
let queue1 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']);
console.time('cost1');
queue1.tap('1', function (name) {
console.log(name, 1);
return 'lily'
});
queue1.tap('2', function (data) {
console.log(2, data);
return 'Tom';
});
queue1.tap('3', function (data) {
console.log(3, data);
});
queue1.callAsync('webpack', err => {
console.log(err);
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost1');
});
// 执行结果:
/*
webpack 1
2 'lily'
3 'Tom'
null
over
cost1: 5.525ms
*/
- usage - tapAsync
let queue2 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']);
console.time('cost2');
queue2.tapAsync('1', function (name, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('1: ', name);
callback(null, 2);
}, 1000)
});
queue2.tapAsync('2', function (data, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('2: ', data);
callback(null, 3);
}, 2000)
});
queue2.tapAsync('3', function (data, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('3: ', data);
callback(null, 3);
}, 3000)
});
queue2.callAsync('webpack', err => {
console.log(err);
console.log('over');
console.timeEnd('cost2');
});
// 执行结果:
/*
1: webpack
2: 2
3: 3
null
over
cost2: 6016.889ms
*/
- usage - promise
let queue3 = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['name']);
console.time('cost3');
queue3.tapPromise('1', function (name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('1:', name);
resolve('1');
}, 1000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('2', function (data, callback) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('2:', data);
resolve('2');
}, 2000)
});
});
queue3.tapPromise('3', function (data, callback) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('3:', data);
resolve('over');
}, 3000)
});
});
queue3.promise('webpack').then(err => {
console.log(err);
console.timeEnd('cost3');
}, err => {
console.log(err);
console.timeEnd('cost3');
});
// 执行结果:
/*
1: webpack
2: 1
3: 2
over
cost3: 6016.703ms
*/
- 原理
class AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook_MY {
constructor() {
this.hooks = [];
}
tapAsync(name, fn) {
this.hooks.push(fn);
}
callAsync() {
let self = this;
var args = Array.from(arguments);
let done = args.pop();
console.log(args);
let idx = 0;
let result = null;
function next(err, data) {
if (idx >= self.hooks.length) return done();
if (err) {
return done(err);
}
let fn = self.hooks[idx++];
if (idx == 1) {
fn(...args, next);
} else {
fn(data, next);
}
}
next();
}
}
Tapable事件流
webpack中的事件归纳如下,这些事件出现的顺序固定,但不一定每次打包所有事件都触发:
| 类型 | 名字 | 事件名 |
|---|---|---|
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | entry-option |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-plugins |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-resolvers |
| [A] | applyPlugins | environment |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-environment |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | run |
| [A] | applyPlugins | normal-module-factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | context-module-factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | compile |
| [A] | applyPlugins | this-compilation |
| [A] | applyPlugins | compilation |
| [F] | applyPluginsParallel | make |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | before-resolve |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | factory |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | resolver |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve-step |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | file |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | directory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | resolve-step |
| [G] | applyPluginsParallelBailResult | result |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | after-resolve |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | create-module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | build-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | normal-module-loader |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | program |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | statement |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate CallExpression |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | var data |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier require |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Literal |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require:amd:array |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Literal |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call require:commonjs:item |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | statement |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate MemberExpression |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | evaluate Identifier console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | call console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | expression console.log |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | expression console |
| [A] | applyPlugins | succeed-module |
| [E] | applyPluginsAsyncWaterfall | before-resolve |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | factory |
| [A] | applyPlugins | build-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | succeed-module |
| [A] | applyPlugins | seal |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunks |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-tree |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-tree |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | should-record |
| [A] | applyPlugins | revive-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-module-order |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-module-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record-modules |
| [A] | applyPlugins | revive-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunk-order |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | optimize-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunk-ids |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record-chunks |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | hash-for-chunk |
| [A] | applyPlugins | chunk-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-hash |
| [A] | applyPlugins | before-chunk-assets |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | global-hash-paths |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | global-hash |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | bootstrap |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | local-vars |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-obj |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | require-extensions |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | startup |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module-require |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | package |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | module |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | package |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | modules |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | render-with-entry |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [A] | applyPlugins | chunk-asset |
| [A] | applyPlugins | additional-chunk-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | record |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | additional-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-chunk-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-chunk-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | optimize-assets |
| [A] | applyPlugins | after-optimize-assets |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | after-compile |
| [C] | applyPluginsBailResult | should-emit |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | emit |
| [B] | applyPluginsWaterfall | asset-path |
| [D] | applyPluginsAsyncSeries | after-emit |
| [A] | applyPlugins | done |
几个关键的事件对应打包的阶段:
- entry-option:初始化options
- run:开始编译
- make:从entry开始递归分析依赖并对依赖进行build
- build-moodule:使用loader加载文件并build模块
- normal-module-loader:对loader加载的文件用acorn编译,生成抽象语法树AST
- program:开始对AST进行遍历,当遇到require时触发call require事件
- seal:所有依赖build完成,开始对chunk进行优化(抽取公共模块、加hash等)
- optimize-chunk-assets:压缩代码
- emit:把各个chunk输出到结果文件
了解以上事件,你可以很容易地写出一个插件。
...未完待续
引用
相关教程推荐:《Web pack入门视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Deep understanding of webpack. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

