Detailed explanation of depth-first traversal of binary trees in Java

In the past two days, I have been doing algorithm questions related to binary trees and taking some study notes. (You don’t even know how to do binary trees? You are really not proficient, and you don’t have to write algorithms or data structures related to binary trees in your daily work. Because I am good at it, I have to study harder!)
Definition
Let’s first look at Wikipedia’s explanation: In computer science, Binary tree (English: Binary tree) is a node with at most two branches ( That is, there is no tree structure with a node with a branch degree greater than 2). Usually branches are called "left subtree" or "right subtree". The branches of a binary tree have left and right order and cannot be reversed at will.
Due to the characteristics defined by the binary tree itself, it has a high degree of local repeatability, so when traversing the binary tree depth-first, it is usually implemented in a recursive way. The code implemented in this way is very concise and beautiful, and it is easier to understand. .
Depth-first traversal
Generally, we have three most common order traversals for depth-first traversal of binary trees: pre-order, mid-order, and post-order.
The traversal order of the preorder is: visit the root node-> traverse the left subtree-> traverse the right subtree
The traversal order of the mid-order is: traverse the left subtree-> ; Access the root node-> Traverse the right subtree
The post-order traversal order is: Traverse the left subtree-> Traverse the right subtree-> Visit the root node
Note The left and right here are the entire subtree, not a node, because we need to traverse the entire tree, so each traversal is performed in this order until the leaf node.
For example, if there is the following binary tree:
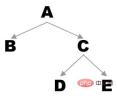
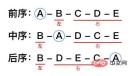
The sequence obtained by preorder traversal is A - B - C - D - E
The sequence obtained by mid-order traversal is B - A - D - C - E
The sequence obtained by post-order traversal is B - D - E - C - A
We will use pre-order traversal. (It is strongly not recommended to use human recursion, at least my brain can’t handle three levels...):
First level of recursion:
Visit the root node first, so the root node is output A, then traverse the left subtree (L1), and then traverse the right subtree (R1);
Second level recursion:
For L1, the root node is visited first, so the output is at this time The root node B, and then find that the left and right subtrees of B are empty, end the recursion;
For R1, visit the root node first, so output the root node C at this time, and then traverse the left subtree ( L2), and then traverse the right subtree (R2);
The third level of recursion:
For L2, the root node is visited first, so the root node D at this time is output, and then found The left and right subtrees of D are empty, and the recursion ends;
For R2, the root node is visited first, so the root node E at this time is output, and then the left and right subtrees of E are found to be empty, and the recursion ends;
Characteristics of front, middle and back order
According to the definition of front, middle and back order, it is not difficult for us to find the following characteristics:
• The first one in the pre-order must be the root node, and the last one in the post-order must be the root node
• The distribution of the left subtree and right subtree of each sort is regular
• For each subtree, a tree that follows the above two rules
#These characteristics are the expression of the order in the definition.
Various derivation
Here are some of the most basic algorithm questions for binary tree traversal:
• Given a binary tree, get the sequence of its pre/middle/post-order traversal;
• Derivation of the post-order (or derivation of the entire binary tree) based on the pre-order and mid-order;
• Based on the post-order and in-order to deduce pre-order (or deduce the entire binary tree);
For binary tree traversal, as mentioned before, recursion is usually used. For recursion, there are templates that can be applied directly:
public void recur(int level, int param) {
// terminator
if (level > MAX_LEVEL) {
// process result
return;
}
// process current logic
process(level, param);
// drill down
recur(level+1, newParam);
// restore current status
}This is a more practical tip mentioned by Brother Chao (Qin Chao) in the algorithm training camp I watched in the past two days (this template is especially good for novices). Follow the three steps above (if there are local variables needed Release or additional processing will be done in step 4) You can write recursive code in a more orderly manner.
Here is an example of deriving post-order based on pre-order and mid-order:
First initialize the two sequences:
int[] preSequence = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int[] inSequence = {2, 3, 1, 6, 7, 8, 5, 9, 4};Through the several features mentioned above, we have The minimum repeated sub-problem can be found. Each recursion
matches the index i where the node value is located in the mid-order according to the first node value of the previous sequence, so that we We can get the front and back parts of index i corresponding to the left and right subtrees respectively, and then traverse the two left and right subtrees respectively, and then output the first node value of the current preorder, which is the root node.
According to the top-down programming method, we can first write the following initial recursive call:
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); preAndInToPost(0, 0, preSequence.length, preSequence, inSequence, result);
The first parameter represents the first element index of the preorder sequence;
The second parameter represents the first element index of the in-order sequence;
The third parameter represents the length of the sequence;
第四个参数表示前序序列;
第五个参数表示后序序列;
第六个参数用于保存结果;
先来考虑终止条件是什么,也就是什么时候结束递归,当我们的根结点为空的时候终止,对应这里就是序列长度为零的时候。
if (length == 0) {
return;
}接着考虑处理逻辑,也就是找到索引 i:
int i = 0;
while (inSequence[inIndex + i] != preSequence[preIndex]) {
i++;
}然后开始向下递归:
preAndInToPost(preIndex + 1, inIndex, i, preSequence, inSequence, result); preAndInToPost(preIndex + i + 1, inIndex + i + 1, length - i - 1, preSequence, inSequence, result); result.add(preSequence[preIndex]);
因为推导的是后序序列,所以顺序如上,添加根结点的操作是在最后的。前三个参数如何得出来的呢,我们走一下第一次遍历就可以得出来。
前序序列的第一个结点 1 在中序序列中的索引为 2,此时
左子树的中序系列起始索引为总序列的第 1 个索引,长度为 2;
左子树的前序序列起始索引为总序列的第 2 个索引,长度为 2;
右子树的中序系列起始索引为总序列的第 3 个索引,长度为 length - 3;
右子树的前序序列起始索引为总序列的第 3 个索引,长度为 length - 3;
完整代码如下:
/**
* 根据前序和中序推导后序
*
* @param preIndex 前序索引
* @param inIndex 中序索引
* @param length 序列长度
* @param preSequence 前序序列
* @param inSequence 中序序列
* @param result 结果序列
*/
private void preAndInToPost(int preIndex, int inIndex, int length, int[] preSequence, int[] inSequence, List<Integer> result) {
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
int i = 0;
while (inSequence[inIndex + i] != preSequence[preIndex]) {
i++;
}
preAndInToPost(preIndex + 1, inIndex, i, preSequence, inSequence, result);
preAndInToPost(preIndex + i + 1, inIndex + i + 1, length - i - 1, preSequence, inSequence, result);
result.add(preSequence[preIndex]);
}参考链接
• 维基百科 - 二叉树(https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91)
推荐教程:《java教程》
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of depth-first traversal of binary trees in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What is the relationship between Java's platform independence and microservices architecture?May 01, 2025 am 12:16 AM
What is the relationship between Java's platform independence and microservices architecture?May 01, 2025 am 12:16 AMJava'splatformindependenceenhancesmicroservicesarchitecturebyofferingdeploymentflexibility,consistency,scalability,andportability.1)DeploymentflexibilityallowsmicroservicestorunonanyplatformwithaJVM.2)Consistencyacrossservicessimplifiesdevelopmentand
 How does GraalVM relate to Java's platform independence goals?May 01, 2025 am 12:14 AM
How does GraalVM relate to Java's platform independence goals?May 01, 2025 am 12:14 AMGraalVM enhances Java's platform independence in three ways: 1. Cross-language interoperability, allowing Java to seamlessly interoperate with other languages; 2. Independent runtime environment, compile Java programs into local executable files through GraalVMNativeImage; 3. Performance optimization, Graal compiler generates efficient machine code to improve the performance and consistency of Java programs.
 How do you test Java applications for platform compatibility?May 01, 2025 am 12:09 AM
How do you test Java applications for platform compatibility?May 01, 2025 am 12:09 AMToeffectivelytestJavaapplicationsforplatformcompatibility,followthesesteps:1)SetupautomatedtestingacrossmultipleplatformsusingCItoolslikeJenkinsorGitHubActions.2)ConductmanualtestingonrealhardwaretocatchissuesnotfoundinCIenvironments.3)Checkcross-pla
 What is the role of the Java compiler (javac) in achieving platform independence?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
What is the role of the Java compiler (javac) in achieving platform independence?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMThe Java compiler realizes Java's platform independence by converting source code into platform-independent bytecode, allowing Java programs to run on any operating system with JVM installed.
 What are the advantages of using bytecode over native code for platform independence?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AM
What are the advantages of using bytecode over native code for platform independence?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AMBytecodeachievesplatformindependencebybeingexecutedbyavirtualmachine(VM),allowingcodetorunonanyplatformwiththeappropriateVM.Forexample,JavabytecodecanrunonanydevicewithaJVM,enabling"writeonce,runanywhere"functionality.Whilebytecodeoffersenh
 Is Java truly 100% platform-independent? Why or why not?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Is Java truly 100% platform-independent? Why or why not?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AMJava cannot achieve 100% platform independence, but its platform independence is implemented through JVM and bytecode to ensure that the code runs on different platforms. Specific implementations include: 1. Compilation into bytecode; 2. Interpretation and execution of JVM; 3. Consistency of the standard library. However, JVM implementation differences, operating system and hardware differences, and compatibility of third-party libraries may affect its platform independence.
 How does Java's platform independence support code maintainability?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How does Java's platform independence support code maintainability?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AMJava realizes platform independence through "write once, run everywhere" and improves code maintainability: 1. High code reuse and reduces duplicate development; 2. Low maintenance cost, only one modification is required; 3. High team collaboration efficiency is high, convenient for knowledge sharing.
 What are the challenges in creating a JVM for a new platform?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM
What are the challenges in creating a JVM for a new platform?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AMThe main challenges facing creating a JVM on a new platform include hardware compatibility, operating system compatibility, and performance optimization. 1. Hardware compatibility: It is necessary to ensure that the JVM can correctly use the processor instruction set of the new platform, such as RISC-V. 2. Operating system compatibility: The JVM needs to correctly call the system API of the new platform, such as Linux. 3. Performance optimization: Performance testing and tuning are required, and the garbage collection strategy is adjusted to adapt to the memory characteristics of the new platform.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







