Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of browser event loop
Detailed explanation of browser event loop
- Guanhuiforward
- 2020-06-13 18:20:092535browse
Preface
Browser event loop, most of the basic interviews will ask, this article will talk about this knowledge point.
Event loop mechanism
The event loop is a set of mechanisms responsible for executing code, collecting and processing events, and executing subtasks in the queue.
In the event loop mechanism, the stack data structure used is the execution context stack. Whenever a function is called, the corresponding execution context will be created and pushed onto the stack; the heap data structure is used It is mainly used to represent a mostly unstructured memory area to store objects; the queue data structure used is the task queue, which is mainly used to store asynchronous tasks. As shown below:
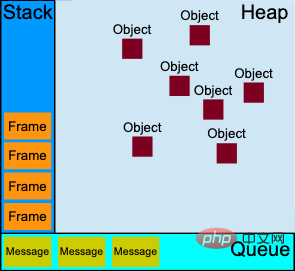
Execution context stack
When the JavaScript code is running, it will enter different In the execution environment, the global environment is first entered when execution begins. At this time, the global context is first created and pushed onto the stack. Then when a function is called, the corresponding function environment is entered. At this time, the corresponding function context is created and pushed onto the stack. When the execution context code on the top of the stack is executed, it will be popped off the stack. The stack mentioned here is the execution context.
Task Queue
In the event loop mechanism, there are multiple task queues, which are divided into macro task queues and micro task queues.
Macro tasks
Macro tasks include setTimeout, setInterval, I/O, and UI rendering.
Microtasks
Microtasks include Promise, Object.observe (obsolete), and MutationObserver (new features of html5).
The process of event loop mechanism
The main thread executes the overall JavaScript code to form an execution context stack. When encountering various task sources, it will The specified asynchronous task is suspended. After receiving the response result, the asynchronous task is placed in the corresponding task queue until only the global context is left in the execution context stack;
Place the microtask queue All task queues in the queue are pushed into the stack according to priority, and the asynchronous tasks of a single task queue are pushed into the stack and executed in a first-in, first-out manner until all micro-task queues are cleared;
Put the macro task queue into The asynchronous tasks in the task queue with the highest priority are pushed into the stack and executed in a first-in, first-out manner;
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until all macro task queues and micro tasks are cleared Queue, global context pop.
Simply put, the process of the event loop mechanism is that after the main thread executes the overall JavaScript code, it distributes the tasks specified by each task source it encounters to each task queue, and then micro- The task queue and macro task queue are pushed into the stack alternately for execution until all task queues are cleared and the global context is popped out of the stack.
Finally
Although Node.js also has an event loop, it is completely different from the browser's event loop. Node.js uses V8 as the js parsing engine, and uses its own designed libuv for I/O processing. libuv is an event-driven cross-platform abstraction layer that encapsulates some underlying features of different operating systems and provides a unified API to the outside world. , the event loop mechanism is also implemented in it. I won’t go into details here. If you want to know more, read the documentation yourself.
thanks for reading!
Recommended tutorial: "JS Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of browser event loop. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!


