Introduction to the method of realizing session sharing in redis
- 尚forward
- 2020-05-12 09:19:023591browse
Session implementation principle
session and cookie are two objects commonly used in web development. Will there be any connection between them?
php Chinese website learning topic: php session (including pictures, texts, videos, cases)
What are cookies?
Cookie is a small piece of text information that is passed between the web server and the browser along with user requests and pages. Cookies contain information that a web application can read each time a user visits a site.
Note: Cookies will be passed to the server with each HTTP request, excluding static files such as js, css, images, etc. This process can be analyzed from fiddler or the network monitoring that comes with IE, considering performance. You can start by minimizing cookies
The process of writing cookies to the browser: We can use the following code to write a cookie in the Asp.net project and send it to the client's browser (for simplicity, I did not set other attributes ).
HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie("RedisSessionId", "string value");Response.Cookies.Add(cookie);
We can see that the cookie written on the server will be written to the browser through the response header Set-Cookie.
What is Session?
Session We can use it to easily save some session-related information on the server side. Such as common login information.
Session implementation principle?
The HTTP protocol is stateless. For multiple requests issued by a browser, the WEB server cannot distinguish whether they originate from the same browser. So in order to distinguish this process, the server will distinguish the request through a sessionid. How is this sessionid sent to the server?
As mentioned earlier, the cookie will be sent to the server with each request, and the cookie is invisible to the user. It is best to use it to save this sessionid. Let's verify it through the following process.
Session["UserId"] = 123;

The relationship between session and cookie is verified again through the above picture. The server generates a cookie setting operation. The sessionid here is used to distinguish the browser. In order to experiment with different browsers, you can try logging in under IE, and then open the same page in chrome. You will find that you still need to log in in chrome because chrome does not have a sessionid at this time. httpOnly means that this cookie will not be operated through js on the browser side to prevent artificial modification of the sessionid.
The default key value of asp.net sessionid is ASP.NET_SessionId. You can modify this default configuration in web.config
<sessionState mode="InProc" cookieName="MySessionId"></sessionState>
Server-side Session reading
How does the server read the value of the session? Session["key value"]. So the question is, why can this Session object be obtained in the Defaule.aspx.cs file, and when was this Session object initialized?
In order to clarify this problem, we can view it by going to the definition.
System.Web.UI.Page ->HttpSessionState(Session)
protected internal override HttpContext Context {
[System.Runtime.TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
get {
if (_context == null) {
_context = HttpContext.Current;
}
return _context;
}
}
public virtual HttpSessionState Session {
get {
if (!_sessionRetrieved) {
/* try just once to retrieve it */
_sessionRetrieved = true;
try {
_session = Context.Session;
}
catch {
// Just ignore exceptions, return null.
}
}
if (_session == null) {
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Session_not_enabled));
}
return _session;
}
}The above paragraph is where the Page object initializes the Session object. You can see that the value of Session comes from HttpContext .Current, and when was HttpContext.Current initialized? Let’s look down.
public sealed class HttpContext : IServiceProvider, IPrincipalContainer
{
internal static readonly Assembly SystemWebAssembly = typeof(HttpContext).Assembly;
private static volatile bool s_eurlSet;
private static string s_eurl;
private IHttpAsyncHandler _asyncAppHandler; // application as handler (not always HttpApplication)
private AsyncPreloadModeFlags _asyncPreloadModeFlags;
private bool _asyncPreloadModeFlagsSet;
private HttpApplication _appInstance;
private IHttpHandler _handler;
[DoNotReset]
private HttpRequest _request;
private HttpResponse _response;
private HttpServerUtility _server;
private Stack _traceContextStack;
private TraceContext _topTraceContext;
[DoNotReset]
private Hashtable _items;
private ArrayList _errors;
private Exception _tempError;
private bool _errorCleared;
[DoNotReset]
private IPrincipalContainer _principalContainer;
[DoNotReset]
internal ProfileBase _Profile;
[DoNotReset]
private DateTime _utcTimestamp;
[DoNotReset]
private HttpWorkerRequest _wr;
private VirtualPath _configurationPath;
internal bool _skipAuthorization;
[DoNotReset]
private CultureInfo _dynamicCulture;
[DoNotReset]
private CultureInfo _dynamicUICulture;
private int _serverExecuteDepth;
private Stack _handlerStack;
private bool _preventPostback;
private bool _runtimeErrorReported;
private PageInstrumentationService _pageInstrumentationService = null;
private ReadOnlyCollection<string> _webSocketRequestedProtocols;
}HttpContext contains our commonly used Request, Response and other objects. HttpContext starts with the ASP.NET pipeline. Taking IIS 6.0 as an example, in the working process w3wp.exe, Aspnet_ispai.dll is used to load the .NET runtime (if the .NET runtime has not been loaded yet).
IIS 6.0 introduces the concept of application pool. A worker process corresponds to an application pool. An application pool can host one or more Web applications, and each Web application is mapped to an IIS virtual directory. Like IIS 5.x, each Web application runs in its own application domain.
If the HTTP request received by HTTP.SYS is the first access to the web application, after the runtime is successfully loaded, an application domain (AppDomain) will be created for the web application through the AppDomainFactory.
Subsequently, a special runtime IsapiRuntime is loaded. IsapiRuntime is defined in the assembly System.Web, and the corresponding namespace is System.Web.Hosting.
IsapiRuntime will take over the HTTP request. IsapiRuntime will first create an IsapiWorkerRequest object to encapsulate the current HTTP request, and pass the IsapiWorkerRequest object to the ASP.NET runtime: HttpRuntime. From this point on, the HTTP request officially enters the ASP.NET pipeline.
According to the IsapiWorkerRequest object, HttpRuntime will create a context (Context) object used to represent the current HTTP request: HttpContext.
I believe that everyone has a good understanding of the Session initialization process and the relationship between session and cookie. Let’s start with the Session sharing implementation plan.
Session sharing implementation plan
1.StateServer method
这种是asp.net提供的一种方式,还有一种是SQLServer方式(不一定程序使用的是SQLServer数据库,所以通用性不高,这里就不介绍了)。也就是将会话数据存储到单独的内存缓冲区中,再由单独一台机器上运行的Windows服务来控制这个缓冲区。
状态服务全称是“ASP.NET State Service ”(aspnet_state.exe)。它由Web.config文件中的stateConnectionString属性来配置。该属性指定了服务所在的服务器,以及要监视的端口。
<sessionState mode="StateServer" stateConnectionString="tcpip=127.0.0.1:42424" cookieless="false" timeout="20" />
在这个例子中,状态服务在当前机器的42424端口(默认端口)运行。要在服务器上改变端口和开启远程服务器的该功能,可编辑HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\aspnet_state\Parameters注册表项中的Port值和AllowRemoteConnection修改成1。
显然,使用状态服务的优点在于进程隔离,并可在多站点中共享。 使用这种模式,会话状态的存储将不依赖于iis进程的失败或者重启,然而,一旦状态服务中止,所有会话数据都会丢失(这个问题redis不会存在,重新了数据不会丢失)。
这里提供一段bat文件帮助修改注册表,可以复制保存为.bat文件执行
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\aspnet_state\Parameters" /v "AllowRemoteConnection" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\aspnet_state\Parameters" /v "Port" /t REG_DWORD /d 42424 /f net stop aspnet_state net start aspnet_state pause

完成这些配置以后还是不能实现共享,虽然站点间的SessionId是一致的,但只有一个站点能够读取的到值,而其它站点读取不到。下面给出解决方案,在Global文件里面添加下面代码
public override void Init()
{
base.Init();
foreach (string moduleName in this.Modules)
{
string appName = "APPNAME";
IHttpModule module = this.Modules[moduleName];
SessionStateModule ssm = module as SessionStateModule;
if (ssm != null)
{
FieldInfo storeInfo = typeof(SessionStateModule).GetField("_store", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
FieldInfo configMode = typeof(SessionStateModule).GetField("s_configMode", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Static);
SessionStateMode mode = (SessionStateMode)configMode.GetValue(ssm);
if (mode == SessionStateMode.StateServer)
{
SessionStateStoreProviderBase store = (SessionStateStoreProviderBase)storeInfo.GetValue(ssm);
if (store == null)//In IIS7 Integrated mode, module.Init() is called later
{
FieldInfo runtimeInfo = typeof(HttpRuntime).GetField("_theRuntime", BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
HttpRuntime theRuntime = (HttpRuntime)runtimeInfo.GetValue(null);
FieldInfo appNameInfo = typeof(HttpRuntime).GetField("_appDomainAppId", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
appNameInfo.SetValue(theRuntime, appName);
}
else
{
Type storeType = store.GetType();
if (storeType.Name.Equals("OutOfProcSessionStateStore"))
{
FieldInfo uribaseInfo = storeType.GetField("s_uribase", BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
uribaseInfo.SetValue(storeType, appName);
object obj = null;
uribaseInfo.GetValue(obj);
}
}
}
break;
}
}
}二.redis实现session共享
下面我们将使用redis来实现共享,首先要弄清楚session的几个关键点,过期时间,SessionId,一个SessionId里面会存在多组key/value数据。基于这个特性我将采用Hash结构来存储,看看代码实现。用到了上一篇提供的RedisBase帮助类。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.SessionState;
using ServiceStack.Redis;
using Com.Redis;
namespace ResidSessionDemo.RedisDemo
{
public class RedisSession
{
private HttpContext context;
public RedisSession(HttpContext context, bool IsReadOnly, int Timeout)
{
this.context = context;
this.IsReadOnly = IsReadOnly;
this.Timeout = Timeout;
//更新缓存过期时间
RedisBase.Hash_SetExpire(SessionID, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(Timeout));
}
/// <summary>
/// SessionId标识符
/// </summary>
public static string SessionName = "Redis_SessionId";
//
// 摘要:
// 获取会话状态集合中的项数。
//
// 返回结果:
// 集合中的项数。
public int Count
{
get
{
return RedisBase.Hash_GetCount(SessionID);
}
}
//
// 摘要:
// 获取一个值,该值指示会话是否为只读。
//
// 返回结果:
// 如果会话为只读,则为 true;否则为 false。
public bool IsReadOnly { get; set; }
//
// 摘要:
// 获取会话的唯一标识符。
//
// 返回结果:
// 唯一会话标识符。
public string SessionID
{
get
{
return GetSessionID();
}
}
//
// 摘要:
// 获取并设置在会话状态提供程序终止会话之前各请求之间所允许的时间(以分钟为单位)。
//
// 返回结果:
// 超时期限(以分钟为单位)。
public int Timeout { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 获取SessionID
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">SessionId标识符</param>
/// <returns>HttpCookie值</returns>
private string GetSessionID()
{
HttpCookie cookie = context.Request.Cookies.Get(SessionName);
if (cookie == null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(cookie.Value))
{
string newSessionID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
HttpCookie newCookie = new HttpCookie(SessionName, newSessionID);
newCookie.HttpOnly = IsReadOnly;
newCookie.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(Timeout);
context.Response.Cookies.Add(newCookie);
return "Session_"+newSessionID;
}
else
{
return "Session_"+cookie.Value;
}
}
//
// 摘要:
// 按名称获取或设置会话值。
//
// 参数:
// name:
// 会话值的键名。
//
// 返回结果:
// 具有指定名称的会话状态值;如果该项不存在,则为 null。
public object this[string name]
{
get
{
return RedisBase.Hash_Get<object>(SessionID, name);
}
set
{
RedisBase.Hash_Set<object>(SessionID, name, value);
}
}
// 摘要:
// 判断会话中是否存在指定key
//
// 参数:
// name:
// 键值
//
public bool IsExistKey(string name)
{
return RedisBase.Hash_Exist<object>(SessionID, name);
}
//
// 摘要:
// 向会话状态集合添加一个新项。
//
// 参数:
// name:
// 要添加到会话状态集合的项的名称。
//
// value:
// 要添加到会话状态集合的项的值。
public void Add(string name, object value)
{
RedisBase.Hash_Set<object>(SessionID, name, value);
}
//
// 摘要:
// 从会话状态集合中移除所有的键和值。
public void Clear()
{
RedisBase.Hash_Remove(SessionID);
}
//
// 摘要:
// 删除会话状态集合中的项。
//
// 参数:
// name:
// 要从会话状态集合中删除的项的名称。
public void Remove(string name)
{
RedisBase.Hash_Remove(SessionID,name);
}
//
// 摘要:
// 从会话状态集合中移除所有的键和值。
public void RemoveAll()
{
Clear();
}
}
}下面是实现类似在cs文件中能直接使用Session["UserId"]的方式,我的MyPage类继承Page实现了自己的逻辑主要做了两件事 1:初始化RedisSession 2:实现统一登录认证,OnPreInit方法里面判断用户是否登录,如果没有登录了则跳转到登陆界面
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
namespace ResidSessionDemo.RedisDemo
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义Page 实现以下功能
/// 1.初始化RedisSession
/// 2.实现页面登录验证,继承此类,则可以实现所有页面的登录验证
/// </summary>
public class MyPage:Page
{
private RedisSession redisSession;
/// <summary>
/// RedisSession
/// </summary>
public RedisSession RedisSession
{
get
{
if (redisSession == null)
{
redisSession = new RedisSession(Context, true, 20);
}
return redisSession;
}
}
protected override void OnPreInit(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnPreInit(e);
//判断用户是否已经登录,如果未登录,则跳转到登录界面
if (!RedisSession.IsExistKey("UserCode"))
{
Response.Redirect("Login.aspx");
}
}
}
}我们来看看Default.aspx.cs是如何使用RedisSession的,至此我们实现了和Asp.netSession一模一样的功能和使用方式。
RedisSession.Remove("UserCode");相比StateServer,RedisSession具有以下优点
1、redis服务器重启不会丢失数据 2.可以使用redis的读写分离个集群功能更加高效读写数据
测试效果,使用nginx和iis部署两个站点做负载均衡,iis1地址127.0.0.1:8002 iis2地址127.0.0.1:9000 nginx代理服务地址127.0.0.1:8003,不懂如何配置的可以去阅读我的nginx+iis实现负载均衡这篇文章。我们来看一下测试结果。
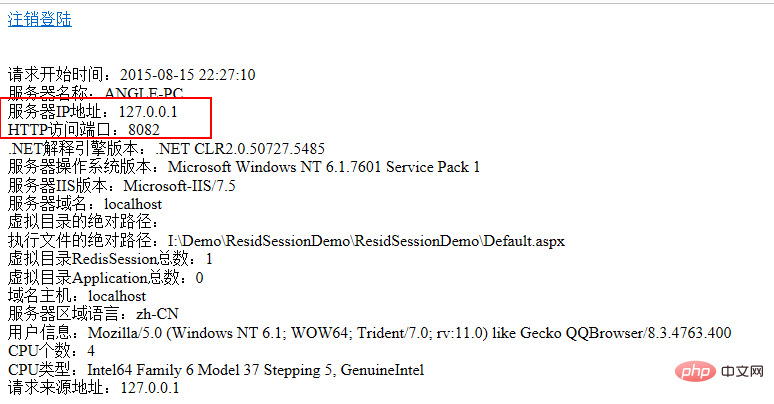
访问127.0.0.1:8003 需要进行登录 用户名为admin 密码为123

登录成功以后,重点关注端口号信息

刷新页面,重点关注端口号信息
可以尝试直接访问iis1地址127.0.0.1:8002 iis2地址127.0.0.1:9000 这两个站点,你会发现都不需要登录了。至此我们的redis实现session功能算是大功告成了。
问题拓展
使用redis实现session告一段落,下面留个问题讨论一下方案。微信开发提供了很多接口,参考下面截图,可以看到获取access_token接口每日最多调用2000次,现在大公司提供的很多接口针对不对级别的用户接口访问次数限制都是不一样的,至于做这个限制的原因应该是防止恶意攻击和流量限制之类的。
那么我的问题是怎么实现这个接口调用次数限制功能。大家可以发挥想象力参与讨论哦,或许你也会碰到这个问题。
先说下我知道的两种方案:
1、使用流量整形中的令牌桶算法,大小固定的令牌桶可自行以恒定的速率源源不断地产生令牌。如果令牌不被消耗,或者被消耗的速度小于产生的速度,令牌就会不断地增多,直到把桶填满。后面再产生的令牌就会从桶中溢出。最后桶中可以保存的最大令牌数永远不会超过桶的大小。
To put it simply: For example, the above access_token interface has a frequency of 2000 times a day, that is, 1 time/minute. The capacity of our token bucket is 2000, which can be stored using the simplest key/value of redis. The key is the user ID, and the value is the number of times the integer storage can be used. Then use a timer to call client.Incr(key) for 1 minute to achieve the number of times. Auto-increment; every time a user accesses this interface, the corresponding client.Decr(key) is used to reduce the number of uses.
But there is a performance problem here. This is only for one user. Assume there are 100,000 users. How to use a timer to implement this self-increment operation? Is it necessary to loop 100,000 times and call the client separately? .Incr(key)? This was not thought through clearly.
2. First judge the total number of direct user visits, and then perform an auto-increment if the conditions are met
For more redis knowledge, please follow redis门tutorial column.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the method of realizing session sharing in redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




