Home >Java >javaTutorial >Singleton pattern and Singleton in java
Singleton pattern and Singleton in java
- angryTomforward
- 2019-11-29 13:46:452428browse
Preface
This article comes from my official account. If you haven’t read it, just take a look. If you have, you can take a look again. I have modified it slightly. Some content, what is explained today is as follows:

1. What is the singleton pattern
[ Singleton Pattern], English name: Singleton Pattern, this pattern is very simple, a type only requires one instance, it is a commonly used software design pattern that belongs to the creation type. A class created through the singleton mode method has only one instance in the current process (if necessary, it may also be a singleton in a thread, for example: only the same instance is used within the thread context).
(Recommended video: java video tutorial)
1. Single An instance class can only have one instance.
2. The singleton class must create its own unique instance.
3. The singleton class must provide this instance to all other objects.
Then we probably know. In fact, to put it bluntly, there will only be one instance during our entire project cycle. When the project stops, the instance is destroyed. When it is restarted, our instance Products again.
The above mentioned the design pattern of a noun [creation type], so what is the design pattern of creation type?
Creational mode: Responsible for object creation. We use this mode to create the object instances we need.
In addition to creation, there are two other types of patterns:
Structural (Structural) pattern: dealing with the combination of classes and objects
Behavioral mode: The responsibilities in the interaction between classes and objects are divided into two design modes:
. We will talk about them later, but I won’t list them here.
Let’s focus on analyzing how to create an object instance in singleton mode starting from 0.
2. How to create singleton mode
There are many ways to implement singleton mode: From "lazy man style" to "hungry man style", and finally " "Double check lock" mode, Here we will slowly explain how to create a singleton step by step.
1. Normal logical sequence of thinking
Since we want to create a single instance, we first need to learn how to create an instance. This is very simple. I believe everyone can create an instance, such as Say something like this:
/// <summary>
/// 定义一个天气类
/// </summary>
public class WeatherForecast
{
public WeatherForecast()
{
Date = DateTime.Now;
}
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
}
[HttpGet]
public WeatherForecast Get()
{
// 实例化一个对象实例
WeatherForecast weather = new WeatherForecast();
return weather;
}
Every time we visit, the time will change, so our instances are always being created and changing:
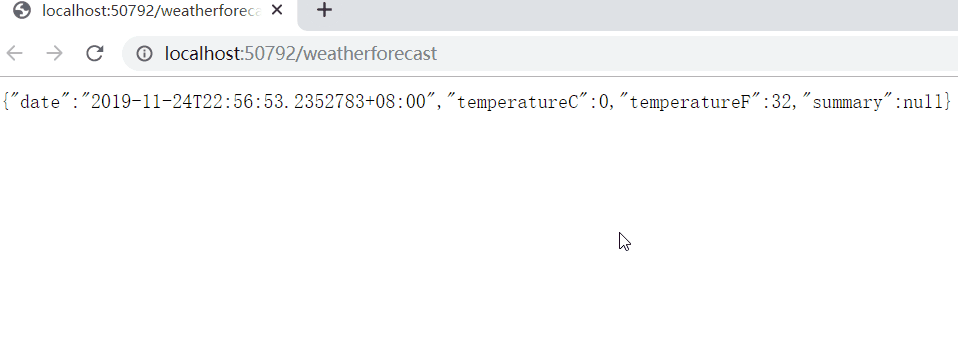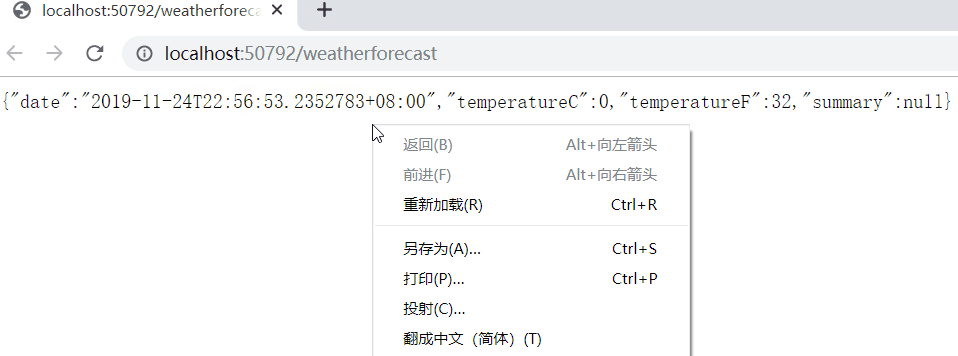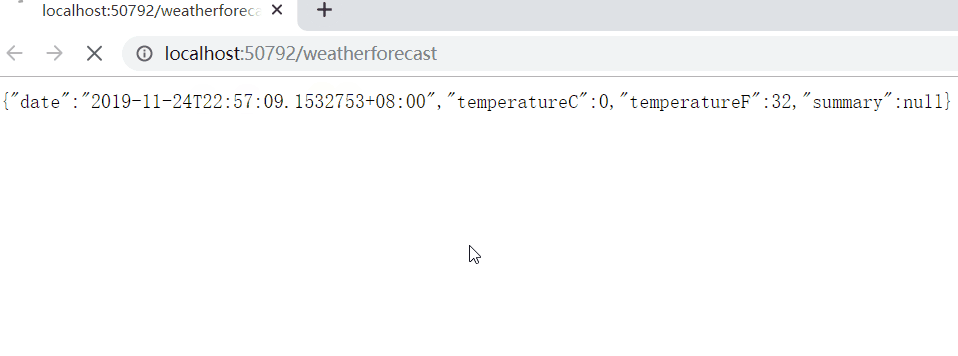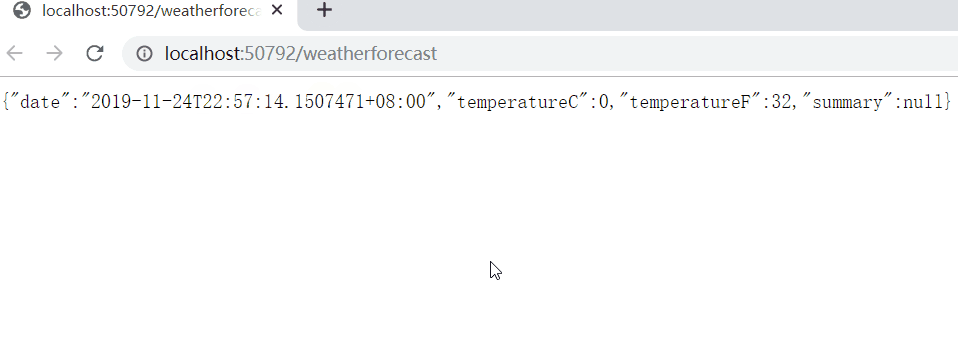
It is necessary to ensure that this instance is unique during the entire system's running cycle, so as to ensure that no problems will occur in the middle.
Okay then, let’s improve and improve. Didn’t we say we want to be the only one? That’s easy to say! Can I just return directly: /// <summary>
/// 定义一个天气类
/// </summary>
public class WeatherForecast
{
// 定义一个静态变量来保存类的唯一实例
private static WeatherForecast uniqueInstance;
// 定义私有构造函数,使外界不能创建该类实例
private WeatherForecast()
{
Date = DateTime.Now;
}
/// <summary>
/// 静态方法,来返回唯一实例
/// 如果存在,则返回
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static WeatherForecast GetInstance()
{
// 如果类的实例不存在则创建,否则直接返回
// 其实严格意义上来说,这个不属于【单例】
if (uniqueInstance == null)
{
uniqueInstance = new WeatherForecast();
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
public DateTime Date { get; set; }public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
} Then we modify the calling method, because our default constructor has been privatized and no more instances are allowed to be created, so we call it directly:
[HttpGet]
public WeatherForecast Get()
{
// 实例化一个对象实例
WeatherForecast weather = WeatherForecast.GetInstance();
return weather;
}Finally let’s take a look at the effect: 
[HttpGet]
public WeatherForecast Get()
{
// 实例化一个对象实例
//WeatherForecast weather = WeatherForecast.GetInstance();
// 多线程去调用
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
var th = new Thread(
new ParameterizedThreadStart((state) =>
{
WeatherForecast.GetInstance();
})
);
th.Start(i);
}
return null;
}Then let’s see what the effect is. According to our thinking, it should only be Walking through the constructor, it’s actually not: 
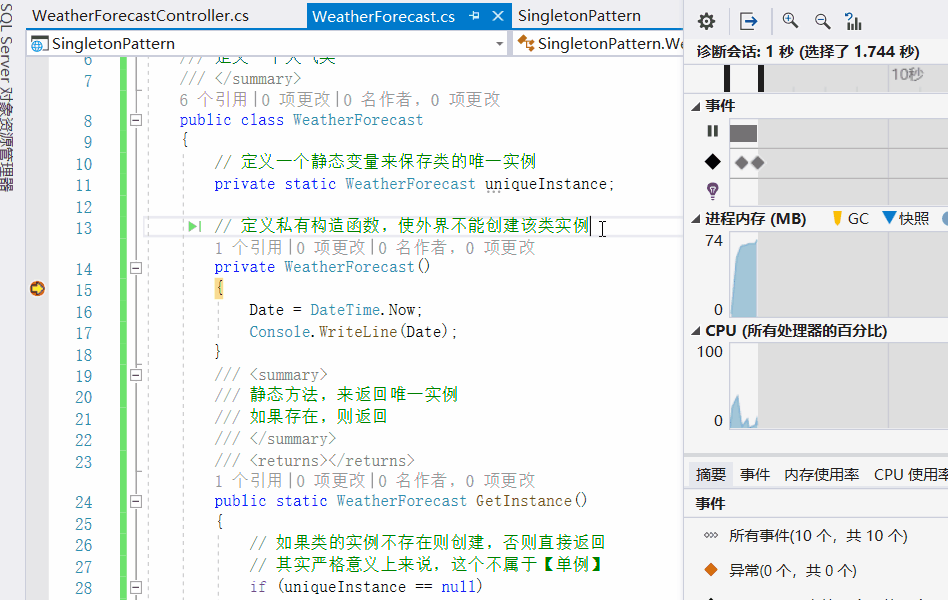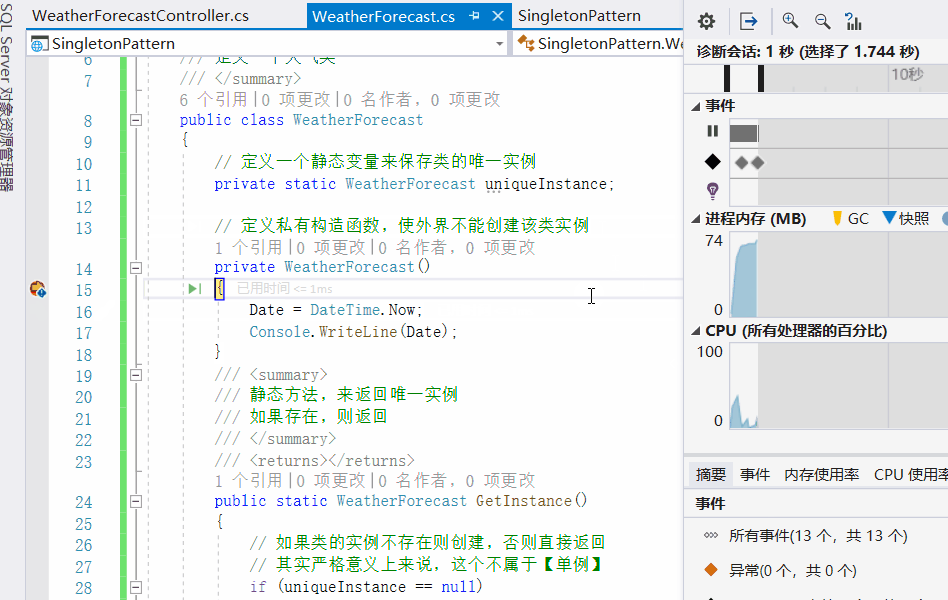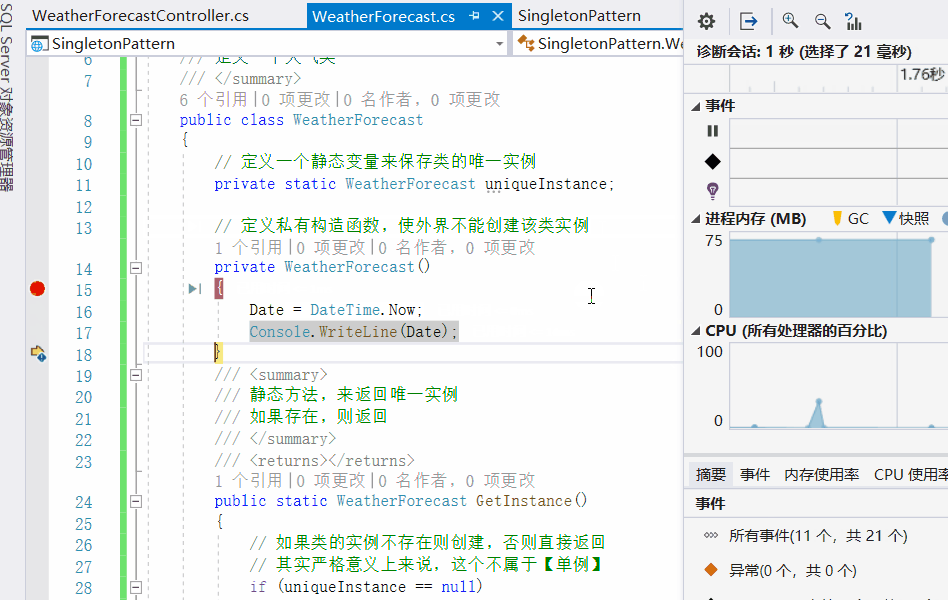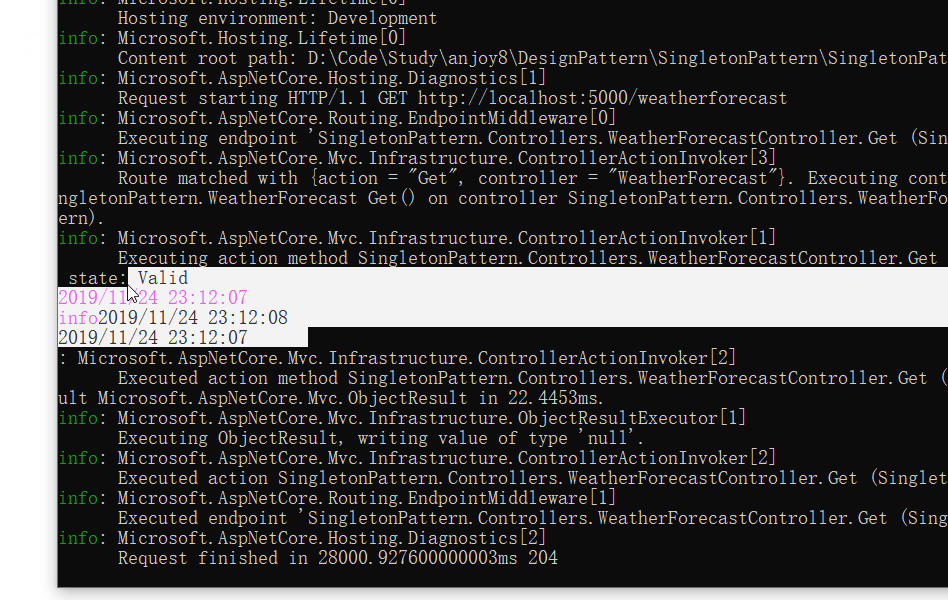
3个线程在第一次访问GetInstance方法时,同时判断(uniqueInstance ==null)这个条件时都返回真,然后都去创建了实例,这个肯定是不对的。那怎么办呢,只要让GetInstance方法只运行一个线程运行就好了,我们可以加一个锁来控制他,代码如下:
public class WeatherForecast
{
// 定义一个静态变量来保存类的唯一实例
private static WeatherForecast uniqueInstance;
// 定义一个锁,防止多线程
private static readonly object locker = new object();
// 定义私有构造函数,使外界不能创建该类实例
private WeatherForecast()
{
Date = DateTime.Now;
}
/// <summary>
/// 静态方法,来返回唯一实例
/// 如果存在,则返回
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static WeatherForecast GetInstance()
{
// 当第一个线程执行的时候,会对locker对象 "加锁",
// 当其他线程执行的时候,会等待 locker 执行完解锁
lock (locker)
{
// 如果类的实例不存在则创建,否则直接返回
if (uniqueInstance == null)
{
uniqueInstance = new WeatherForecast();
}
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
}
这个时候,我们再并发测试,发现已经都一样了,这样就达到了我们想要的效果,但是这样真的是最完美的么,其实不是的,因为我们加锁,只是第一次判断是否为空,如果创建好了以后,以后就不用去管这个 lock 锁了,我们只关心的是 uniqueInstance 是否为空,那我们再完善一下:
/// <summary>
/// 定义一个天气类
/// </summary>
public class WeatherForecast
{
// 定义一个静态变量来保存类的唯一实例
private static WeatherForecast uniqueInstance;
// 定义一个锁,防止多线程
private static readonly object locker = new object();
// 定义私有构造函数,使外界不能创建该类实例
private WeatherForecast()
{
Date = DateTime.Now;
}
/// <summary>
/// 静态方法,来返回唯一实例
/// 如果存在,则返回
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static WeatherForecast GetInstance()
{
// 当第一个线程执行的时候,会对locker对象 "加锁",
// 当其他线程执行的时候,会等待 locker 执行完解锁
if (uniqueInstance == null)
{
lock (locker)
{
// 如果类的实例不存在则创建,否则直接返回
if (uniqueInstance == null)
{
uniqueInstance = new WeatherForecast();
}
}
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
}
这样才最终的完美实现我们的单例模式!搞定。
2、幽灵事件:指令重排
当然,如果你看完了上边的那四步已经可以出师了,平时我们就是这么使用的,也是这么想的,但是真的就是万无一失么,有一个 JAVA 的朋友提出了这个问题,C# 中我没有听说过,是我孤陋寡闻了么:
单例模式的幽灵事件,时令重排会偶尔导致单例模式失效。
是不是听起来感觉很高大上,而不知所云,没关系,咱们平时用不到,但是可以了解了解:
为何要指令重排?
指令重排是指的 volatile,现在的CPU一般采用流水线来执行指令。一个指令的执行被分成:取指、译码、访存、执行、写回、等若干个阶段。然后,多条指令可以同时存在于流水线中,同时被执行。
指令流水线并不是串行的,并不会因为一个耗时很长的指令在“执行”阶段呆很长时间,而导致后续的指令都卡在“执行”之前的阶段上。
相反,流水线是并行的,多个指令可以同时处于同一个阶段,只要CPU内部相应的处理部件未被占满即可。比如说CPU有一个加法器和一个除法器,那么一条加法指令和一条除法指令就可能同时处于“执行”阶段, 而两条加法指令在“执行”阶段就只能串行工作。
相比于串行+阻塞的方式,流水线像这样并行的工作,效率是非常高的。
然而,这样一来,乱序可能就产生了。比如一条加法指令原本出现在一条除法指令的后面,但是由于除法的执行时间很长,在它执行完之前,加法可能先执行完了。再比如两条访存指令,可能由于第二条指令命中了cache而导致它先于第一条指令完成。
一般情况下,指令乱序并不是CPU在执行指令之前刻意去调整顺序。CPU总是顺序的去内存里面取指令,然后将其顺序的放入指令流水线。但是指令执行时的各种条件,指令与指令之间的相互影响,可能导致顺序放入流水线的指令,最终乱序执行完成。这就是所谓的“顺序流入,乱序流出”。
这个是从网上摘录的,大概意思看看就行,理解双检锁失效原因有两个重点
1、编译器的写操作重排问题.
例 : B b = new B();
上面这一句并不是原子性的操作,一部分是new一个B对象,一部分是将new出来的对象赋值给b.
直觉来说我们可能认为是先构造对象再赋值.但是很遗憾,这个顺序并不是固定的.再编译器的重排作用下,可能会出现先赋值再构造对象的情况.
2、结合上下文,结合使用情景.
理解了1中的写操作重排以后,我卡住了一下.因为我真不知道这种重排到底会带来什么影响.实际上是因为我看代码看的不够仔细,没有意识到使用场景.双检锁的一种常见使用场景就是在单例模式下初始化一个单例并返回,然后调用初始化方法的方法体内使用初始化完成的单例对象.
三、Singleton = 单例 ?
上边我们说了很多,也介绍了很多单例的原理和步骤,那这里问题来了,我们在学习依赖注入的时候,用到的 Singleton 的单例注入,是不是和上边说的一回事儿呢,这里咱们直接多多线程测试一下就行:
/// <summary>
/// 定义一个心情类
/// </summary>
public class Feeling
{
public Feeling()
{
Date = DateTime.Now;
}
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
}
// 单例注册到容器内
services.AddSingleton<Feeling>();
这里重点表扬下评论区的@我是你帅哥 小伙伴,及时的发现了我文章的漏洞,笔芯!
紧接着我们就控制器注入服务,然后多线程测试:
private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger;
private readonly Feeling _feeling;
public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger, Feeling feeling)
{
_logger = logger;
_feeling = feeling;
}
[HttpGet]
public WeatherForecast Get()
{
// 实例化一个对象实例
//WeatherForecast weather = WeatherForecast.GetInstance();
// 多线程去调用
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
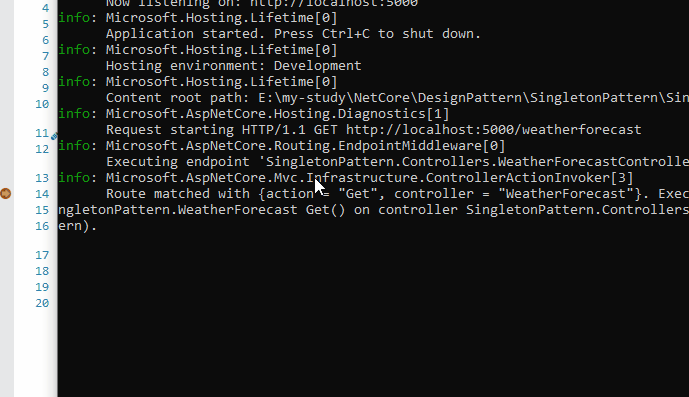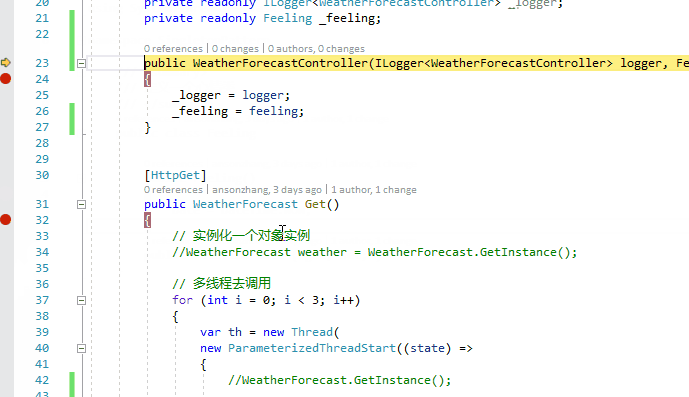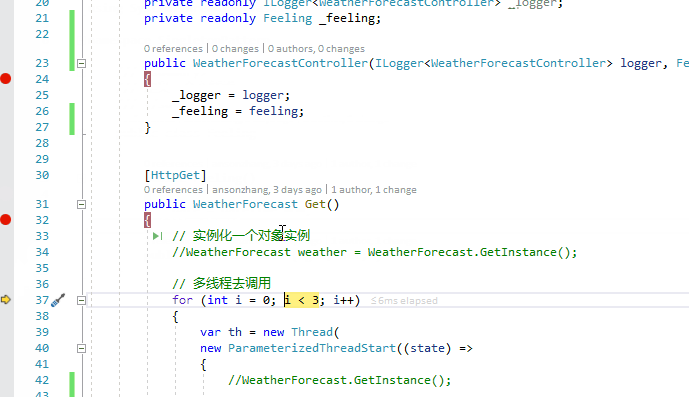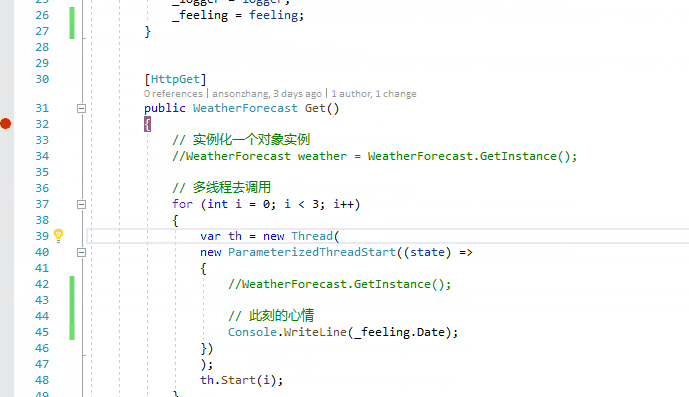
var th = new Thread(
new ParameterizedThreadStart((state) =>
{
//WeatherForecast.GetInstance();
// 此刻的心情
Console.WriteLine(_feeling.Date);
})
);
th.Start(i);
}
return null;
}
测试的结果,情理之中,只在我们项目初始化服务的时候,进入了一次构造函数:
It’s the same as what we said above, Singleton is a singleton, and it’s also a double-check lock type, because the conclusion can be seen that when we use the singleton mode, we can directly use dependency injection Sigleton can suffice and is very convenient.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Singleton Mode
[Excellent] Advantages of Singleton Mode:
(1). Guaranteed uniqueness: Prevent other objects from being instantiated and ensure the uniqueness of the instance;
(2) Globality: After the data is defined, the current instance and data can be used anywhere in the entire project;
[Inferior], Disadvantages of the singleton mode:
(1), Memory resident: Because the singleton has the longest life cycle, it exists in the entire development system. If data is added all the time, or is resident , will cause a certain amount of memory consumption.
The following content is from Baidu Encyclopedia:
Advantages
1. Instance control
The singleton mode will prevent other The object instantiates its own copy of the singleton object, ensuring that all objects access the unique instance.
2. Flexibility
Because the class controls the instantiation process, the class can flexibly change the instantiation process.
Disadvantages
1. Overhead
Although the number is small, if an instance of the class exists every time an object requests a reference, There will still be some overhead required. This problem can be solved by using static initialization.
2. Possible development confusion
When using singleton objects (especially objects defined in class libraries), developers must remember that they cannot use newKeyword instantiates the object. Because the library source code may not be accessible, application developers may unexpectedly find themselves unable to instantiate this class directly.
3. Object lifetime
cannot solve the problem of deleting a single object. In languages that provide memory management (such as those based on the .NET Framework), only a singleton class can cause the instance to be deallocated because it contains a private reference to the instance. In some languages (such as C), other classes can delete object instances, but this results in dangling references in the singleton class.
This article comes from php Chinese website, java tutorial column, welcome to learn!
The above is the detailed content of Singleton pattern and Singleton in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

