MongoDB – Attribute schema built using schema
- 步履不停Original
- 2019-07-01 16:37:042956browse

Simple description:
Enter directly into the attribute understanding mode. It is particularly suitable for the following situations:
- There is a large document, but it actually has some similar fields, and a subset of these fields has the same characteristics. In the end, it is necessary to compare these subsets Fields are sorted or queried;
- In fact, not all documents will have the required sorting fields;
- Or the above two conditions are met
In fact, considering performance reasons, Many indexes may be needed to take care of these subsets in order to optimize searches. But creating more indexes will only lead to performance degradation. The attribute pattern provides a great solution for this situation.
Example:
An order data document actually has a lot of time that needs to be recorded, such as creation time, payment time, shipping time, etc. When designing the data structure, of course the first thing that comes to mind is the following: 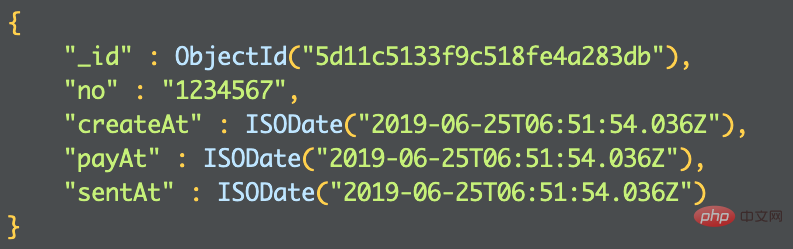
In fact, this design does not have much of a problem when there are relatively few time types, but combined with In actual business scenarios, of course the time required for an order will not be too short. Sometimes in order to optimize the sorting, we have to create corresponding ones. So, now comes the problem. If you create indexes one by one based on so many fields, you may create a lot of them, which will reduce the number of orders. Overall query performance. Then it is very appropriate to use the attribute mode at this time. As shown below:
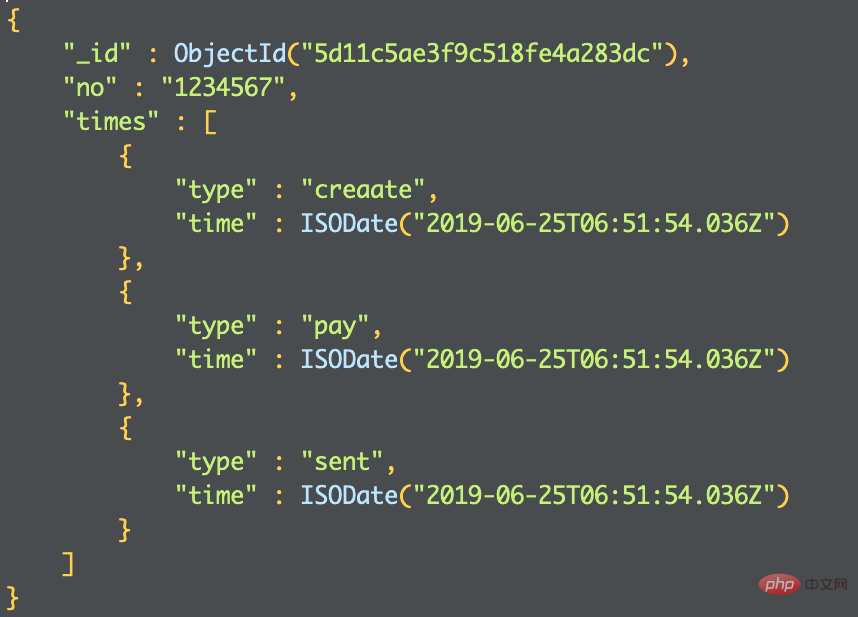 If this mode is considered in the order data structure, there is no need to repeatedly index similar field subsets, which greatly improves query efficiency.
If this mode is considered in the order data structure, there is no need to repeatedly index similar field subsets, which greatly improves query efficiency.
Conclusion:
Attribute mode provides simpler document indexing for many similar fields in each document. By moving this subset of data into a key-value subdocument, we can use undefined field names, add additional qualifiers to the information, and more clearly illustrate the relationship between the original fields and values. When we use attribute pattern, queries become simpler and faster since fewer indexes are required.
For more SQL-related technical articles, please visit the SQL Tutorial column to learn!
The above is the detailed content of MongoDB – Attribute schema built using schema. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

