Home >Java >javaTutorial >In-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples)
In-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples)
- 不言forward
- 2019-01-31 10:35:393085browse
This article brings you an in-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
I believe everyone uses Spring transaction management a lot, but it may only be limited to a @Transactional annotation or configuring transaction-related things in XML. In any case, dailymay is enough for us. But as a programmer, whether it is for an interview or to better control the code you write, you should learn more about the details of Spring transactions.
Here I throw out a few questions to see if everyone can answer them instantly:
If nested calls contain transaction methods, In Spring transaction management, which knowledge point does this belong to?
The framework we use may be
Hibernate/JPAorMybatis. We all know that the bottom layer requires asession/connectionObjects are used to help us perform operations. To ensure the integrity of the transaction, we need to use the same session/connectionobject for multiple groups of database operations, and we know that the objects managed by Spring IOC are allby default. Singleton, why does this not cause thread safety issues when we use it? What exactly is Spring doing internally?- What is the BPP that people call?
- What are the important interfaces for Spring transaction management?
1. Basic knowledge required to read this article
My classmates who read this articleDefaultEveryone is familiar with Spring Have a certain understanding of business-related knowledge. (ps: If you don’t know the specific article, read it and come back here)
We all know that Spring transactions are one of the best practices of Spring AOP, so let’s talk about the basic knowledge of AOP (simple Configuration, use) need to be known first. If you want to understand AOP more comprehensively, you can read this article: Important knowledge points of AOP (terminology introduction, comprehensive use). When talking about AOP, we have to talk about the underlying principle of AOP: the dynamic proxy design pattern. At this point, you already have a basic understanding of AOP. So we can use XML/annotations to configure Spring transaction management. In IOC learning, what you can know is the life cycle of Beans in Spring (leading to BPP objects) and the objects managed by IOC are singletons by default: singleton design pattern, if there is a singleton object"State" (with member variables), so many threads accessing this singleton object may cause thread insecurity. So what is thread safety? , there are many ways to solve thread safety, but one of them is: let each thread have its own variable: ThreadLocal
If you don’t know much about the knowledge points I mentioned above, it is recommended to click on the blue Go in and learn some words.
2. Two examples of unreliable intuition
2.1 The first exampleMy friend asked me an example before: Exception is thrown in the Service layer and captured in the Controller layer. If there is an exception in the Service, will the transaction be rolled back?// Service方法
@Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception {
Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23);
employeeRepository.save(employee);
// 假设这里出了Exception
int i = 1 / 0;
return employee;
}
// Controller调用
@RequestMapping("/add")
public Employee addEmployee() {
Employee employee = null;
try {
employee = employeeService.addEmployee();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return employee;
}My first reaction: It won’t be rolled back.
- What I thought at the time was this: because the Service layer has thrown an exception and it was caught by the Controller. Whether to roll back or not should be determined by the logic in the Controller's catch code block. If the catch code block does not roll back, it should not roll back.
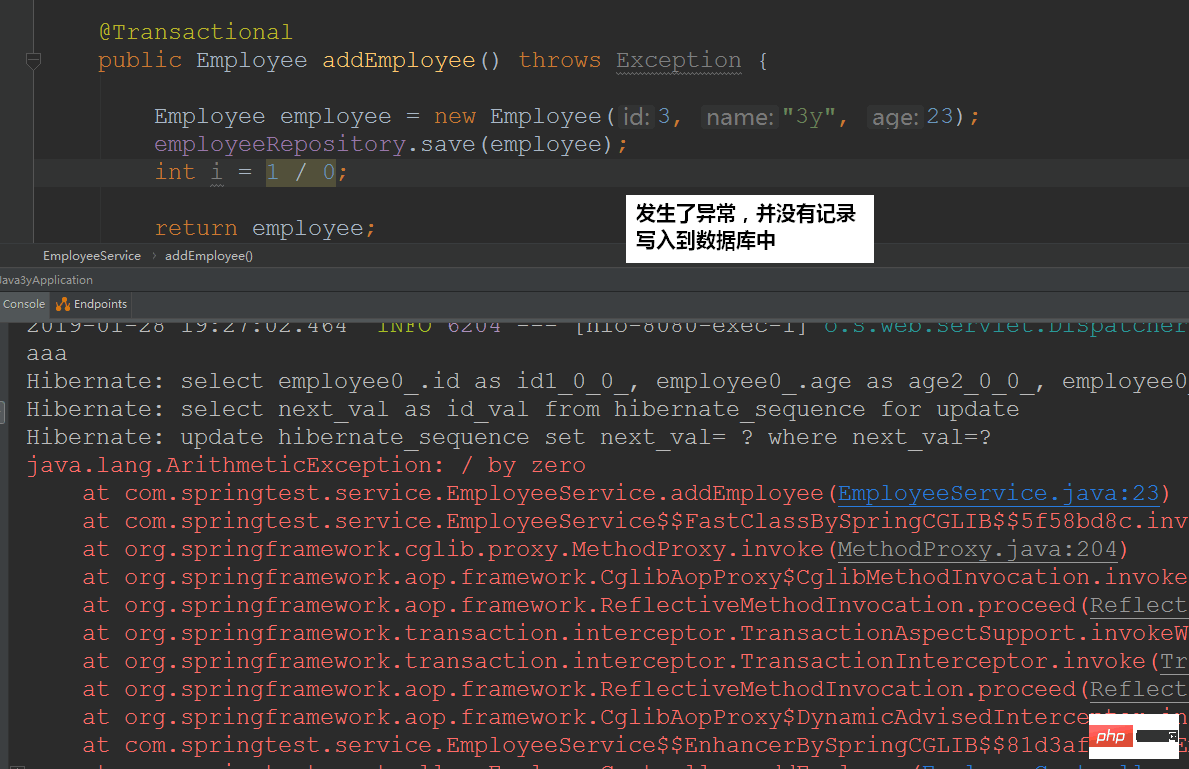
By default checked exceptions do not result in the transactional interceptor marking the transaction for rollback and instances of RuntimeException and its subclasses doConclusion: If it is a compile-time exception, it will not be automatically rolled back.
If it is a runtime exception, it will be automatically rolled back!
2.2 The second exampleThe second example comes from the Zhihu@LiuShu article. The corresponding URL will be given at the end of the articleWe all You know, methods surrounded by
@Transactional annotations can be managed by Spring transactions, then if I use a method without a transaction under the current class to call a method with a transaction, what will happen if we call this time? Will there be any business?
// 没有事务的方法去调用有事务的方法
public Employee addEmployee2Controller() throws Exception {
return this.addEmployee();
}
@Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception {
employeeRepository.deleteAll();
Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23);
// 模拟异常
int i = 1 / 0;
return employee;
}My first instinct is: This is related to the propagation mechanism of Spring transactions. In fact, this has nothing to do with the Spring transaction propagation mechanism, let me describe it below:
- Spring transaction management uses AOP, and the bottom layer of AOP Dynamic proxy is used. So if we mark the annotation
@Transactional
on a class or method, aproxy object will be generated.
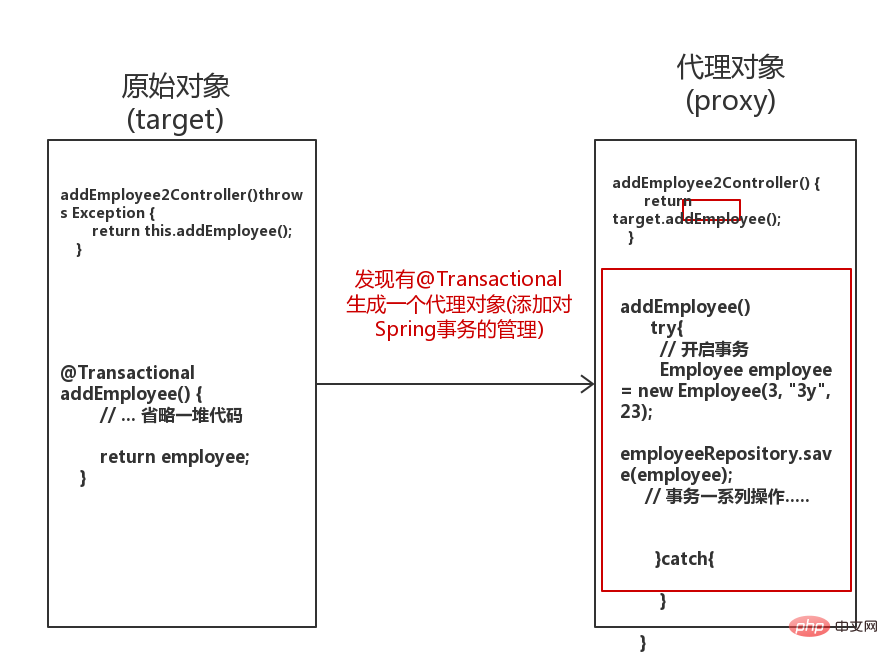
显然地,我们拿到的是代理(Proxy)对象,调用addEmployee2Controller()方法,而addEmployee2Controller()方法的逻辑是target.addEmployee(),调用回原始对象(target)的addEmployee()。所以这次的调用压根就没有事务存在,更谈不上说Spring事务传播机制了。
In-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples):
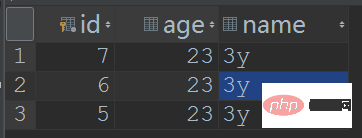
测试结果:压根就In-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples)
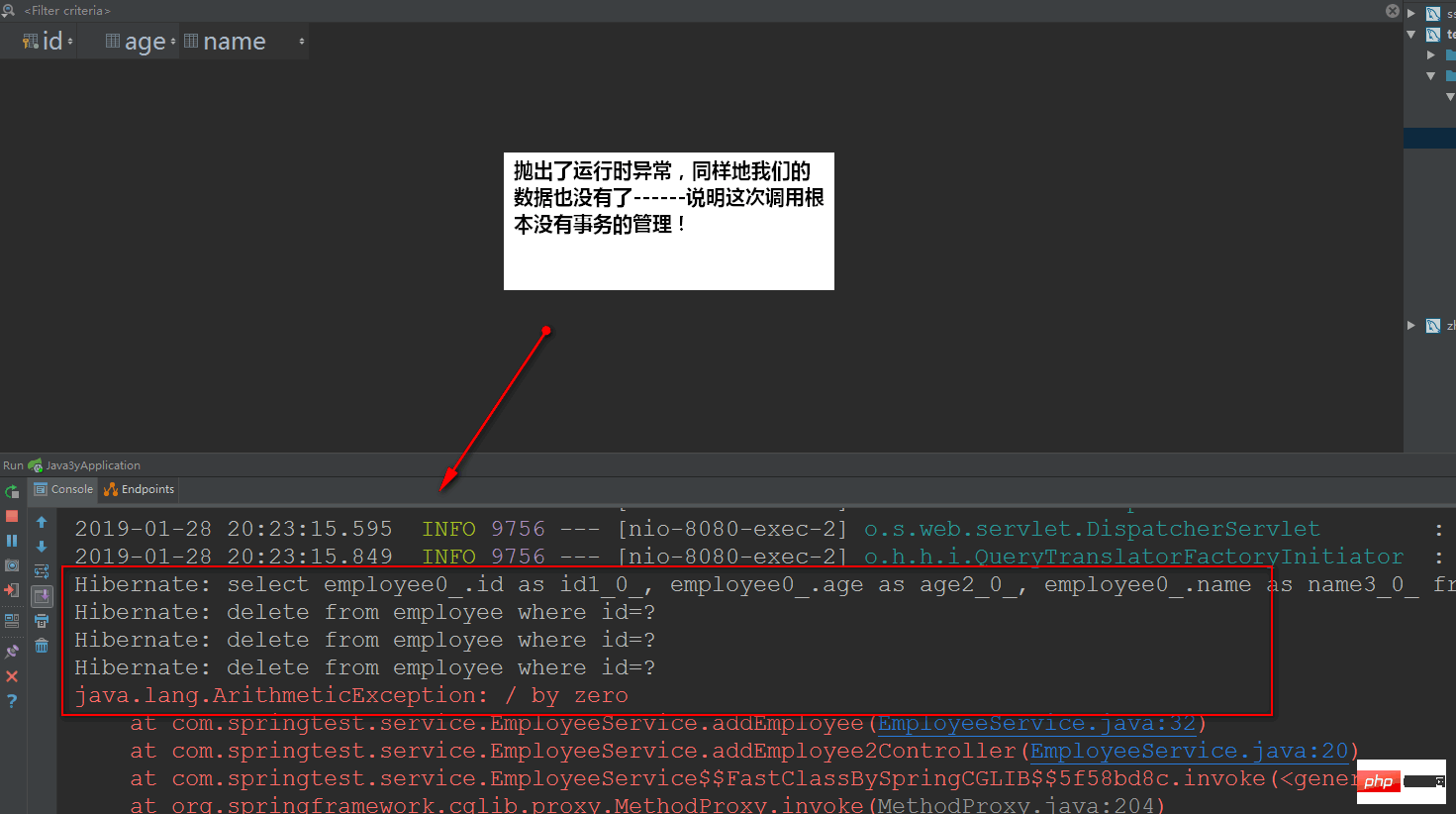
2.2.1再延伸一下
从上面的测试我们可以发现:如果是在本类中没有事务的方法来调用标注注解@Transactional方法,最后的结论是没有事务的。那如果我将这个标注注解的方法移到别的Service对象上,有没有事务?
@Service
public class TestService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Transactional
public Employee addEmployee() throws Exception {
employeeRepository.deleteAll();
Employee employee = new Employee("3y", 23);
// 模拟异常
int i = 1 / 0;
return employee;
}
}
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
// 没有事务的方法去调用别的类有事务的方法
public Employee addEmployee2Controller() throws Exception {
return testService.addEmployee();
}
}测试结果:
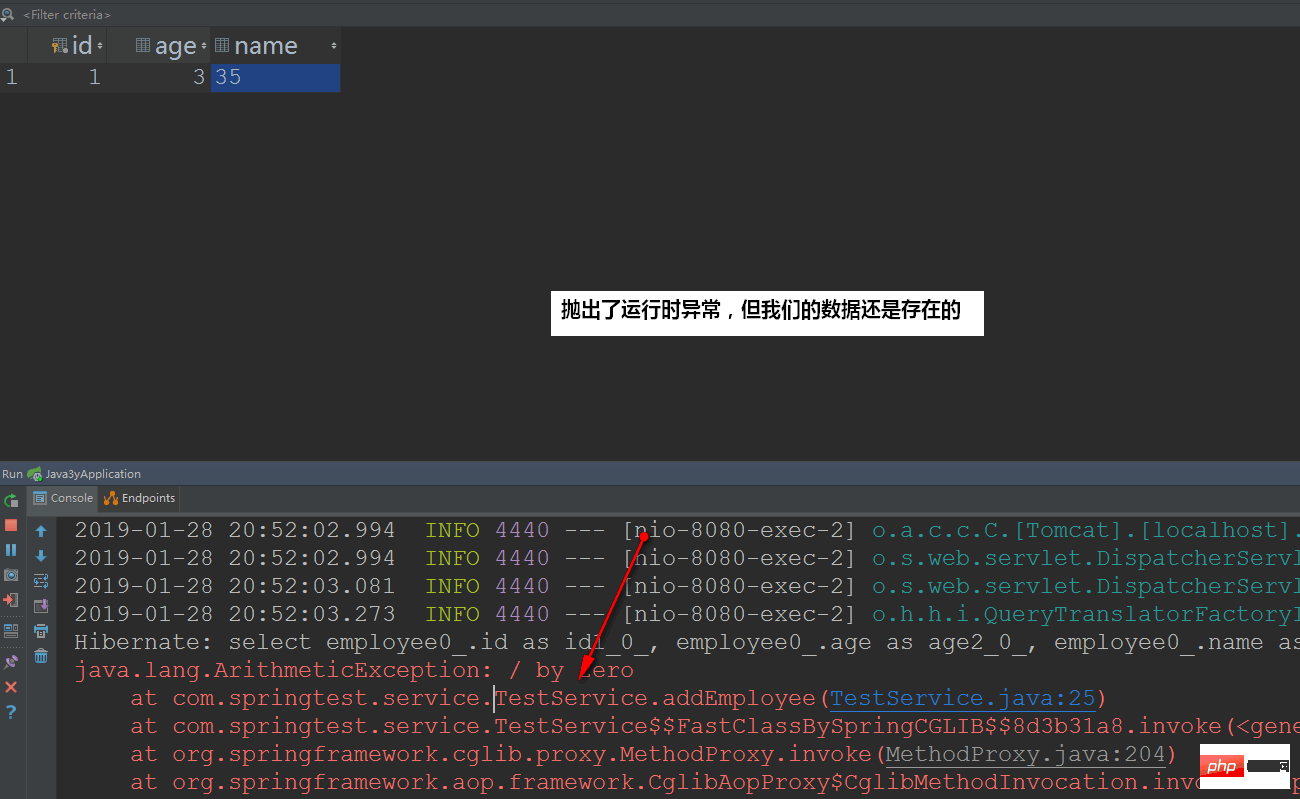
因为我们用的是代理对象(Proxy)去调用addEmployee()方法,那就当然有事务了。
看完这两个例子,有没有觉得3y的直觉是真的水!
三、Spring事务传播机制
如果嵌套调用含有事务的方法,在Spring事务管理中,这属于哪个知识点?
在当前含有事务方法内部调用其他的方法(无论该方法是否含有事务),这就属于Spring事务传播机制的知识点范畴了。
Spring事务基于Spring AOP,Spring AOP底层用的动态代理,动态代理有两种方式:
基于接口代理(JDK代理)
基于接口代理,凡是类的方法非public修饰,或者用了static关键字修饰,那这些方法都不能被Spring AOP增强
基于CGLib代理(子类代理)
基于子类代理,凡是类的方法使用了private、static、final修饰,那这些方法都不能被Spring AOP增强
至于为啥以上的情况不能增强,用你们的脑瓜子想一下就知道了。
值得说明的是:那些不能被Spring AOP增强的方法并不是不能在事务环境下工作了。只要它们被外层的事务方法调用了,由于Spring事务管理的传播级别,内部方法也可以工作在外部方法所启动的事务上下文中。
至于Spring事务传播机制的几个级别,我在这里就不贴出来了。这里只是再次解释“啥情况才是属于Spring事务传播机制的范畴”。
四、多线程问题
我们使用的框架可能是
Hibernate/JPA或者是Mybatis,都知道的底层是需要一个session/connection对象来帮我们执行操作的。要保证事务的完整性,我们需要多组数据库操作要使用同一个session/connection对象,而我们又知道Spring IOC所管理的对象默认都是单例的,这为啥我们在使用的时候不会引发线程安全问题呢?内部Spring到底干了什么?
回想一下当年我们学Mybaits的时候,是怎么编写Session工具类?
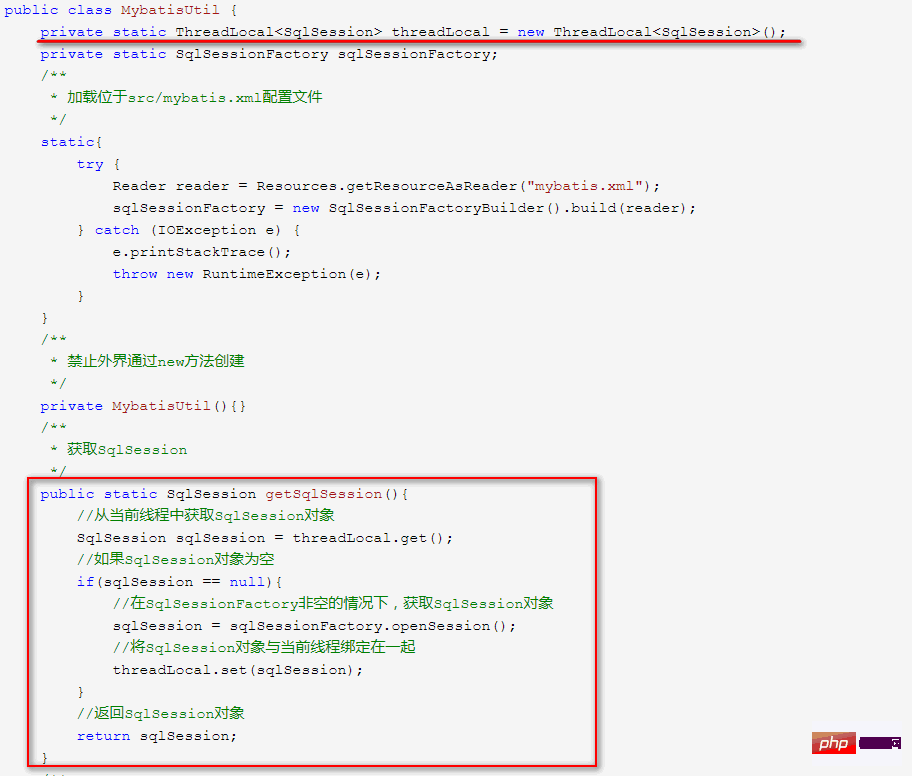
没错,用的就是ThreadLocal,同样地,Spring也是用的ThreadLocal。
以下内容来源《精通 Spring4.x》
我们知道在一般情况下,只有无状态的Bean才可以在多线程环境下共享,在Spring中,绝大部分Bean都可以声明为singleton作用域。就是因为Spring对一些Bean(如RequestContextHolder、TransactionSynchronizationManager、LocaleContextHolder等)中非线程安全状态的“状态性对象”采用ThreadLocal封装,让它们也成为线程安全的“状态性对象”,因此,有状态的Bean就能够以singleton的方式在多线程中工作。
我们可以试着点一下进去TransactionSynchronizationManager中看一下:
5. What is BPP?
The full name of BBP is: BeanPostProcessor, which is commonly known as Object post-processor
In short, our objects can be processed through BeanPostProcessor "Processing".
Spring Bean management (or Bean life cycle) is also a frequently tested knowledge point. I will reorganize it in the autumn recruitment. Here are the steps, because they are more important, so I’ll post them here:
- ResouceLoader loads the configuration information
- BeanDefintionReader parses the configuration information and generates One BeanDefintion
- BeanDefintion is managed by BeanDefintionRegistry
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor processes the configuration information (that is, processing the configuration information, generally through PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer To implement)
- Instantiate Bean
- If the Bean
is configured/implemented
InstantiationAwareBean, the corresponding method is called - Use BeanWarpper to complete property configuration (dependency) between objects ##If the Bean
- is configured/implemented
Aware interface, then call the corresponding method
If the Bean is configured with the before method of BeanPostProcessor, then call - If the Bean is configured
- init-method
Or implement InstantiationBean, then call the corresponding method
If the Bean is configured with the after method of BeanPostProcessor, call - Put the object into the HashMap
- Finally, if the destroy or DisposableBean method is configured, the destruction operation is performed
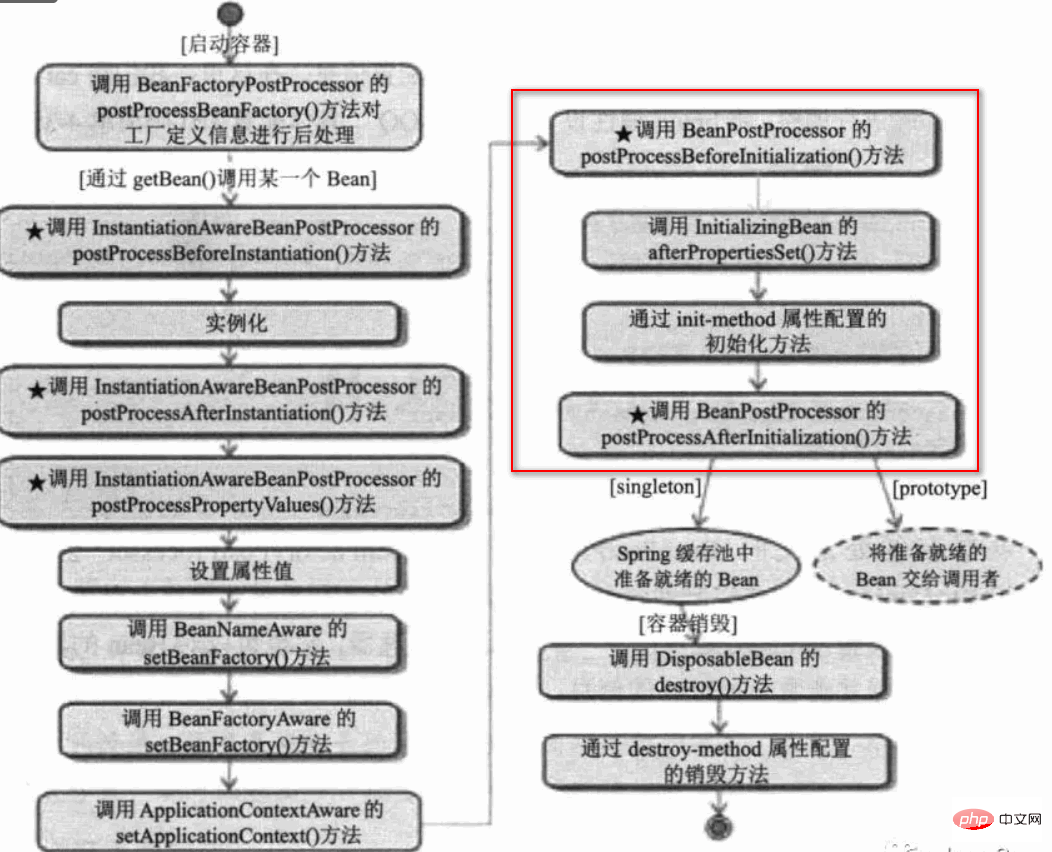 There are also pictures about BPP:
There are also pictures about BPP:
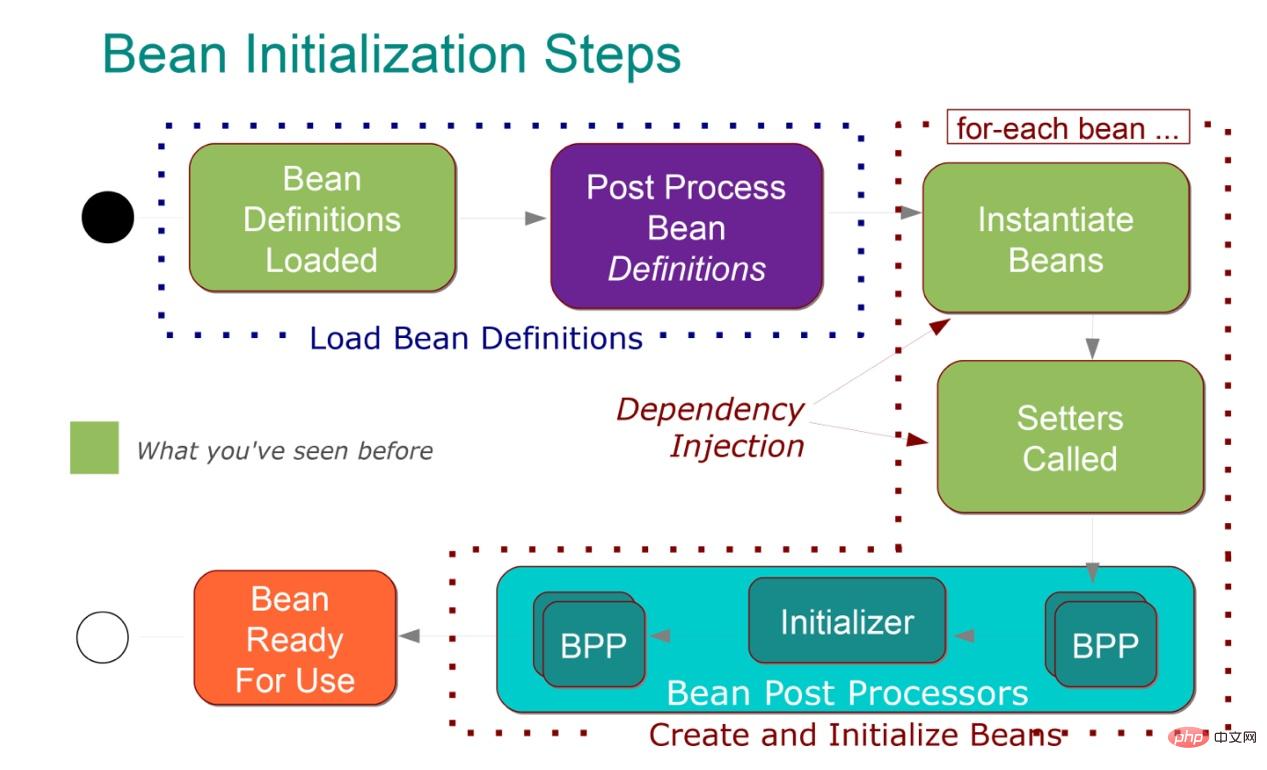 5.1 Why specifically talk about BPP?
5.1 Why specifically talk about BPP?
The bottom layer of Spring AOP programming uses dynamic proxy technology, and the
proxy objectmust be used when calling. So how does Spring do it?
I only need to write a BPP, and in the postProcessBeforeInitialization or postProcessAfterInitialization method, judge the object to see if it needs to be woven into the aspect logic. If so, then I will generate a Proxy object, and then return this proxy object, then what is finally injected into the container is naturally the proxy object.Spring provides BeanPostProcessor, which allows us to "process
" the objects in need! 6. Understand several important interfaces of Spring transactions
Spring transactions can be divided into two types:
- Programmatic transactions (through code To implement transactions)
- Declarative transactions (implement transactions through configuration)
- Programmatic transactions are relatively simple to implement in Spring. Because declarative transactions encapsulate a lot of things (generally we use them simply, but everything inside is very complex), it is much more difficult to implement declarative transactions.
There are the following important interfaces in programmatic transactions:
- TransactionDefinition: defines Spring-compatible
- transaction attributes
(such as transactions Isolation level, transaction propagation, transaction timeout, read-only status)
TransactionStatus: Represents the specific - running status of the transaction
(obtains transaction running status information, also You can use this interfaceIndirectRollback transactions and other operations)
PlatformTransactionManager: Transaction manager interface (defines a set of behaviors, and the specific implementation is handed over to different persistence Framework to complete --- - analogy
JDBC)
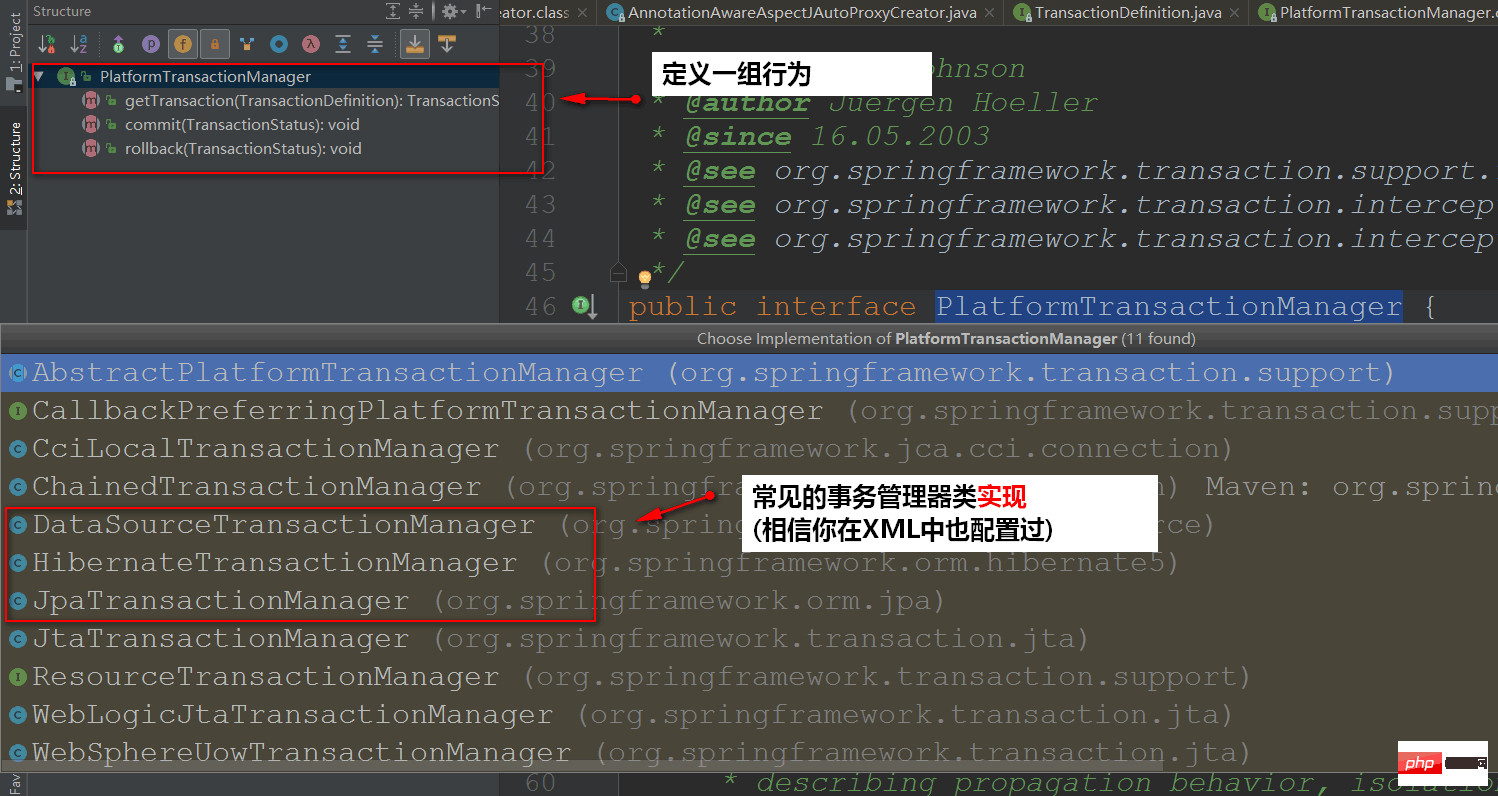 In declarative transactions, in addition to the TransactionStatus and PlatformTransactionManager interfaces, there are Several important interfaces:
In declarative transactions, in addition to the TransactionStatus and PlatformTransactionManager interfaces, there are Several important interfaces:
- TransactionProxyFactoryBean: Generate proxy object
- TransactionInterceptor: Implement object interception
- TransactionAttrubute: transaction configuration data
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of Spring transactions (with examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Detailed introduction to Spring transaction principles
- Spring transactions (JDBC) for transactions in java
- How to do asynchronous operation after spring transaction commit
- How to understand spring transactions and the use of declarative transactions
- Relevant introduction to Spring transaction management (with code)

