Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >How does JavaScript implement inheritance? Six common inheritance methods in js
How does JavaScript implement inheritance? Six common inheritance methods in js
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2018-10-17 14:28:228740browse
How to implement inheritance in JavaScript? This article will introduce to you six common inheritance methods in js. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Preface
A very important aspect of object-oriented programming is object inheritance. By inheriting the B object, the A object can directly possess all the properties and methods of the B object. This is very useful for code reuse.
Most object-oriented programming languages implement object inheritance through "classes". Traditionally, JavaScript language inheritance is not implemented through classes (ES6 introduced the class syntax), but through "prototypes". So what are the common inheritance methods in JS?
If you need the source code of this article, please click Six Common Inheritance Methods
If you think the article is of some help to you, please post it on my GitHub blog Like and follow, thank you very much!
Method 1. Prototype chain inheritance
The key to this method is:The prototype of the subtype is an instance object of the parent type.
//父类型
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.play = [1, 2, 3]
this.setName = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () { }
//子类型
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person() // 子类型的原型为父类型的一个实例对象
var s1 = new Student(15000)
var s2 = new Student(14000)
console.log(s1,s2)
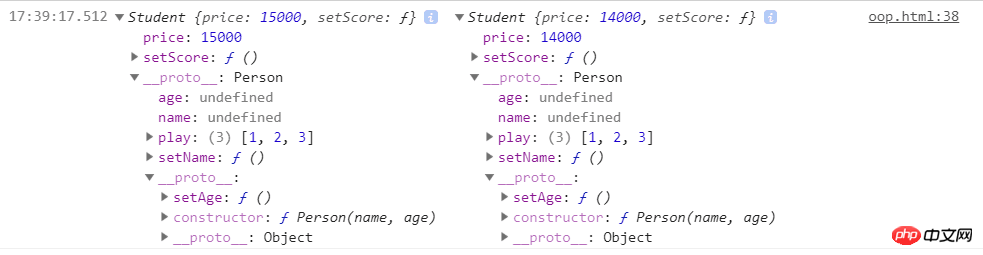
But the essence of this method is to point the prototype of the subclass to the instance of the parent class, so Instances of subclasses can access Student.prototype, which is the instance of Person, through __proto__, so that they can access the private methods of the parent class, and then point to the prototype of the parent class through __proto__. Method on the parent class prototype. So the private and public methods and properties of the parent class are treated as the public properties of the subclass
The subclass inherits the properties and methods of the parent class by treating the private properties and public methods of the parent class as Our own public properties and methods, we all know that when operating basic data types, we operate on values, and when operating on reference data types, we operate on addresses. If there are reference type properties in the private properties of the parent class , then it will be used as a public attribute when inherited by a subclass, so when subclass 1 operates this attribute, it will affect subclass 2.
s1.play.push(4) console.log(s1.play, s2.play) console.log(s1.__proto__ === s2.__proto__)//true console.log(s1.__proto__.__proto__ === s2.__proto__.__proto__)//true
The play attribute in s1 changes, and at the same time, the play attribute in s2 will also change accordingly.
Another thing to note is that When we need to add a new method to a subclass or override a method of the parent class, remember to put it after the statement that replaces the prototype
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
// Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }//在这里写子类的原型方法和属性是无效的,
//因为会改变原型的指向,所以应该放到重新指定之后
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student(15000)
console.log(s1)
Features:
Added prototype methods/prototype attributes to the parent class, which can be accessed by subclasses
-
Simple and easy to implement
Disadvantages:
Unable to implement multiple inheritance
All properties from the prototype object are shared by all instances
When creating a subclass instance, parameters cannot be passed to the parent class constructor
-
If you want to add attributes and methods to a subclass, they must be executed after
Student.prototype = new Person()and cannot be placed in the constructor
Method Two: Borrowing Constructor Inheritance
The key to this method is:Use a general call() in the subtype constructor to call the parent type constructor
<script>
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setName = function () {}
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age) // 相当于: this.Person(name, age)
/*this.name = name
this.age = age*/
this.price = price
}
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)</script>
This method only implements partial inheritance. If the prototype of the parent class also has methods and attributes, the subclass cannot get these methods and attributes.
console.log(s1.setAge())//Uncaught TypeError: s1.setAge is not a function
Features:
Solve the problem of subclass instances sharing parent class reference attributes in prototype chain inheritance
When creating a subclass instance, you can pass parameters to the parent class
You can implement multiple inheritance (call multiple parent class objects)
Disadvantages:
The instance is not an instance of the parent class, but an instance of the subclass
can only Inherit the instance properties and methods of the parent class, but cannot inherit the prototype properties and methods
-
Function reuse cannot be achieved. Each subclass has a copy of the parent class instance function, which affects performance
Method 3: Prototype chain borrows the combined inheritance of constructors
The key to this method is:By calling the parent class constructor, inherit the properties of the parent class and retain the passed parameters Advantages, and then use the parent class instance as the prototype of the subclass to achieve function reuse.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this,name,age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//组合继承也是需要修复构造函数指向的
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
var s2 = new Student('Jack', 22, 14000)
console.log(s1)
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(p1.constructor) //Person
这种方式融合原型链继承和构造函数的优点,是 JavaScript 中最常用的继承模式。不过也存在缺点就是无论在什么情况下,都会调用两次构造函数:一次是在创建子类型原型的时候,另一次是在子类型构造函数的内部,子类型最终会包含父类型对象的全部实例属性,但我们不得不在调用子类构造函数时重写这些属性。
优点:
可以继承实例属性/方法,也可以继承原型属性/方法
不存在引用属性共享问题
可传参
函数可复用
缺点:
调用了两次父类构造函数,生成了两份实例
方式四: 组合继承优化1
这种方式通过父类原型和子类原型指向同一对象,子类可以继承到父类的公有方法当做自己的公有方法,而且不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = Person.prototype
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1)

但这种方式没办法辨别是对象是子类还是父类实例化
console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person)//true true console.log(s1.constructor)//Person
优点:
不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点
缺点:
没办法辨别是实例是子类还是父类创造的,子类和父类的构造函数指向是同一个。
方式五: 组合继承优化2
借助原型可以基于已有的对象来创建对象,var B = Object.create(A)以A对象为原型,生成了B对象。B继承了A的所有属性和方法。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () {}
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype)//核心代码
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//核心代码
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person) // true true
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(s1)
同样的,Student继承了所有的Person原型对象的属性和方法。目前来说,最完美的继承方法!
方式六:ES6中class 的继承
ES6中引入了class关键字,class可以通过extends关键字实现继承,还可以通过static关键字定义类的静态方法,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。
ES5 的继承,实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(Parent.apply(this))。ES6 的继承机制完全不同,实质是先将父类实例对象的属性和方法,加到this上面(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。
需要注意的是,class关键字只是原型的语法糖,JavaScript继承仍然是基于原型实现的。
class Person {
//调用类的构造方法
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
//定义一般的方法
showName() {
console.log("调用父类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
}
let p1 = new Person('kobe', 39)
console.log(p1)
//定义一个子类
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, salary) {
super(name, age)//通过super调用父类的构造方法
this.salary = salary
}
showName() {//在子类自身定义方法
console.log("调用子类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age, this.salary);
}
}
let s1 = new Student('wade', 38, 1000000000)
console.log(s1)
s1.showName()
优点:
语法简单易懂,操作更方便
缺点:
并不是所有的浏览器都支持class关键字
总结:以上就是本篇文的全部内容,代码很简单,大家可以动手试试。希望能对大家的学习有所帮助,更多相关教程请访问JavaScript视频教程,jQuery视频教程,bootstrap教程!
The above is the detailed content of How does JavaScript implement inheritance? Six common inheritance methods in js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills






