Home >Java >javaTutorial >What are Java serialization and deserialization? Implementation methods of Java serialization and deserialization
What are Java serialization and deserialization? Implementation methods of Java serialization and deserialization
- 不言forward
- 2018-10-13 14:55:573540browse
This article brings you what is Java serialization and deserialization? The implementation methods of Java serialization and deserialization have certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Serialization and deserialization are a relatively basic knowledge point in Java, but I believe that many people can only understand a few sentences, or even don’t understand it. If you dig deeper and ask how Java implements it, Serialization and deserialization may be overwhelming! I don’t know how to explain, what is serialization, what is deserialization, what scenarios will it be used in, etc. The interviewer said: Do you know how the underlying serialization and deserialization are implemented? Let's discuss some things about serialization and deserialization.
First of all, we need to clarify the conceptual things, what is serialization and deserialization:
Java is the process of converting Java objects into byte sequences, and Java deserialization is Refers to the process of restoring a sequence of bytes into a Java object.
Serialization: The main function of object serialization is to ensure the integrity and deliverability of objects when transferring and saving objects. Serialization is to convert an object into an ordered byte stream for transmission on the network or saving in a local file. The serialized byte stream saves the status of the Java object and related description information. The core function of the serialization mechanism is the preservation and reconstruction of object state.
Deserialization: After the client obtains the serialized object byte stream from the file or network, it reconstructs the object through deserialization based on the object status and description information saved in the byte stream.
Essentially, serialization is to write the entity object state into an ordered byte stream in a certain format, and deserialization is to reconstruct the object from the ordered byte stream and restore the object state. It's similar to the concept of file compression and decompression.
Why serialization and deserialization are necessary:
We know that when processes communicate remotely, they can send various types of data to each other, including text, pictures, audio, video, etc. , and these data will be transmitted on the network in the form of binary sequences.
So, when two Java processes communicate, can object transfer between processes be achieved? The answer is yes, so how to do it? This requires Java serialization and deserialization
In other words: the sender needs to convert this Java object into a byte sequence and then transmit it on the network; on the other hand, the receiver needs to Recover Java objects from a sequence of sections.
After figuring out why Java serialization and deserialization are needed, we will naturally think about the benefits of Java serialization.
First, the persistence of data is achieved. Data can be permanently saved to the hard disk through serialization (usually stored in a file).
The second is to use serialization to achieve remote communication, that is, to transmit the byte sequence of the object on the network.
In general, it can be summarized as the following points:
(1) Permanently save the object and save the byte sequence of the object to a local file or database;
(2) Objects are transmitted and received in the network in the form of byte streams through serialization;
(3) Objects are transferred between processes through serialization;
The serialization algorithm generally does the following things in steps :
(1) Output the class metadata related to the object instance.
(2) Recursively output the superclass description of the class until there are no more superclasses.
(3) After the class metadata is completed, start outputting the actual data values of the object instance from the top-level superclass.
(4) Recursively output instance data from top to bottom
So how to implement serialization and deserialization in Java?
1: Serialization and deserialization API in JDK class library
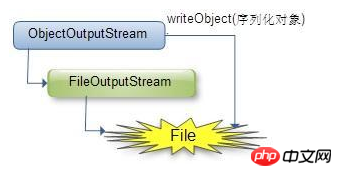
(1) java.io.ObjectOutputStream: Represents the object output stream;
its writeObject(Object obj) method can serialize the obj object specified by the parameter and write the obtained byte sequence to a target output stream;
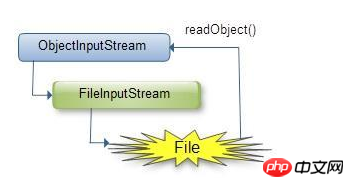
(2) java.io.ObjectInputStream: represents the object input stream;
Its readObject() method reads byte sequences from the source input stream, deserializes them into an object, and returns it;
2: Implement serialization requirements
Only objects of classes that implement the Serializable or Externalizable interface can be serialized, otherwise an exception will be thrown!
Three: Methods to implement Java object serialization and deserialization
Assume a User class, and its objects need to be serialized. There are three methods as follows:
(1) If the User class only implements the Serializable interface, it can be serialized and deserialized in the following ways
ObjectOutputStream uses the default serialization method to serialize the non-transient instance variables of the User object. .
ObjcetInputStream uses the default deserialization method to deserialize non-transient instance variables of the User object.
(2) If the User class only implements the Serializable interface and also defines readObject(ObjectInputStream in) and writeObject(ObjectOutputSteam out), the following methods are used for serialization and deserialization.
ObjectOutputStream调用User对象的writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out)的方法进行序列化。
ObjectInputStream会调用User对象的readObject(ObjectInputStream in)的方法进行反序列化。
(3)若User类实现了Externalnalizable接口,且User类必须实现readExternal(ObjectInput in)和writeExternal(ObjectOutput out)方法,则按照以下方式进行序列化与反序列化。
ObjectOutputStream调用User对象的writeExternal(ObjectOutput out))的方法进行序列化。
ObjectInputStream会调用User对象的readExternal(ObjectInput in)的方法进行反序列化。
四 :JDK类库中序列化的步骤
1 . 创建一个对象输出流,可以包装一个其它类型的目标输出流,如文件输出流:
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\os.out"));2 . 通过对象输出流的writeObject()方法写对象:
os.writeObject(new User("zhangsan", "123456", "male"));五 : JDK类库中反序列化的步骤
1 . 创建一个对象输入流,它可以包装一个其它类型输入流,如文件输入流:
ObjectInputStream ois= new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.out"));2 .通过对象输出流的readObject()方法读取对象:
User user = (User) ois.readObject();
为保证正确读取数据,完成反序列化,必须保证向对象输出流写对象的顺序与从对象输入流中读对象的顺序一致。
举个栗子:
public class SerialDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
FileOutputStream outputos = new FileOutputStream("object.out");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(outputos );
User user1 = new User("zhangsan", "123456", "male");
oos.writeObject(user1);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
//反序列化
FileInputStream inputos= new FileInputStream("object.out");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(inputos);
User user2 = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(user2.getUserName()+ " " +
user2.getPassword() + " " + user2.getSex());
//反序列化的输出结果为:zhangsan123456 male
}
}
public class User implements Serializable {
private String userName;
private String password;
private String sex;
//全参构造方法、get和set方法
}
相关的注意事项:
1、序列化时,只对对象的状态进行保存,而不管对象的方法;
2、当一个父类实现序列化,子类自动实现序列化,不需要显式实现Serializable接口;
3、当一个对象的实例变量引用其他对象,序列化该对象时也把引用对象进行序列化;
4、并非所有的对象都可以序列化,至于为什么不可以,有很多原因了,比如:
安全方面的原因,比如一个对象拥有private,public等field,对于一个要传输的对象,比如写到文件,或者进行RMI传输等等,在序列化进行传输的过程中,这个对象的private等域是不受保护的;
资源分配方面的原因,比如socket,thread类,如果可以序列化,进行传输或者保存,也无法对他们进行重新的资源分配,而且,也是没有必要这样实现;
5、声明为static和transient类型的成员数据不能被序列化。因为static代表类的状态,transient代表对象的临时数据。
6、序列化运行时使用一个称为 serialVersionUID 的版本号与每个可序列化类相关联,该序列号在反序列化过程中用于验证序列化对象的发送者和接收者是否为该对象加载了与序列化兼容的类。为它赋予明确的值。显式地定义serialVersionUID有两种用途:
在某些场合,希望类的不同版本对序列化兼容,因此需要确保类的不同版本具有相同的serialVersionUID;
在某些场合,不希望类的不同版本对序列化兼容,因此需要确保类的不同版本具有不同的serialVersionUID。
7、Java有很多基础类已经实现了serializable接口,比如String,Vector等。但是也有一些没有实现serializable接口的;
8、如果一个对象的成员变量是一个对象,那么这个对象的数据成员也会被保存!这是能用序列化解决深拷贝的重要原因;
The above is the detailed content of What are Java serialization and deserialization? Implementation methods of Java serialization and deserialization. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

