Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >What are the position attributes of css? Introduction to position attribute and usage in css
What are the position attributes of css? Introduction to position attribute and usage in css
- 不言Original
- 2018-08-16 10:43:555020browse
This article brings you what are the position attributes of css? The introduction to the position attribute and usage in CSS has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Introduction to position attribute
(1) The position attribute in css has been around since CSS2. This attribute specifies the positioning type of the element. All major browsers support the position attribute.
(2) There are four optional values for the position attribute in CSS: static, relative, absolute, and fixed. They are introduced separately below. (Actually, there is an inheritance, but this is unique to IE and will not be discussed here)
position: static (default value)< ;/h3>
1, basic introduction
(1) static is the default value. Indicates that there is no positioning, or it does not have the positioning attribute.
(2) If the element's position attribute value is static (or the position attribute is not set), the element appears in the normal flow (ignoring top, bottom, left, right or z-index declarations).
2, usage example
css:
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #C9FFFF;
}
</style>
html:
<div></div> <input>
We do not set the postion attribute value of the element, then the default display effect is as follows :
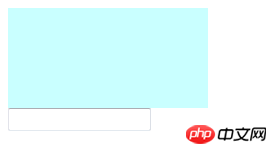
<div class="position-static"></div> <input type="text"/> <h3 id="position: relative(相对定位)"> position: relative(相对定位)</h3>
1, basic introduction
(1) relative generates relatively positioned elements and positions them relative to their normal position.
(2) The process of relative positioning is as follows:
First generate an element in the default way (static) (and the element floats like a layer).
Then move relative to the previous position. The direction and amplitude of the movement are determined by the left, right, top, and bottom attributes. The position before the offset remains unchanged.
2, sample code
The following code sets the text input box position to relative (relative positioning), and moves it 15 pixels to the right and 15 pixels upward relative to the default position.
css:
div {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #C9FFFF;
}
input {
position: relative;
left: 15px;
top: -15px;
}
html:
<div></div> <input>
The operation effect is as follows:
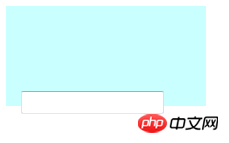
(1)absolute generates absolutely positioned elements.
(2) An absolutely positioned element uses the left, right, top, and bottom attributes to perform absolute positioning relative to its closest parent element with a positioning attribute.
(3) If there is no such parent element, it is relative to the body element, that is, relative to the browser window.
At the same time, use the top attribute to move the title element upward so that it covers the upper border of the parent container.
Finally, the horizontal centering of this absolutely positioned element is achieved through the combination of left and margin-left.
#box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
-webkit-box-flex:1;
border: 1px solid #28AE65;
border-radius:6px;
padding: 20px;
position: relative;
font-size: 12px;
}
#title {
background: #FFFFFF;
color: #28AE65;
font-size: 15px;
text-align: center;
width: 70px;
height: 20px;
line-height: 20px;
position: absolute;
top: -10px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -35px;
}html:
<div> <div>标题</div> 欢迎来到php中文网 </div>The operation effect is as follows:
 ##1, basic introduction
##1, basic introduction
(2) Fixed-positioned elements will not change with the scroll bar of the browser window, nor will they be affected by the flow of the document, but will always be located somewhere in the view within the browser window.
2, sample code
css:
input {
position: fixed;
bottom: 10px;
}
html:
<ol> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> <li>数据</li> </ol> <input>
The running effect is as follows:
##(2) You can see that no matter How to scroll the scroll bar, the input box is always at the bottom of the window. 
css background-position attribute_html/css_WEB-ITnose
Understand css position attribute_html/css_WEB-ITnose
The above is the detailed content of What are the position attributes of css? Introduction to position attribute and usage in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

