Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of commonly used classic algorithm examples in javascript_javascript skills
Detailed explanation of commonly used classic algorithm examples in javascript_javascript skills
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 15:29:581400browse
The examples in this article describe common algorithms in JavaScript. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
Entry-level algorithm-Linear search-time complexity O(n)--equivalent to HelloWorld
in the algorithm world
//线性搜索(入门HelloWorld)
//A为数组,x为要搜索的值
function linearSearch(A, x) {
for (var i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
if (A[i] == x) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
Binary search (also called half search) - suitable for sorted linear structures - time complexity O(logN)
//二分搜索
//A为已按"升序排列"的数组,x为要查询的元素
//返回目标元素的下标
function binarySearch(A, x) {
var low = 0, high = A.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
var mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2); //下取整
if (x == A[mid]) {
return mid;
}
if (x < A[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
}
else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
Bubble sort -- time complexity O(n^2)
//冒泡排序
function bubbleSort(A) {
for (var i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
var sorted = true;
//注意:内循环是倒着来的
for (var j = A.length - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (A[j] < A[j - 1]) {
swap(A, j, j - 1);
sorted = false;
}
}
if (sorted) {
return;
}
}
}
Selection sort -- Time complexity O(n^2)
//选择排序
//思路:找到最小值的下标记下来,再交换
function selectionSort(A) {
for (var i = 0; i < A.length - 1; i++) {
var k = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j < A.length; j++) {
if (A[j] < A[k]) {
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i) {
var t = A[k];
A[k] = A[i];
A[i] = t;
println(A);
}
}
return A;
}
Insertion sort -- time complexity O(n^2)
//插入排序
//假定当前元素之前的元素已经排好序,先把自己的位置空出来,
//然后前面比自己大的元素依次向后移,直到空出一个"坑",
//然后把目标元素插入"坑"中
function insertSort(A) {
for (var i = 1; i < A.length; i++) {
var x = A[i];
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && A[j] > x; j--) {
A[j + 1] = A[j];
}
if (A[j + 1] != x) {
A[j + 1] = x;
println(A);
}
}
return A;
}
String reversal -- time complexity O(logN)
//字符串反转(比如:ABC -> CBA)
function inverse(s) {
var arr = s.split('');
var i = 0, j = arr.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
var t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
i++;
j--;
}
return arr.join('');
}
A conclusion about stability ranking:
A simple sorting algorithm based on comparison, that is, a sorting algorithm with a time complexity of O(N^2), which can usually be considered to be a stable sorting
Other advanced sorting algorithms, such as merge sort, heap sort, bucket sort (usually the time complexity of such algorithms can be optimized to n*LogN), can usually be considered to be unstable sorting
Singly linked listimplementation
<script type="text/javascript">
function print(msg) {
document.write(msg);
}
function println(msg) {
print(msg + "<br/>");
}
//节点类
var Node = function (v) {
this.data = v; //节点值
this.next = null; //后继节点
}
//单链表
var SingleLink = function () {
this.head = new Node(null); //约定头节点仅占位,不存值
//插入节点
this.insert = function (v) {
var p = this.head;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new Node(v);
}
//删除指定位置的节点
this.removeAt = function (n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return;
}
var preNode = this.getNodeByIndex(n - 1);
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
}
//取第N个位置的节点(约定头节点为第0个位置)
//N大于链表元素个数时,返回最后一个元素
this.getNodeByIndex = function (n) {
var p = this.head;
var i = 0;
while (p.next != null && i < n) {
p = p.next;
i++;
}
return p;
}
//查询值为V的节点,
//如果链表中有多个相同值的节点,
//返回第一个找到的
this.getNodeByValue = function (v) {
var p = this.head;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
if (p.data == v) {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
//打印输出所有节点
this.print = function () {
var p = this.head;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
print(p.data + " ");
}
println("");
}
}
//测试单链表L中是否有重复元素
function hasSameValueNode(singleLink) {
var i = singleLink.head;
while (i.next != null) {
i = i.next;
var j = i;
while (j.next != null) {
j = j.next;
if (i.data == j.data) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//单链表元素反转
function reverseSingleLink(singleLink) {
var arr = new Array();
var p = singleLink.head;
//先跑一遍,把所有节点放入数组
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
arr.push(p.data);
}
var newLink = new SingleLink();
//再从后向前遍历数组,加入新链表
for (var i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newLink.insert(arr[i]);
}
return newLink;
}
var linkTest = new SingleLink();
linkTest.insert('A');
linkTest.insert('B');
linkTest.insert('C');
linkTest.insert('D');
linkTest.print();//A B C D
var newLink = reverseSingleLink(linkTest);
newLink.print();//D C B A
</script>
About the selection of adjacency matrix and adjacency list :
Adjacency matrix and adjacency list are the basic storage methods of graphs,
In the case of sparse graph (that is, when the edges are far smaller than the vertices), it is more suitable to use adjacency list storage (relative to the matrix N*N, the adjacency list only stores edges and vertices with values, and does not store null values. More efficient storage)
In the case of dense graph (that is, in the case of remote vertices), it is more suitable to store it with an adjacency matrix (when there is a lot of data, you need to traverse it. If you use a linked list to store it, you have to jump around frequently. , lower efficiency)
Heap:
Almost complete binary tree: A binary tree except that one or several leaves at the rightmost position may be missing. In terms of physical storage, arrays can be used to store it. If the vertex of A[j] has left and right child nodes, then the left node is A[2j], the right node is A[2j 1], and the parent vertex of A[j] Stored in A[j/2]
Heap: itself is an almost complete binary tree, and the value of the parent node is not less than the value of the child node . Application scenarios: priority queue, finding the maximum or sub-maximum value; and inserting a new element into the priority queue.
Note: In all the heaps discussed below, it is agreed that the element at index 0 only takes place, and the valid elements start from subscript 1
According to the definition of heap, you can use the following code to test whether an array is a heap:
//测试数组H是否为堆
//(约定有效元素从下标1开始)
//时间复杂度O(n)
function isHeap(H) {
if (H.length <= 1) { return false; }
var half = Math.floor(H.length / 2); //根据堆的性质,循环上限只取一半就够了
for (var i = 1; i <= half; i++) {
//如果父节点,比任何一个子节点 小,即违反堆定义
if (H[i] < H[2 * i] || H[i] < H[2 * i + 1]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
Node adjustment siftUp
In some cases, if the value of an element in the heap changes (for example, after 10,8,9,7 becomes 10,8,9,20, 20 needs to be adjusted upward), it no longer meets the definition of the heap. , when you need to adjust upward, you can use the following code to achieve
//堆中的节点上移
//(约定有效元素从下标1开始)
function siftUp(H, i) {
if (i <= 1) {
return;
}
for (var j = i; j > 1; j = Math.floor(j / 2)) {
var k = Math.floor(j / 2);
//发现 子节点 比 父节点大,则与父节点交换位置
if (H[j] > H[k]) {
var t = H[j];
H[j] = H[k];
H[k] = t;
}
else {
//说明已经符合堆定义,调整结束,退出
return;
}
}
}
The node is adjusted downward by siftDown (since there is an upward adjustment, there is naturally a downward adjustment)
//堆中的节点下移
//(约定有效元素从下标1开始)
//时间复杂度O(logN)
function siftDown(H, i) {
if (2 * i > H.length) { //叶子节点,就不用再向下移了
return;
}
for (var j = 2 * i; j < H.length; j = 2 * j) {
//将j定位到 二个子节点中较大的那个上(很巧妙的做法)
if (H[j + 1] > H[j]) {
j++;
}
var k = Math.floor(j / 2);
if (H[k] < H[j]) {
var t = H[k];
H[k] = H[j];
H[j] = t;
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
Add new element to the heap
//向堆H中添加元素x
//时间复杂度O(logN)
function insert(H, x) {
//思路:先在数组最后加入目标元素x
H.push(x);
//然后向上推
siftUp(H, H.length - 1);
}
Remove elements from the heap
//删除堆H中指定位置i的元素
//时间复杂度O(logN)
function remove(H, i) {
//思路:先把位置i的元素与最后位置的元素n交换
//然后数据长度减1(这样就把i位置的元素给干掉了,但是整个堆就被破坏了)
//需要做一个决定:最后一个元素n需要向上调整,还是向下调整
//依据:比如比原来该位置的元素大,则向上调整,反之向下调整
var x = H[i]; //先把原来i位置的元素保护起来
//把最后一个元素放到i位置
//同时删除最后一个元素(js语言的优越性体现!)
H[i] = H.pop();
var n = H.length - 1;
if (i == n + 1) {
//如果去掉的正好是最后二个元素之一,
//无需再调整
return ;
}
if (H[i] > x) {
siftUp(H, i);
}
else {
siftDown(H, i);
}
}
//从堆中删除最大项
//返回最大值
//时间复杂度O(logN)
function deleteMax(H) {
var x = H[1];
remove(H, 1);
return x;
}
Heap sort :
This is a very clever sorting algorithm. The essence lies in making full use of the characteristics of the data structure "heap" (the first element must be the largest), and each element can be moved up or down with time retest. It is relatively low, only O(logN). In terms of space, there is no need to resort to additional storage space, just exchange elements within the array itself.
Things:
1. First swap the first element (i.e. the largest element) with the last element - the purpose is to sink the maximum value to the bottom and ignore it in the next round
2. After 1, the remaining elements are usually no longer a heap. At this time, just use siftDown to adjust the new first element downward. After the adjustment, the new maximum element will naturally rise to the position of the first element
3. Repeat 1 and 2, and the large elements will sink to the bottom one by one, and finally the entire array will be in order.
Time complexity analysis: Creating a heap requires O(n) cost, each siftDown cost is O(logN), and up to n-1 elements can be adjusted, so the total cost is O(N) (N-1)O(logN) , the final time complexity is O(NLogN)
//堆中的节点下移
//(约定有效元素从下标1开始)
//i为要调整的元素索引
//n为待处理的有效元素下标范围上限值
//时间复杂度O(logN)
function siftDown(H, i, n) {
if (n >= H.length) {
n = H.length;
}
if (2 * i > n) { //叶子节点,就不用再向下移了
return;
}
for (var j = 2 * i; j < n; j = 2 * j) {
//将j定位到 二个子节点中较大的那个上(很巧妙的做法)
if (H[j + 1] > H[j]) {
j++;
}
var k = Math.floor(j / 2);
if (H[k] < H[j]) {
var t = H[k];
H[k] = H[j];
H[j] = t;
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
//对数组的前n个元素进行创建堆的操作
function makeHeap(A, n) {
if (n >= A.length) {
n = A.length;
}
for (var i = Math.floor(n / 2); i >= 1; i--) {
siftDown(A, i, n);
}
}
//堆排序(非降序排列)
//时间复杂度O(nlogN)
function heapSort(H) {
//先建堆
makeHeap(H, H.length);
for (var j = H.length - 1; j >= 2; j--) {
//首元素必然是最大的
//将最大元素与最后一个元素互换,
//即将最大元素沉底,下一轮不再考虑
var x = H[1];
H[1] = H[j];
H[j] = x;
//互换后,剩下的元素不再满足堆定义,
//把新的首元素下调(以便继续维持堆的"形状")
//调整完后,剩下元素中的最大值必须又浮到了第一位
//进入下一轮循环
siftDown(H, 1, j - 1);
}
return H;
}
Regarding building a heap, if you understand the principle, you can also reverse the idea and do it in reverse
function makeHeap2(A, n) {
if (n >= A.length) {
n = A.length;
}
for (var i = Math.floor(n / 2); i <= n; i++) {
siftUp(A, i);
}
}
Search and merge disjoint sets
//定义节点Node类
var Node = function (v, p) {
this.value = v; //节点的值
this.parent = p; //节点的父节点
this.rank = 0; //节点的秩(默认为0)
}
//查找包含节点x的树根节点
var find = function (x) {
var y = x;
while (y.parent != null) {
y = y.parent;
}
var root = y;
y = x;
//沿x到根进行“路径压缩”
while (y.parent != null) {
//先把父节点保存起来,否则下一行调整后,就弄丢了
var w = y.parent;
//将目标节点挂到根下
y.parent = root;
//再将工作指针,还原到 目标节点原来的父节点上,
//继续向上逐层压缩
y = w
}
return root;
}
//合并节点x,y对应的两个树
//时间复杂度O(m) - m为待合并的子集合数量
var union = function (x, y) {
//先找到x所属集合的根
var u = find(x);
//再找到y所属集合的根
var v = find(y);
//把rank小的集合挂到rank大的集合上
if (u.rank <= v.rank) {
u.parent = v;
if (u.rank == v.rank) {
//二个集合的rank不分伯仲时
//给"胜"出方一点奖励,rank+1
v.rank += 1;
}
}
else {
v.parent = u;
}
}
Induction method:
Let’s first look at the two recursive implementations of sorting
//选择排序的递归实现
//调用示例: selectionSort([3,2,1],0)
function selectionSortRec(A, i) {
var n = A.length - 1;
if (i < n) {
var k = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (A[j] < A[k]) {
k = j
}
}
if (k != i) {
var t = A[k];
A[k] = A[i];
A[i] = t;
}
selectionSortRec(A, i + 1);
}
}
//插入排序递归实现
//调用示例:insertSortRec([4,3,2,1],3);
function insertSortRec(A, i) {
if (i > 0) {
var x = A[i];
insertSortRec(A, i - 1);
var j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && A[j] > x) {
A[j + 1] = A[j];
j--;
}
A[j + 1] = x;
}
}
Recursive programs are usually easy to understand and the code is easy to implement. Let’s look at two small examples:
Find the maximum value from the array
//在数组中找最大值(递归实现)
function findMax(A, i) {
if (i == 0) {
return A[0];
}
var y = findMax(A, i - 1);
var x = A[i - 1];
return y > x ? y : x;
}
var A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var test = findMax(A,A.length);
alert(test);//返回9
There is an array that has been sorted in ascending order. Check whether there are two numbers in the array, and their sum is exactly x?
//5.33 递归实现
//A为[1..n]已经排好序的数组
//x为要测试的和
//如果存在二个数的和为x,则返回true,否则返回false
function sumX(A, i, j, x) {
if (i >= j) {
return false;
}
if (A[i] + A[j] == x) {
return true;
}
else if (A[i] + A[j] < x) {
//i后移
return sumX(A, i + 1, j, x);
}
else {
//j前移
return sumX(A, i, j - 1, x);
}
}
var A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
var test1 = sumX(A,0,A.length-1,9);
alert(test1); //返回true
递归程序虽然思路清晰,但通常效率不高,一般来讲,递归实现,都可以改写成非递归实现,上面的代码也可以写成:
//5.33 非递归实现
function sumX2(A, x) {
var i = 0, j = A.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
if (A[i] + A[j] == x) {
return true;
}
else if (A[i] + A[j] < x) {
//i后移
i++;
}
else {
//j前移
j--;
}
}
return false;
}
var A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
var test2 = sumX2(A,9);
alert(test2);//返回true
递归并不总代表低效率,有些场景中,递归的效率反而更高,比如计算x的m次幂,常规算法,需要m次乘法运算,下面的算法,却将时间复杂度降到了O(logn)
//计算x的m次幂(递归实现)
//时间复杂度O(logn)
function expRec(x, m) {
if (m == 0) {
return 1;
}
var y = expRec(x, Math.floor(m / 2));
y = y * y;
if (m % 2 != 0) {
y = x * y
}
return y;
}
当然,这其中并不光是递归的功劳,其效率的改进 主要依赖于一个数学常识: x^m = [x^(m/2)]^2,关于这个问题,还有一个思路很独特的非递归解法,巧妙的利用了二进制的特点
//将10进制数转化成2进制
function toBin(dec) {
var bits = [];
var dividend = dec;
var remainder = 0;
while (dividend >= 2) {
remainder = dividend % 2;
bits.push(remainder);
dividend = (dividend - remainder) / 2;
}
bits.push(dividend);
bits.reverse();
return bits.join("");
}
//计算x的m次幂(非递归实现)
//很独特的一种解法
function exp(x, m) {
var y = 1;
var bin = toBin(m).split('');
//先将m转化成2进制形式
for (var j = 0; j < bin.length; j++) {
y = y * 2;
//如果2进制的第j位是1,则再*x
if (bin[j] == "1") {
y = x * y
}
}
return y;
}
//println(expRec(2, 5));
//println(exp(2, 5));
再来看看经典的多项式求值问题:
给定一串实数An,An-1,...,A1,A0 和一个实数X,计算多项式Pn(x)的值
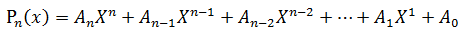
著名的Horner公式:
已经如何计算:
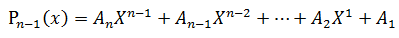
显然有:
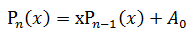
这样只需要 N次乘法+N次加法
//多项式求值
//N次乘法+N次加法搞定,伟大的改进!
function horner(A, x) {
var n = A.length - 1
var p = A[n];
for (var j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p = x * p + A[n - j - 1];
}
return p;
}
//计算: y(2) = 3x^3 + 2x^2 + x -1;
var A = [-1, 1, 2, 3];
var y = horner(A, 2);
alert(y);//33
多数问题:
一个元素个数为n的数组,希望快速找出其中大于出现次数>n/2的元素(该元素也称为多数元素)。通常可用于选票系统,快速判定某个候选人的票数是否过半。最优算法如下:
//找出数组A中“可能存在”的多数元素
function candidate(A, m) {
var count = 1, c = A[m], n = A.length - 1;
while (m < n && count > 0) {
m++;
if (A[m] == c) {
count++;
}
else {
count--;
}
}
if (m == n) {
return c;
}
else {
return candidate(A, m + 1);
}
}
//寻找多数元素
//时间复杂度O(n)
function majority(A) {
var c = candidate(A, 0);
var count = 0;
//找出的c,可能是多数元素,也可能不是,
//必须再数一遍,以确保结果正确
for (var i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
if (A[i] == c) {
count++;
}
}
//如果过半,则确定为多数元素
if (count > Math.floor(A.length / 2)) {
return c;
}
return null;
}
var m = majority([3, 2, 3, 3, 4, 3]);
alert(m);
以上算法基于这样一个结论:在原序列中去除两个不同的元素后,那么在原序列中的多数元素在新序列中还是多数元素
证明如下:
如果原序列的元素个数为n,多数元素出现的次数为x,则 x/n > 1/2
去掉二个不同的元素后,
a)如果去掉的元素中不包括多数元素,则新序列中 ,原先的多数元素个数/新序列元素总数 = x/(n-2) ,因为x/n > 1/2 ,所以 x/(n-2) 也必然>1/2
b)如果去掉的元素中包含多数元素,则新序列中 ,原先的多数元素个数/新序列元素总数 = (x-1)/(n-2) ,因为x/n > 1/2 =》 x>n/2 代入 (x-1)/(n-2) 中,
有 (x-1)/(n-2) > (n/2 -1)/(n-2) = 2(n-2)/(n-2) = 1/2
下一个问题:全排列
function swap(A, i, j) {
var t = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = t;
}
function println(msg) {
document.write(msg + "<br/>");
}
//全排列算法
function perm(P, m) {
var n = P.length - 1;
if (m == n) {
//完成一个新排列时,输出
println(P);
return;
}
for (var j = m; j <= n; j++) {
//将起始元素与后面的每个元素交换
swap(P, j, m);
//在前m个元素已经排好的基础上
//再加一个元素进行新排列
perm(P, m + 1);
//把j与m换回来,恢复递归调用前的“现场",
//否则因为递归调用前,swap已经将原顺序破坏了,
//导致后面生成排序时,可能生成重复
swap(P, j, m);
}
}
perm([1, 2, 3], 0);
//1,2,3
//1,3,2
//2,1,3
//2,3,1
//3,2,1
//3,1,2
分治法:
要点:将问题划分成二个子问题时,尽量让子问题的规模大致相等。这样才能最大程度的体现一分为二,将问题规模以对数折半缩小的优势。
//打印输出(调试用)
function println(msg) {
document.write(msg + "<br/>");
}
//数组中i,j位置的元素交换(辅助函数)
function swap(A, i, j) {
var t = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = t;
}
//寻找数组A中的最大、最小值(分治法实现)
function findMinMaxDiv(A, low, high) {
//最小规模子问题的解
if (high - low == 1) {
if (A[low] < A[high]) {
return [A[low], A[high]];
}
else {
return [A[high], A[low]];
}
}
var mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
//在前一半元素中寻找子问题的解
var r1 = findMinMaxDiv(A, low, mid);
//在后一半元素中寻找子问题的解
var r2 = findMinMaxDiv(A, mid + 1, high);
//把二部分的解合并
var x = r1[0] > r2[0] ? r2[0] : r1[0];
var y = r1[1] > r2[1] ? r1[1] : r2[1];
return [x, y];
}
var r = findMinMaxDiv([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 0, 7);
println(r); //1,8
//二分搜索(分治法实现)
//输入:A为已按非降序排列的数组
//x 为要搜索的值
//low,high搜索的起、止索引范围
//返回:如果找到,返回下标,否则返回-1
function binarySearchDiv(A, x, low, high) {
if (low > high) {
return -1;
}
var mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (x == A[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x < A[mid]) {
return binarySearchDiv(A, x, low, mid - 1);
}
else {
return binarySearchDiv(A, x, mid + 1, high);
}
}
var f = binarySearchDiv([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], 4, 0, 6);
println(f); //3
//将数组A,以low位置的元素为界,划分为前后二半
//n为待处理的索引范围上限
function split(A, low, n) {
if (n >= A.length - 1) {
n = A.length - 1;
}
var i = low;
var x = A[low];
//二个指针一前一后“跟随”,
//最前面的指针发现有元素比分界元素小时,换到前半部
//后面的指针再紧跟上,“夫唱妇随”一路到头
for (var j = low + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (A[j] <= x) {
i++;
if (i != j) {
swap(A, i, j);
}
}
}
//经过上面的折腾后,除low元素外,其它的元素均以就位
//最后需要把low与最后一个比low位置小的元素交换,
//以便把low放在分水岭位置上
swap(A, low, i);
return [A, i];
}
var A = [5, 1, 2, 6, 3];
var b = split(A, 0, A.length - 1);
println(b[0]); //3,1,2,5,6
//快速排序
function quickSort(A, low, high) {
var w = high;
if (low < high) {
var t = split(A, low, w); //分治思路,先分成二半
w = t[1];
//在前一半求解
quickSort(A, low, w - 1);
//在后一半求解
quickSort(A, w + 1, high);
}
}
var A = [5, 6, 4, 7, 3];
quickSort(A, 0, A.length - 1);
println(A); //3,4,5,6,7
split算法的思想应用:
设A[1..n]是一个整数集,给出一算法重排数组A中元素,使得所有的负整数放到所有非负整数的左边,你的算法的运行时间应当为Θ(n)
function sort1(A) {
var i = 0, j = A.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
if (A[i] >= 0 && A[j] >= 0) {
j--;
}
else if (A[i] < 0 && A[j] < 0) {
i++;
}
else if (A[i] > 0 && A[j] < 0) {
swap(A, i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
else {
i++;
j--;
}
}
}
function sort2(A) {
if (A.length <= 1) { return; }
var i = 0;
for (var j = i + 1; j < A.length; j++) {
if (A[j] < 0 && A[i] >= 0) {
swap(A, i, j);
i++;
}
}
}
var a = [1, -2, 3, -4, 5, -6, 0];
sort1(a);
println(a);//-6,-2,-4,3,5,1,0
var b = [1, -2, 3, -4, 5, -6, 0];
sort2(b);
println(b);//-2,-4,-6,1,5,3,0
希望本文所述对大家JavaScript程序设计有所帮助。
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

