Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Analysis of patch source code of vue virtual dom
Analysis of patch source code of vue virtual dom
- 不言Original
- 2018-06-29 15:21:261839browse
This article mainly introduces the patch source code analysis of vue virtual dom. The content is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give you a reference.
This article introduces the patch source code analysis of vue virtual dom and shares it with everyone. The details are as follows:
Source code directory: src/core/vdom/patch.js
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
const canMove = !removeOnly
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) { // 开始索引大于结束索引,进不了
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode已经被移走了。
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // 索引加1。是去对比下一个节点。比如之前start=a[0],那现在start=a[1],改变start的值后再去对比start这个vnode
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))// 把节点b移到树的最右边
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { old.end.d=new.start.d
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)// Vnode moved left,把d移到c的左边。=old.start->old.end
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) {
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm) // 创建新节点,后面执行了nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref)
} else {
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !vnodeToMove) {
warn(
'It seems there are duplicate keys that is causing an update error. ' +
'Make sure each v-for item has a unique key.'
)
}
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// same key but different element. treat as new element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm)
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) // 删除旧的c,removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && (
(
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
) || (
isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) &&
a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory &&
isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error)
)
)
)
}
/**
* 比较新旧vnode节点,根据不同的状态对dom做合理的更新操作(添加,移动,删除)整个过程还会依次调用prepatch,update,postpatch等钩子函数,在编译阶段生成的一些静态子树,在这个过程
* @param oldVnode 中由于不会改变而直接跳过比对,动态子树在比较过程中比较核心的部分就是当新旧vnode同时存在children,通过updateChildren方法对子节点做更新,
* @param vnode
* @param insertedVnodeQueue
* @param removeOnly
*/
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
// 用于静态树的重用元素。
// 注意,如果vnode是克隆的,我们只做这个。
// 如果新节点不是克隆的,则表示呈现函数。
// 由热重加载api重新设置,我们需要进行适当的重新渲染。
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode)
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}
function insertBefore (parentNode, newNode, referenceNode) {
parentNode.insertBefore(newNode, referenceNode);
}
/**
*
* @param vnode根据vnode的数据结构创建真实的dom节点,如果vnode有children则会遍历这些子节点,递归调用createElm方法,
* @param insertedVnodeQueue记录子节点创建顺序的队列,每创建一个dom元素就会往队列中插入当前的vnode,当整个vnode对象全部转换成为真实的dom 树时,会依次调用这个队列中vnode hook的insert方法
* @param parentElm
* @param refElm
* @param nested
*/
let inPre = 0
function createElm (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm, nested) {
vnode.isRootInsert = !nested // 过渡进入检查
if (createComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)) {
return
}
const data = vnode.data
const children = vnode.children
const tag = vnode.tag
if (isDef(tag)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (data && data.pre) {
inPre++
}
if (
!inPre &&
!vnode.ns &&
!(
config.ignoredElements.length &&
config.ignoredElements.some(ignore => {
return isRegExp(ignore)
? ignore.test(tag)
: ignore === tag
})
) &&
config.isUnknownElement(tag)
) {
warn(
'Unknown custom element: <' + tag + '> - did you ' +
'register the component correctly? For recursive components, ' +
'make sure to provide the "name" option.',
vnode.context
)
}
}
vnode.elm = vnode.ns
? nodeOps.createElementNS(vnode.ns, tag)
: nodeOps.createElement(tag, vnode)
setScope(vnode)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__WEEX__) {
// in Weex, the default insertion order is parent-first.
// List items can be optimized to use children-first insertion
// with append="tree".
const appendAsTree = isDef(data) && isTrue(data.appendAsTree)
if (!appendAsTree) {
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
if (appendAsTree) {
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
} else {
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && data && data.pre) {
inPre--
}
} else if (isTrue(vnode.isComment)) {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createComment(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
} else {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createTextNode(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
}
function insert (parent, elm, ref) {
if (isDef(parent)) {
if (isDef(ref)) {
if (ref.parentNode === parent) {
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref)
}
} else {
nodeOps.appendChild(parent, elm)
}
}
}
function removeVnodes (parentElm, vnodes, startIdx, endIdx) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
const ch = vnodes[startIdx]
if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(ch.tag)) {
removeAndInvokeRemoveHook(ch)
invokeDestroyHook(ch)
} else { // Text node
removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
}
}
##updateChildren method mainly passes while Loop to compare the child nodes of the two trees to update dom, and change the old one by comparing the new one to achieve the purpose of unifying the old and new.
a, b, c, d, etc. , different codenames represent different vnode, such as:
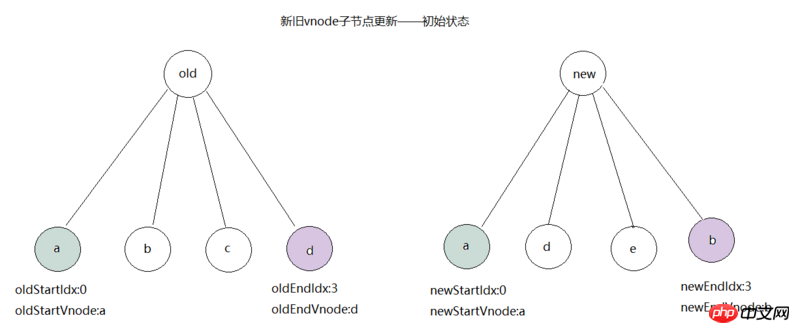
oldStartVnode=a, newStartVnode=a;If the sameVnode(oldStartVnode,newStartVnode) logic is hit, directly call the patchVnode(oldStartVnode,newStartVnode,insertedVnodeQueue) method to update the node a, then set the oldStartIdx and newStartIdx indexes to 1 respectively, as shown in the figure:
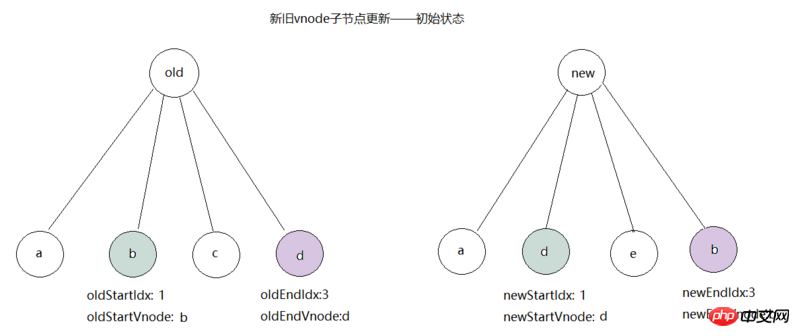
aAfter that, we start the second comparison. At this time, oldStartVnode=b,newEndVnode=b; hits the sameVnode(oldStartVnode,newEndVnode) logic, and then calls patchVnode( oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) method to update the nodeb, and then call canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm)), Move node b to the far right of the tree, and finally index oldStartIdx to 1 and newEndIdx to index -1, as shown in the figure:
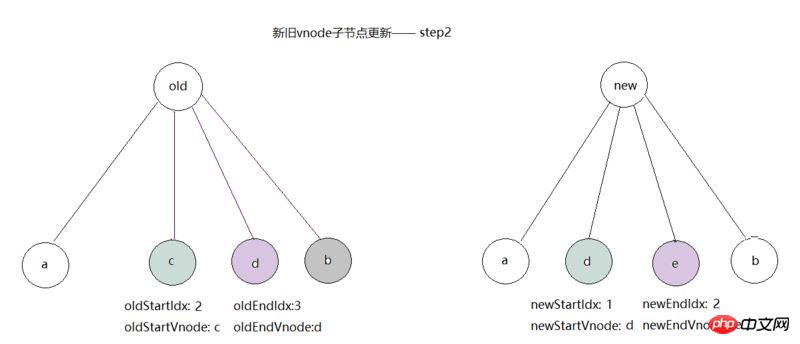
b, we start the third comparison. At this time, oldEndVnode=d, newStartVnode=d; hits sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode) Logic, call patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) method to update the node d, and then call canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode. elm), move d to the left of c. Finally, index oldEndIdx to -1 and newStartIdx to index 1, as shown in the figure:
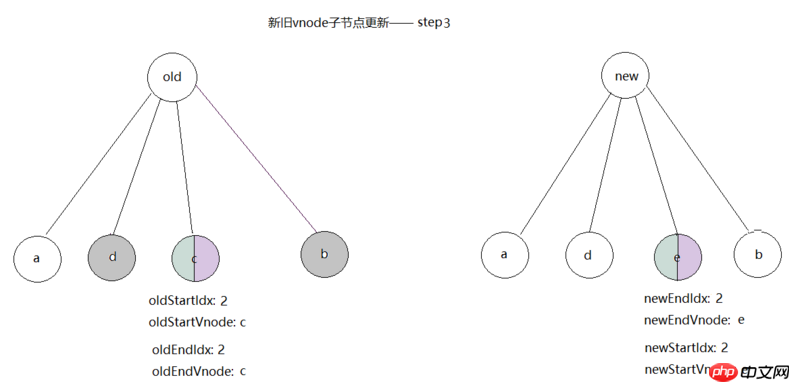 ##After updating
##After updating
, we start the fourth comparison. At this time newStartVnode=e, node e does not exist in the old tree, so it should be inserted as a new element, call createElm( newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm), and then the nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref) method is executed to insert e before c , then index newStartIdx as 1, as shown in the figure: After
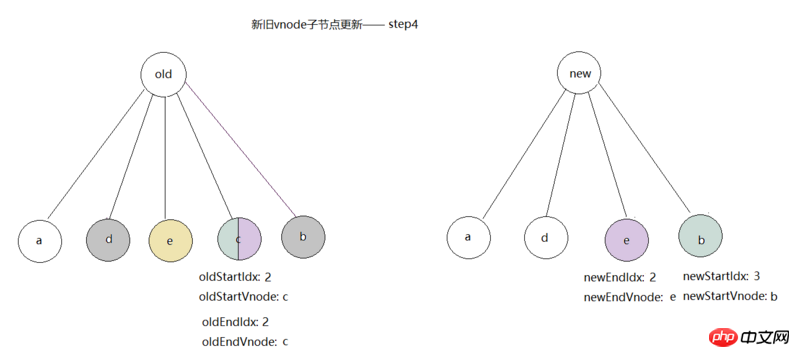 is inserted into node
is inserted into node
, we can see newStartIdx is already greater than newEndIdx, while loop has been completed. Then call removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) to delete the old c, as shown in the final figure:
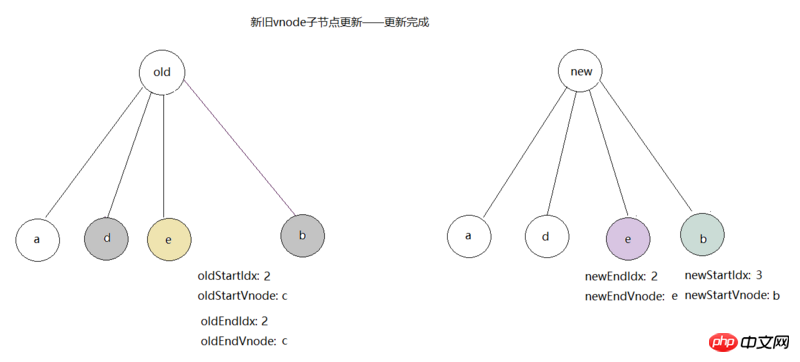
has completed the update of the child nodes of the old tree through the above steps. In fact, only relatively small dom operations are used, which improves the performance, and as the child nodes become more complex, this The improvement effect is more obvious. vnodeAfter generating dom through the patch method, mounted hook will be called. At this point, the entire vue instance is created Completed, when the watcher of this vue instance observes data changes, it will call the render method twice to generate a new vnode, Then call the patch method to compare the old and new vnode to update dom. The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone's study , please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website for more related content!
Related recommendations:
Introduction to using Vue to dynamically generate formsHow to use Vue-resource to complete interaction in VUEThe above is the detailed content of Analysis of patch source code of vue virtual dom. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

