Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Detailed explanation of the steps to use setInc in thinkphp3.2.0
Detailed explanation of the steps to use setInc in thinkphp3.2.0
- php中世界最好的语言Original
- 2018-05-19 13:59:561769browse
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the steps to use thinkphp3.2.0 setInc. What are the precautions when using thinkphp3.2.0 setInc? The following is a practical case, let’s take a look.
Let’s take a look at the official example of setInc first:
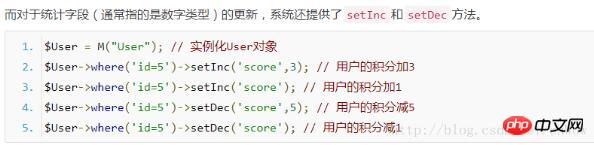
Requires a field and A self-increasing value (default is 1)
We use the following example to analyze step by step how its underlying implementation is implemented:
<?php
namespace Home\Controller;
use Think\Controller;
class TestController extends Controller {
public function test() {
$tb_test = M('test');
$tb_test->where(['id'=>1])->setInc('test_number',2); //每次添加2
dump($tb_test->getLastSql());
//string(67) "UPDATE `tb_test` SET `test_number`=test_number+2 WHERE ( `id` = 1 )"
}
}
Chapter The first step is to find the source code of the setInc method:
Here I used the phpstrom global search method and found that setInc is in proj\ThinkPHP\Library\Think\Model.class. Under php
/**
* 字段值增长
* @access public
* @param string $field 字段名
* @param integer $step 增长值
* @return boolean
*/
public function setInc($field,$step=1) {
return $this->setField($field,array('exp',$field.'+'.$step));
}
you can see that the setField method is used here, and then use exp custom expression to set $field = $field $step. At this point, we understand a little bit about the principle.
But the question comes again. How is setField implemented? Under the same file, find the setField method:
/**
* 设置记录的某个字段值
* 支持使用数据库字段和方法
* @access public
* @param string|array $field 字段名
* @param string $value 字段值
* @return boolean
*/
public function setField($field,$value='') {
if(is_array($field)) {
$data = $field;
}else{
$data[$field] = $value;
}
return $this->save($data);
}
Here we see the commonly used save method, where $data[$field] = $ value; is actually $data['test_number'] = array("exp","test_number 2")
Let’s look at the most commonly used save method:
/**
* 保存数据
* @access public
* @param mixed $data 数据
* @param array $options 表达式
* @return boolean
*/
public function save($data='',$options=array()) {
if(empty($data)) {
// 没有传递数据,获取当前数据对象的值
if(!empty($this->data)) {
$data = $this->data;
// 重置数据
$this->data = array();
}else{
$this->error = L('_DATA_TYPE_INVALID_');
return false;
}
}
// 数据处理
$data = $this->_facade($data);
// 分析表达式
$options = $this->_parseOptions($options);
$pk = $this->getPk();
if(!isset($options['where']) ) {
// 如果存在主键数据 则自动作为更新条件
if(isset($data[$pk])) {
$where[$pk] = $data[$pk];
$options['where'] = $where;
unset($data[$pk]);
}else{
// 如果没有任何更新条件则不执行
$this->error = L('_OPERATION_WRONG_');
return false;
}
}
if(is_array($options['where']) && isset($options['where'][$pk])){
$pkValue = $options['where'][$pk];
}
if(false === $this->_before_update($data,$options)) {
return false;
}
$result = $this->db->update($data,$options);
if(false !== $result) {
if(isset($pkValue)) $data[$pk] = $pkValue;
$this->_after_update($data,$options);
}
return $result;
}
The most important thing is $options = $this->_parseOptions($options); and $result = $this->db->update($data,$options); The former changes the parameters Converted into a string array for splicing sql, the latter calls the update method under proj\tptest\ThinkPHP\Library\Think\Db.class.php:
/**
* 更新记录
* @access public
* @param mixed $data 数据
* @param array $options 表达式
* @return false | integer
*/
public function update($data,$options) {
$this->model = $options['model'];
$sql = 'UPDATE '
.$this->parseTable($options['table'])
.$this->parseSet($data)
.$this->parseWhere(!empty($options['where'])?$options['where']:'')
.$this->parseOrder(!empty($options['order'])?$options['order']:'')
.$this->parseLimit(!empty($options['limit'])?$options['limit']:'')
.$this->parseLock(isset($options['lock'])?$options['lock']:false)
.$this->parseComment(!empty($options['comment'])?$options['comment']:'');
return $this->execute($sql,$this->parseBind(!empty($options['bind'])?$options['bind']:array()));
}
In the end, actually It uses the execute method of the driver class proj\ThinkPHP\Library\Think\Db\Driver\Mysql.class.php.
/**
* 执行语句
* @access public
* @param string $str sql指令
* @return integer|false
*/
public function execute($str) {
$this->initConnect(true);
if ( !$this->_linkID ) return false;
$this->queryStr = $str;
//释放前次的查询结果
if ( $this->queryID ) { $this->free(); }
N('db_write',1);
// 记录开始执行时间
G('queryStartTime');
$result = mysql_query($str, $this->_linkID) ;
$this->debug();
if ( false === $result) {
$this->error();
return false;
} else {
$this->numRows = mysql_affected_rows($this->_linkID);
$this->lastInsID = mysql_insert_id($this->_linkID);
return $this->numRows;
}
}
Finally, use the lowest level mysql_query to execute the SQL statement.
So far, the source code of setInc has been roughly reviewed. I believe everyone has a better understanding of how setInc is executed.
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
Access array elements in double quotes in php How to handle error reporting
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the steps to use setInc in thinkphp3.2.0. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

