Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Vue packaging optimization code spliting_vue.js
Vue packaging optimization code spliting_vue.js
- 不言Original
- 2018-04-10 14:45:431387browse
This article mainly introduces the code spliting of Vue packaging optimization in detail. Now I will share it with you. Friends in need can refer to it
In the era of http1, a more common performance optimization is to merge http. Regarding the number of requests, we usually merge many js codes together, but if the size of a js package is particularly large, it is a bit overkill for performance improvement. And if we reasonably split all the code, peel off the first-screen and non-first-screen code, split the business code and basic library code, and then load a certain piece of code when it is needed, next time if If you need to use it again, read it from the cache. Firstly, you can make better use of the browser cache. Secondly, it can improve the loading speed of the first screen, which greatly improves the user experience.
Core idea
Separation of business code and basic library
This is actually easy to understand. Business code is usually updated and iterated frequently, while basic library Usually updates are slow. If you split it here, you can make full use of the browser cache to load the basic library code.
Asynchronous loading on demand
This mainly solves the problem of the first screen request size. When accessing the first screen, we only need to load the logic required for the first screen, and Not the code that loads all routes.
Practical
Recently, I used vuetify to transform an internal system. At the beginning, I used the most commonly used webpack configuration, and the functions were quickly developed. However, once I packaged it, I found that The effect is not very obvious. There are many large packages.
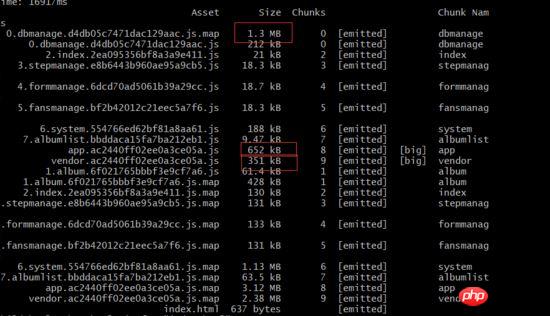
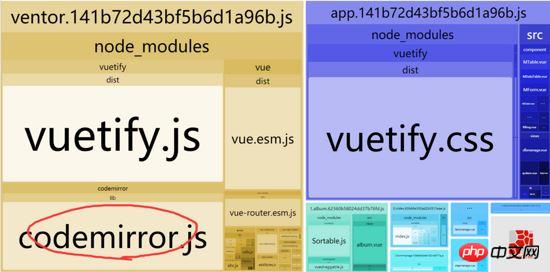
Here we look at the packaging distribution. The webpack-bundle-analyzer is used here. You can clearly see vue and vuetify. There are cases where modules are packaged repeatedly.
Here we will post the configuration first and use it for analysis later:
const path = require('path')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
const generateHtml = new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: '逍遥系统',
template: './src/index.html',
minify: {
removeComments: true
}
})
module.exports = {
entry: {
vendor: ['vue', 'vue-router', 'vuetify'],
app: './src/main.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist'),
filename: '[name].[hash].js',
chunkFilename:'[id].[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue'],
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'public': path.resolve(__dirname, './public')
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
loaders: {
}
// other vue-loader options go here
}
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
objectAssign: 'Object.assign'
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
},
{
test: /\.styl$/,
loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'stylus-loader']
}
]
},
devServer: {
historyApiFallback: true,
noInfo: true
},
performance: {
hints: false
},
devtool: '#eval-source-map',
plugins: [
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin(),
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist']),
generateHtml,
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'ventor'
}),
]
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
module.exports.devtool = '#source-map'
// http://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/workflow/production.html
module.exports.plugins = (module.exports.plugins || []).concat([
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: '"production"'
}
}),
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({
sourceMap: true,
compress: {
warnings: false
}
}),
new webpack.LoaderOptionsPlugin({
minimize: true
})
])
}
## CommonChunkPlugin
ventor entrance Here we find that all referenced modules under node_module, such as axios, are not filtered out, so they are packaged into app.js. Here we do the separationentry: {
vendor: ['vue', 'vue-router', 'vuetify', 'axios'],
app: './src/main.js'
},
Then there is another problem here. It is impossible for me to enter the module manually. At this time, we may need to automatically separate the ventor. Here we need to introduce minChunks. In the configuration, we You can package and modify the configuration of all modules referenced under mode_module as follows
entry: {
//vendor: ['vue', 'vue-router', 'vuetify', 'axios'], //删除
app: './src/main.js'
}
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks: ({ resource }) => (
resource &&
resource.indexOf('node_modules') >= 0 &&
resource.match(/\.js$/)
)
}),
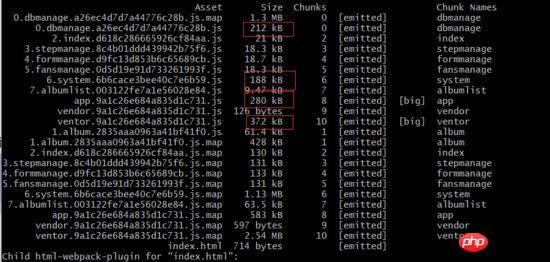
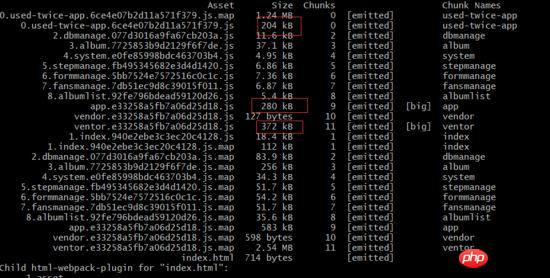
After the optimization of the above steps, let’s look at the file distribution and find that Modules under node_module are all collected under vendor.
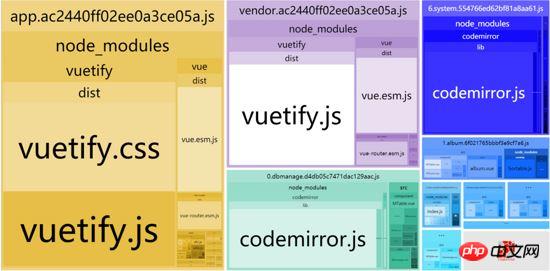
// const dbmanage = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "dbmanage" */'../views/dbmanage.vue') // const system = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "system" */'../views/system.vue') import dbmanage from '../views/dbmanage.vue' import system from '../views/system.vue'At this time, when we repackage, we can find that the codemirror has been packaged, so the question is, is this good?
async
The answer to the above question is yes, no. Obviously, ventor is our entry code, that is, the first Screen, we don’t need to load this codemirror component at all. We first restore the routing modification just now, but then there is a new problem. Our codemirror is packaged into two single pages at the same time, and some of them are packaged by themselves. Components such as MTable or MDataTable are also packaged repeatedly. And the codemirror is very large, loading two single pages at the same time will also cause a big performance problem. To put it simply, after we load the codemirror on the first single page, we should not load it again on the second page. . To solve this problem, here we can use CommonsChunkPlugin's async and the count method in minChunnks to determine the quantity. As long as it is reused more than two times, including two asynchronously loaded modules (that is, the chunk generated by import ()), we will consider it It can be marked as public. Here we add a configuration.new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
async: 'used-twice',
minChunks: (module, count) => (
count >= 2
),
})
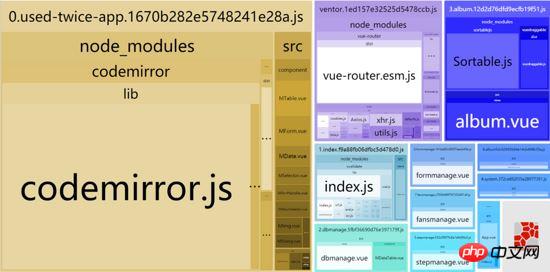
再次打包,我们发现所有服用的组件被重新打到了 0.used-twice-app.js中了,这样各个单页面大小也有所下降,平均小了近10k左右

可是,这里我们发现vuetify.js和vuetify.css实在太庞大了,导致我们的打包的代码很大,这里,我们考虑把它提取出来,这里为了避免重复打包,需要使用external,并将vue以及vuetify的代码采用cdn读取的方式,首先修改index.html
//css引入 <link href='https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto:300,400,500,700|Material+Icons' rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"> <link href="https://unpkg.com/vuetify/dist/vuetify.min.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="stylesheet"> //js引入 <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vuetify/dist/vuetify.js"></script> //去掉main.js中之前对vuetifycss的引入 //import 'vuetify/dist/vuetify.css'
再修改webpack配置,新增externals
externals: {
'vue':'Vue',
"vuetify":"Vuetify"
}
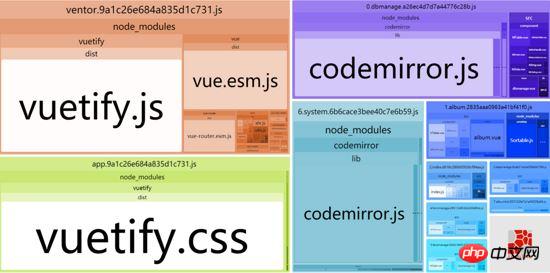
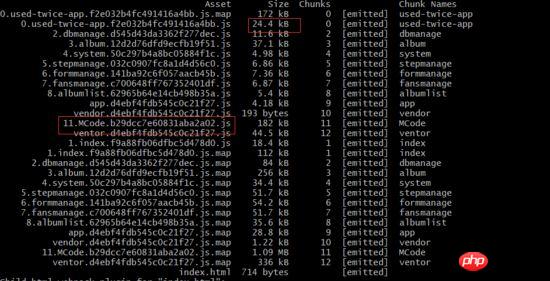
再重新打包,可以看到vue相关的代码已经没有了,目前也只有used-twice-app.js比较大了,app.js缩小了近200kb。

但是新问题又来了,codemirror很大,而used-twice又是首屏需要的,这个打包在首屏肯定不是很好,这里我们要将system和dbmanage页面的codemirror组件改为异步加载,单独打包,修改如下:
// import MCode from "../component/MCode.vue"; //注释掉
components: {
MDialog,
MCode: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "MCode" */'../component/MCode.vue')
},
重新打包下,可以看到 codemirror被抽离了,首屏代码进一步得到了减少,used-twice-app.js代码缩小了近150k。

做了上面这么多的优化之后,业务测的js基本都被拆到了50kb一下(忽略map文件),算是优化成功了。
总结
可能会有朋友会问,单独分拆vue和vuetify会导致请求数增加,这里我想补充下,我们的业务现在已经切换成http2了,由于多路复用,并且加上浏览器缓存,我们分拆出的请求数其实也算是控制在合理的范畴内。
这里最后贴一下优化后的webpack配置,大家一起交流学习下哈。
const path = require('path')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
const generateHtml = new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: '逍遥系统',
template: './src/index.html',
minify: {
removeComments: true
}
})
module.exports = {
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist'),
filename: '[name].[hash].js',
chunkFilename:'[id].[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue'],
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'public': path.resolve(__dirname, './public')
}
},
externals: {
'vue':'Vue',
"vuetify":"Vuetify"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
loaders: {
}
// other vue-loader options go here
}
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
objectAssign: 'Object.assign'
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
},
{
test: /\.styl$/,
loader: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'stylus-loader']
}
]
},
devServer: {
historyApiFallback: true,
noInfo: true
},
performance: {
hints: false
},
devtool: '#eval-source-map',
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist']),
generateHtml
]
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
module.exports.devtool = '#source-map'
module.exports.plugins = (module.exports.plugins || []).concat([
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin(),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'ventor',
minChunks: ({ resource }) => (
resource &&
resource.indexOf('node_modules') >= 0 &&
resource.match(/\.js$/)
)
}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
async: 'used-twice',
minChunks: (module, count) => (
count >= 2
),
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: '"production"'
}
}),
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({
sourceMap: true,
compress: {
warnings: false
}
}),
new webpack.LoaderOptionsPlugin({
minimize: true
})
])
}
相关推荐:
如何修改Vue.js中scoped模式下的子组件内部标签样式
Vue中computed与methods的区别详解_vue.js
The above is the detailed content of Vue packaging optimization code spliting_vue.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

