Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Summary of Ajax that novices must learn
Summary of Ajax that novices must learn
- php中世界最好的语言Original
- 2018-04-02 16:18:301873browse
This time I will bring you a summary of Ajax that novices must learn. What are the Ajax summaries that novices must learn? Here are practical cases, let’s take a look.
1. Introduction to Ajax, advantages and disadvantages, application scenarios and technologies
Introduction to Ajax:
Asynchronous Javascript And XML (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)
It is not a single technology, but a combination of organically utilizing a series of technologies related to interactive web applications Body
AJAX is a technology for creating fast, dynamic web pages. AJAX enables web pages to update asynchronously by exchanging small amounts of data with the server in the background. This means that parts of a web page can be updated without reloading the entire page.
Advantages:
No page refresh, good user experience.
Asynchronous communication, faster response capability.
Reduce redundant requests and reduce server burden
Based on standardized and widely supported technology, no need to download plug-ins or applets
Disadvantages:
ajax kills the back button, which is the browser back mechanism of destruction.
There are certain security issues.
The support for search engines is relatively weak.
Destroys the exception mechanism of the program.
Unable to access directly with URL
ajax application scenario
Scenario 1. Data verification
Scenario 2. Fetch data on demand
Scenario 3. Automatically update the page
AJAX contains the following five parts:
ajax is not a new technology, but several original technologies combination of. It is composed of the following technologies.
Represented using CSS and XHTML.
Use the DOM model for interaction and dynamic display.
Data exchange and operation technology, using XML and XSLT
Use XMLHttpRequest to communicate asynchronously with the server.
Use javascript to bind and call.
Among the above technologies, except for the XmlHttpRequest object, all other technologies are based on web standards and have been widely used. Although XMLHttpRequest has not yet been adopted by W3C , but it is already a de facto standard, because almost all major browsers currently support it

The first picture especially illustrates the structure and structure of traditional Web applications. The structural difference between Web applications using AJAX technology
The main difference is actually not JavaScript, not HTML/XHTML and CSS, but the use of XMLHttpRequest to asynchronously request XML data from the server
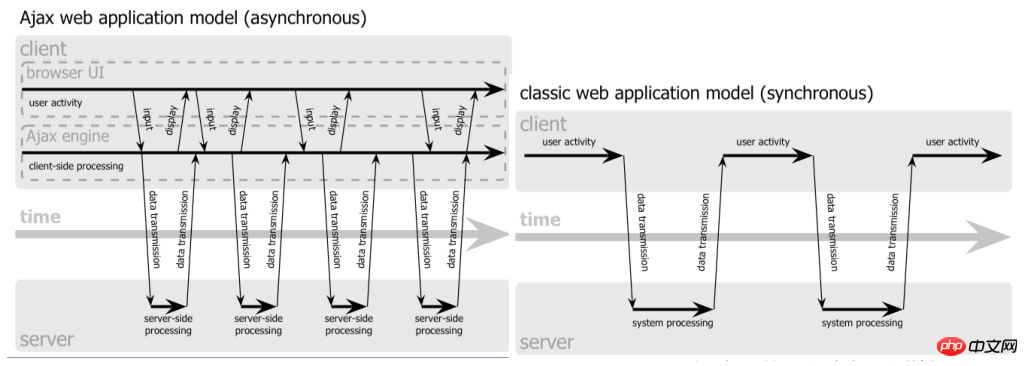
Let’s look at the second picture again. In the traditional Web application model, the user experience is fragmented. Click ->wait->see the new page->click again ->Wait some more. After adopting AJAX technology, most of the calculation work is completed by the server without the user noticing.

2. Steps to create ajax
The principle of Ajax is simply to send an asynchronous request to the server through the XmlHttpRequest object, obtain data from the server, and then use javascript to operate the DOM and update the page. The most critical step in this is to obtain the request data from the server. Creating ajax natively can be divided into the following four steps
1. Create an XMLHttpRequest object
The core of Ajax is the XMLHttpRequest object, which is implemented by Ajax The key is to send asynchronous requests, receive responses and execute callbacks through it.
All modern browsers (IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Safari and Opera) have built-in XMLHttpRequest objects.
Syntax for creating XMLHttpRequest objects:
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
Older versions of Internet Explorer (IE5 and IE6) use ActiveX objects:
var xhr = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
To cope with all modern browsers, including IE5 and IE6, please check whether the browser supports the XMLHttpRequest object. If supported, an XMLHttpRequest object is created. If it is not supported, create an ActiveXObject:
Compatible with each browser's tool function for creating Ajax
function createRequest (){
try {
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
}catch (tryMS){
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject("Msxm12.XMLHTTP");
} catch (otherMS) {
try {
xhr = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}catch (failed) {
xhr = null;
}
}
}
return xhr;
}
2. Prepare the request
Initialize the XMLHttpRequest object and accept three parameters:
xhr.open(method,url,async);
The first parameter represents a string of request type, its value can be GET or POST .
GET request:
xhr.open("GET",demo.php?name=tsrot&age=24,true);
POST request:
xhr.open("POST",demo.php,true);
The second parameter is the URL to which the request is to be sent. .
The third parameter is true or false, indicating whether the request is issued in asynchronous or synchronous mode. (The default is true, false is generally not recommended)
false: Requests issued in synchronous mode will suspend the execution of all javascript code until the server gets a response. If the browser is connected to the network When there is a problem or when downloading the file, the page will hang all the time.
true: For requests issued in asynchronous mode, while the request object is sending and receiving data, the browser can continue to load the page and execute other javascript codes
3. Send a request
xhr.send();
Generally, the parameters submitted using Ajax are mostly simple strings. You can directly use the GET method to write the parameters to be submitted. to the url parameter of the open method. At this time, the parameter of the send method is null or empty.
GET request:
xhr.open("GET",demo.php?name=tsrot&age=24,true);
xhr.send(null);
POST request:
If you need to POST data like an HTML form, please use setRequestHeader()To add HTTP header. Then specify the data you want to send in the send() method:
xhr.open("POST",demo.php,true);
xhr.setRequestHeder("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8");
xhr.sen
4. Processing the response
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
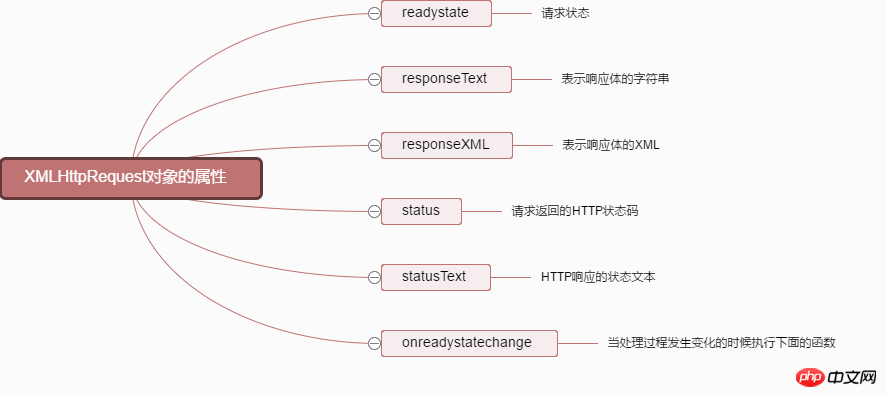
onreadystatechange: Execute the following function when the processing process changes
readyState: Ajax processing process
0: The request is not initialized (open( has not been called yet) ) ).
1: The request has been established, but has not been sent (send() has not been called yet).
2: The request has been sent and is being processed (usually the content header can be obtained from the response now).
3: The request is being processed; usually some data is available in the response, but the server has not yet completed generating the response.
4: The response is complete; you can get and use the server's response.
status attribute:
200: "OK"
404: Page not found
responseText: Get response data in string form
responseXML: Get response data in XML form
The object is converted to JSON format using JSON .stringify
Convert json to object format using JSON.parse()
The return value is generally a json string, you can use JSON.parse (xhr.responseText)Convert to JSON object
从服务器传回的数据是json格式,这里做一个例子说明,如何利用
1、首先需要从XMLHttpRequest对象取回数据这是一个JSON串,把它转换为真正的JavaScript对象。使用JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)转化为JSON对象
2、遍历得到的数组,向DOM中添加新元素
function example(responseText){
var salep= document.getElementById("sales");
var sales = JSON.parse(responseText);
for(var i=0;i<sales.length;i++){
var sale = sales[i];
var p = document.createElement("p");
p.setAttribute("class","salseItem");
p.innerHTML = sale.name + sale.sales;
salsep.appendChild(p);
}
}
5、完整例子
var xhr = false;
if(XMLHttpRequest){
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
}else{
xhr = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
};
if(xhr) {//如果xhr创建失败,还是原来的false
xhr.open("GET","./data.json",true);
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200){
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText).name);
}
}
}data.json
{
"name":"tsrot",
"age":24
}这个过程是一定要记在脑子里的
function ajax(url, success, fail){
// 1. 创建连接
var xhr = null;
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2. 连接服务器
xhr.open('get', url, true)
// 3. 发送请求
xhr.send(null);
// 4. 接受请求
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState == 4){
if(xhr.status == 200){
success(xhr.responseText);
} else { // fail
fail && fail(xhr.status);
}
}
}
}XMLHttpRequest 在异步请求远程数据时的工作流程
谈谈JSONP
要访问web服务器的数据除了XMLHttpRequest外还有一种方法是JSONP
如果HTML和JavaScript与数据同时在同一个机器上,就可以使用XMLHttpRequest
什么是JSONP?
JSONP(JSON with Padding)是一个非官方的协议,它允许在服务器端集成Script tags返回至客户端,通过javascript callback的形式实现跨域访问(这仅仅是JSONP简单的实现形式)
JSONP有什么用?
由于同源策略的限制,XmlHttpRequest只允许请求当前源(域名、协议、端口)的资源,为了实现跨域请求,可以通过script标签实现跨域请求,然后在服务端输出JSON数据并执行回调函数,从而解决了跨域的数据请求
如何使用JSONP?
在客户端声明回调函数之后,客户端通过script标签向服务器跨域请求数据,然后服务端返回相应的数据并动态执行回调函数
用XMLHttpRequest时,我们得到一个字符串;要用JSON.parse把字符串转化成对象,使用jsonp时,script标志会解析并执行返回的代码,等我们处理数据时,已经是一个JavaScript对象了
简单实例
<meta content="text/html; charset=utf-8" http-equiv="Content-Type" />
<script type="text/javascript">
function jsonpCallback(result) {
alert(result.a);
alert(result.b);
alert(result.c);
for(var i in result) {
alert(i+":"+result[i]);//循环输出a:1,b:2,etc.
}
}
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://crossdomain.com/services.php?callback=jsonpCallback"></script>
<!--callback参数指示生成JavaScript代码时要使用的函数jsonpcallback-->
注意浏览器的缓存问题
在末尾增加一个随机数可避免频繁请求同一个链接出现的缓存问题
`
三、 jQuery中的Ajax
jQuery中的ajax封装案例
//ajax请求后台数据
var btn = document.getElementsByTagName("input")[0];
btn.onclick = function(){
ajax({//json格式
type:"post",
url:"post.php",
data:"username=poetries&pwd=123456",
asyn:true,
success:function(data){
document.write(data);
}
});
}
//封装ajax
function ajax(aJson){
var ajx = null;
var type = aJson.type || "get";
var asyn = aJson.asyn || true;
var url = aJson.url; // url 接收 传输位置
var success = aJson.success;// success 接收 传输完成后的回调函数
var data = aJson.data || '';// data 接收需要附带传输的数据
if(window.XMLHttpRequest){//兼容处理
ajx = new XMLHttpRequest();//一般浏览器
}else
{
ajx = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");//IE6+
}
if (type == "get" && data)
{
url +="/?"+data+"&"+Math.random();
}
//初始化ajax请求
ajx.open( type , url , asyn );
//规定传输数据的格式
ajx.setRequestHeader('content-type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
//发送ajax请求(包括post数据的传输)
type == "get" ?ajx.send():ajx.send(aJson.data);
//处理请求
ajx.onreadystatechange = function(aJson){
if(ajx.readState == 4){
if (ajx.status == 200 && ajx.status<300)//200是HTTP 请求成功的状态码
{
//请求成功处理数据
success && success(ajx.responseText);
}else{
alert("请求出错"+ajx.status);
}
}
}
jQuery中的Ajax的一些方法
jquery对Ajax操作进行了封装,在jquery中的$.ajax()方法属于最底层的方法,第2层是load() 、$.get() 、$.post();第3层是$.getScript() 、$.getJSON() ,第2层使用频率很高
load()方法
load()方法是jquery中最简单和常用的ajax方法,能载入远程HTML代码并插入DOM中 结构为:load(url,[data],[callback])
使用url参数指定选择符可以加载页面内的某些元素 load方法中url语法:url selector 注意:url和选择器之间有一个空格
传递方式
load()方法的传递方式根据参数data来自动指定,如果没有参数传递,则采用GET方式传递,反之,采用POST
回调参数
必须在加载完成后才执行的操作,该函数有三个参数 分别代表请求返回的内容、请求状态、XMLHttpRequest对象
只要请求完成,回调函数就会被触发
$("#testTest").load("test.html",function(responseText,textStatus,XMLHttpRequest){
//respnoseText 请求返回的内容
//textStatus 请求状态 :sucess、error、notmodified、timeout
//XMLHttpRequest
})
load方法参数
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| url | String | 请求HTML页面的URL地址 |
| data(可选) | Object | 发送至服务器的key / value数据 |
| callback(可选) | Function | 请求完成时的回调函数,无论是请求成功还是失败 |
$.get() and $.post() methods
load() method is usually used to obtain static data files from the web server. If you need to pass some parameters to the page in the server in the project, you can use $.get() and $.post() or $.ajax()Method
Note: The $.get() and $.post() methods are in jquery Global function
$.get() method
$.get()method uses GET method to make asynchronous requests
The structure is: $.get(url,[data],callback,type)
If the content format returned by the server is an xml document, the Content-Type type code needs to be set on the server side As follows: header("Content-Type:text/xml:charset=utf-8") //php
$.get() method parameter analysis
| Parameters | Type | Description |
| url | String | The address of the requested HTML page |
| data(optional) | Object | Sent to the server The key/value data will be appended to the request URL as QueryString |
| callback (optional) | Function | Callback function for successful loading (only This method is called only when the return status of the Response is success) |
| type (optional) | String | The format of the content returned by the server, including xml , html, script, json, text and _default |
$.post() method
It has the same structure and usage as the $.get() method, with the following differences
The GET request will pass the parameters followed by Zhang Nai's URL, while the POST request will be sent to the web server as the entity content of the Http message. In the ajax request, this difference is invisible to the user
The GET method has a size limit on the transmitted data (usually no larger than 2KB), while the amount of data transmitted using the POST method is much larger than the GET method (theoretically not limited)
The data requested by GET method will be cached by the browser, so others can read the data from the browser's history, such as account number and password. In some cases, the GET method will bring serious security problems, while POST can relatively avoid these problems.
The data passed by the GET and POST methods cannot be obtained on the server side. same. In PHP, use
$_GET[]for GET method; use$_POST[]for POST method; both methods can be used for$_REQUEST[]Get
Summary
Use load(), $.get() and # The ##$.post() method completes some conventional Ajax programs. If you need complex Ajax programs, you need to use $.ajax()method
$.ajax() method
$.ajax() method is the lowest level Ajax implementation of jquery, and its structure is $.ajax(options)
$.ajax() method. The parameters are key / value Exists, all parameters are optional
$.ajax() method common parameter analysis
| Type | Description | |
| String | (Default is the current page address)Send Requested address | |
| String | The request method (POST or GET) defaults to GET | |
| Number | Set request timeout (milliseconds) | |
| String | Expected server The type returned. The available types are as follows | xml: Returns an XML document, which can be processed with jquery
html: Returns plain text HTML information, and the included script tag will also be executed when inserted into the DOM Script: Returns plain text javascript code. Results are not automatically cached unless the cache parameter is set. Note: When making remote requests, all POST requests will be converted to GET requests json: Return JSON data jsonp: JSONP format, when calling a function using jsonp format, for example: myurl?call back=?, jquery will automatically replace the latter one? is the correct function name to execute the callback function text: Returns a plain text string |
| Function | A function that can modify the XMLHttpRequest object before sending the request, such as adding a custom HTTP header. If false is returned in beforeSend, this Ajax request can be canceled. The XMLHttpRequest object is the only parameter | Function(XMLHttpRequest){
This;//The options parameters passed when calling this Ajax request } |
| Function | Callback function after the request is completed (called when the request succeeds or fails) | Parameters: XMLHttpRequest object and a string describing the successful request type
Function(XMLHttpRequest,textStatus){ This;//The options parameters passed when calling this Ajax request } |
| Function | The callback function called after a successful request has two parameters | (1) Data returned by the server and processed according to the dataType parameter
(2) A string describing the status Function(data,textStatus){ //data may be xmlDoc, ``jsonObj, html, text, etc. This;//The options parameters passed when calling this Ajax request } |
| Function | Function called when the request fails | |
| Boolean | Default is true. Indicates whether to trigger the global Ajax event. Setting it to false will not trigger it. AjaxStart or AjaxStop can be used to control various Ajax events |
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Ajax that novices must learn. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

