Home >Web Front-end >H5 Tutorial >Summary of development skills for Vue components
Summary of development skills for Vue components
- php中世界最好的语言Original
- 2018-03-27 15:52:292116browse
This time I will bring you a summary of the development skills of Vue components. What are the precautions for Vue component development? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Preface As I near graduation, I wrote a simple personal blog. The project address is click me to visit the project address (please ask for a star by the way). This article is the first in a series of summaries. Next, I will imitate a low-profile version of Element's dialog box and pop-up components step by step. TextVue single file component development
When using vue-cli to initialize a project, you will find that there are A HelloWorld.vue file, this is the basic development model of single-file components.// 注册
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<p>A custom component!</p>'
})
// 创建根实例
new Vue({
el: '#example'
})Next, start writing a dialog component.
Dialog
The basic style of the target dialog component is as shown in the figure: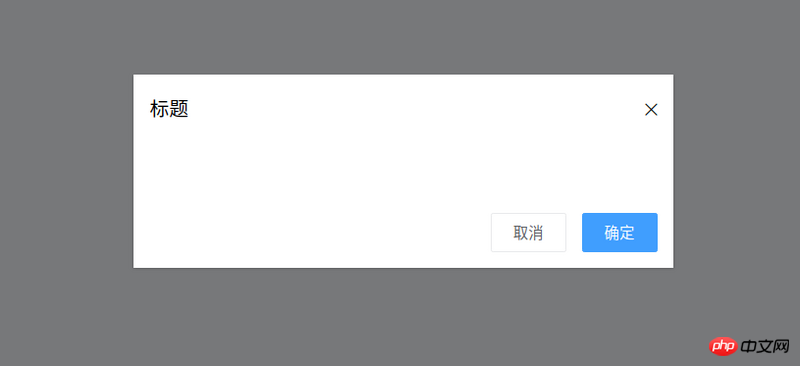
- The dialog component needs a titleprops to indicate the pop-up window title
- The dialog component needs to emit OK when the OK button is pressed
Event (that is, tell the parent component that it is confirmed)
- Similarly, the dialog component needs to emit a cancellation event
- The dialog component needs Provide a slot to facilitate customized content
<template>
<p class="ta-dialogwrapper">
<p class="ta-dialog">
<p class="ta-dialogheader">
<span>{{ title }}</span>
<i class="ios-close-empty" @click="handleCancel()"></i>
</p>
<p class="ta-dialogbody">
<slot></slot>
</p>
<p class="ta-dialogfooter">
<button @click="handleCancel()">取消</button>
<button @click="handleOk()">确定</button>
</p>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Dialog',
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: '标题'
},
},
methods: {
handleCancel() {
this.$emit('cancel')
},
handleOk() {
this.$emit('ok')
},
},
}
</script>This completes the development of the dialog component. The usage method is as follows:
<ta-dialog title="弹窗标题" @ok="handleOk" @cancel="handleCancel"> <p>我是内容</p> </ta-dialog>At this time, I discovered a problem. When using v-if or v-show to control the display of the pop-up window, there is no animation! ! ! , looks very stiff. Coach, I want to add animation. At this time, the transition component comes into play. Using the transition component combined with css can create many animations with good effects. Next, enhance the dialog component animation. The code is as follows:
<template>
<transition name="slide-down">
<p class="ta-dialogwrapper" v-if="isShow">
// 省略
</p>
</transition>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
isShow: true
}
},
methods: {
handleCancel() {
this.isShow = false
this.$emit('cancel')
},
handleOk() {
this.isShow = true
this.$emit('ok')
},
},
}
</script> You can see that the transition component receives a nameprops, so how to write css to complete the animation? A very simple way, just write two key class (css className) styles:
.slide-down-enter-active {
animation: dialog-enter ease .3s;
}
.slide-down-leave-active {
animation: dialog-leave ease .5s;
}
@keyframes dialog-enter {
from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(-20px);
}
to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
}
@keyframes dialog-leave {
from {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
to {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(-20px);
}
} It is so simple to develop a good dynamic effect. Note that the name of the transition component is slide-down, and the key classNames of the written animation are slide-down-enter-active and slide-down-leave-active.
Encapsulate Dialog to make MessageBox
The method of using Element's MessageBox is as follows:this.$confirm('此操作将永久删除该文件, 是否继续?', '提示', {
confirmButtonText: '确定',
cancelButtonText: '取消',
type: 'warning'
}).then(() => {
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '删除成功!'
});
}).catch(() => {
this.$message({
type: 'info',
message: '已取消删除'
});
});When I saw this code, I felt so magical. So magical, so magical (exclamation three times in a row). Take a closer look, this component is actually an encapsulated dialog,
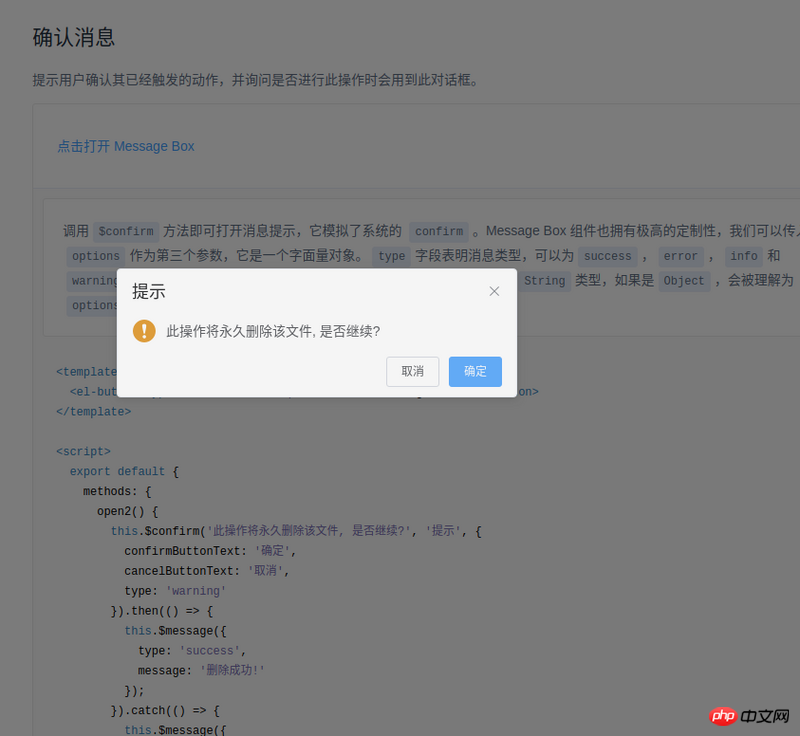
- The usage method of Element is this.$confirm. Isn’t this just a matter of hanging it on Vue’s prototype?
- Element's then means OK, catch means cancel, just promise.
import Vue from 'vue'
import MessgaeBox from './src/index'
const Ctur = Vue.extend(MessgaeBox)
let instance = null
const callback = action => {
if (action === 'confirm') {
if (instance.showInput) {
instance.resolve({ value: instance.inputValue, action })
} else {
instance.resolve(action)
}
} else {
instance.reject(action)
}
instance = null
}
const showMessageBox = (tip, title, opts) => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const propsData = { tip, title, ...opts }
instance = new Ctur({ propsData }).$mount()
instance.reject = reject
instance.resolve = resolve
instance.callback = callback
document.body.appendChild(instance.$el)
})
const confirm = (tip, title, opts) => showMessageBox(tip, title, opts)
Vue.prototype.$confirm = confirmAt this point, you may be wondering what to do As for callback, I actually wrote an encapsulated dialog and named it MessageBox.In its code, there are two methods:
onCancel() {
this.visible = false
this.callback && (this.callback.call(this, 'cancel'))
},
onConfirm() {
this.visible = false
this.callback && (this.callback.call(this, 'confirm'))
},Yes, it is callback when confirming and canceling . I would also like to talk about Vue.extend, which introduces MessageBox into the code. Instead of using new MessageBox directly, I use new Ctur because this can define data (not just props), for example:
instance = new Ctur({ propsData }).$mount()At this time, there is actually no MessageBox on the page. We need to execute:
document.body.appendChild(instance.$el)If you do this directly, you may find that there is no animation when the MessageBox is opened, but there is animation when it is closed. The solution is also very simple. Keep it invisible when
appendChild, and then use code like this:
Vue.nextTick(() => instance.visible = true)This way there will be animation. Summary
- Achieve good animation through transition and css. Among them, the name of the transition component determines the two key classes for writing css, named [name]-enter-active and [name]-leave-active
Inherit the constructor of a component through Vue.extend (I don’t know how to say it properly, so I’ll just say this first), and then through this constructor, you can implement component-related properties Customization (usage scenario: js calling component)
When js calls the component, in order to maintain the animation effect of the component, you can first document.body.appendChild and then Vue.nextTick(() => ; instance.visible = true)
At this point, the simple Vue component development is summarized. The relevant code I wrote is at the address, https://github .com/mvpzx/elapse/tree/master/be/src/components
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
The order of operating Vue rendering and plug-in loading
Node.js crawling Douban data example
The above is the detailed content of Summary of development skills for Vue components. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- AlloyTouch full-screen scrolling plug-in creates a smooth H5 page in 30 seconds
- HTML5 actual combat and analysis of touch events (touchstart, touchmove and touchend)
- Detailed explanation of image drawing examples in HTML5 canvas 9
- Regular expressions and new HTML5 elements
- How to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server

