 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial How to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server
How to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the serverHow to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server
A simple Node project that implements drag-and-drop upload of multiple files can be downloaded from github. You can download it first: https://github.com/Johnharvy/upLoadFiles/.
Unzip the downloaded zip format package. It is recommended to use webstom to run the project and start the project through app.js. If it prompts that the node.exe execution environment cannot be found, please specify your node. exe installation location. The express framework I use here is version 3.21.2.
Let’s briefly introduce how the drag effect is achieved.
Let’s look at the code first:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="js/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="js/EventUtil.js"></script>
<title>uploadFile</title>
<style>
#a1{width:100px;height:100px;background: #aaaaaa;text-align:center;line-height:100px;color:rgba(81, 49, 202, 0.72);
margin:150px auto;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a1">拖拽到此</div>
<div id="out-input"></div>
<script>
var a1=document.getElementById("a1");
function handleEvent(event){
var info ="",
output= document.getElementById("out-input"),
files,i,len;
EventUtil.preventDefault(event); //阻止事件的默认行为
var formData =new FormData();
if(event.type == "drop"){
files=event.dataTransfer.files;
i = 0;
len= files.length;
while( i< len){
info += files[i].name +"("+ files[i].type + "," +files[i].size +"bytes)<br/>";
formData.append("file"+i,files[i]);
i++;
}
output.innerHTML = info;
$.ajax({
type:"post",
url:"/uploadFile",
data:formData,
async: false,
cache: false,
contentType: false,
processData: false, //此处指定对上传数据不做默认的读取字符串的操作
success:function(rs){
console.log(rs);
},
error:function(r){
alert("文件上传出错!");
}
});
}
}
EventUtil.addHandler(a1, "dragenter", handleEvent);
EventUtil.addHandler(a1, "dragover", handleEvent);
EventUtil.addHandler(a1, "drop", handleEvent);
</script>
</body>
</html> The html content is very simple, one shows the allowed drag range, and the other is a div block used to display the content of the uploaded file.
Js part:
Here I have prepared an EventUtil interface object. You can also think of it as a small library for processing events. Its function is to encapsulate Different methods for binding the same events in various browsers are shown. In order to implement the event binding method common to all browsers, the EventUtil object is used to implement it uniformly. You can simply take a look at its implementation code. It is very simple.
When the browser detects the three event situations of dragging, the default behaviors of "dragenter", "dragover" and "drag" will be blocked. When it is the "drag" situation, our Custom events.
Because we are uploading files, an instance of FormData is used here. Files are added to the object through append() to become a queue file. After uploading to the server, it will be parsed in queue order. Properties object. In the event, "event.dataTransfer.files" is used to obtain the files stored in the event.
Another thing to note here is that jquery's ajax method needs to configure processData to false when uploading file objects, which means that the default operation of reading strings is not used. The reason is that by default, the data passed in through the data option, if it is an object (technically speaking, as long as it is not a string), will be processed and converted into a query string to match the default content type "application/x-www-form" -urlencoded". If you want to send DOM tree information or other information that you do not want to convert, you need to set it to false.
After the file is uploaded successfully, the console will print "{infor:"success"}" information.
This is the end of the front-end part. Let’s look at the code on the Node.js side.
The file structure is as follows:
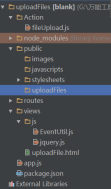
Let’s first look at routing - the content in app.js:
var express = require('express');
var routes = require('./routes');
var user = require('./routes/user');
var http = require('http');
var path = require('path');
var app = express();
// all environments
app.set('port', process.env.PORT || 3000);
app.set('view engine', 'jade');
app.use(express.favicon());
app.use(express.logger('dev'));
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded());
app.use(express.methodOverride());
app.use(app.router);
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname)));
exports.app=app;
var uploadAction=require("./Action/fileUpload");
//路由事件监听
uploadAction.uploadTest.uploadFile();
//文件上传监听
// development only
if ('development' == app.get('env')) {
app.use(express.errorHandler());
}
app.get('/users', user.list);
http.createServer(app).listen(app.get('port'), function(){
console.log('Express server listening on port ' + app.get('port'));
});and initial There are a few differences in app.js. I exported the app object for reuse in fileUpload.js, then introduced the fileUpload.js module, and obtained the uploadTest object that saves all methods of the module through the interface object and called the uploadFile method. .
Okay, finally let’s look at the fileUpload.js file:
var multipart = require('connect-multiparty');
var App=require("../app");
var path = require('path');
var fs=require("fs");
var app=App.app;
var uploadTest={};
function uploadFile(){
app.post("/uploadFile", multipart(),function(req,res) {
var i=0;
while(i != null){
if(req.files["file"+i]) upLoad(i);
else{ i= null; res.json({infor:"success"});return;}
i++;
}
//上传队列文件
function upLoad(index){
var filename = req.files["file"+index].originalFilename || path.basename(req.files["file"+index].path);
//path接口可以指定文件的路径和文件名称,"\结尾默认为路径,字符串结尾默认为文件名"
var targetPath = path.dirname("") + '/public/uploadFiles/' + filename;
//fs创建指定路径的文件并将读取到的文件内容写入
fs.createReadStream(req.files["file"+index].path).pipe(fs.createWriteStream(targetPath));
}
});
}
uploadTest.uploadFile=uploadFile;
exports.uploadTest=uploadTest;
nodeJs is always very simple and powerful, and it is highly creative, which is what I Reasons to like it. We see that there are actually very few key codes here. Let me briefly introduce the logical process of implementing file upload:
•Get the file name of the uploaded file
•Set the file The storage location, and the file name
•Read the content stream of the file and create a new file to write the content stream
In order to achieve uploading multiple files, I also do Some matching operations are performed, which are very intuitive and not difficult to understand.
After the file is successfully uploaded, it will appear under the uploadFiles file under the public file.
The modules used in the file are recorded in package.json and can be installed by entering the same-level directory address of package.json and using the command "npm install". If you directly run the project file downloaded from github, there is no need to install it.
The above is the implementation method introduced by the editor to combine NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server. I hope it will be helpful to you. If you have any questions, please Leave me a message and I will reply to you in time. I would also like to thank you all for your support of the PHP Chinese website!
For more related articles on the implementation method of combining NodeJS and HTML5 to drag and drop multiple files to upload to the server, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AMThere is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AMHTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, standardized by W3C. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, multimedia support and form enhancements, improving web structure, user experience and SEO effects. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, such as, ,, etc., to make the web page structure clearer and the SEO effect better. HTML5 supports multimedia elements and no third-party plug-ins are required, improving user experience and loading speed. HTML5 enhances form functions and introduces new input types such as, etc., which improves user experience and form verification efficiency.
 H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AMHow to write clean and efficient HTML5 code? The answer is to avoid common mistakes by semanticizing tags, structured code, performance optimization and avoiding common mistakes. 1. Use semantic tags such as, etc. to improve code readability and SEO effect. 2. Keep the code structured and readable, using appropriate indentation and comments. 3. Optimize performance by reducing unnecessary tags, using CDN and compressing code. 4. Avoid common mistakes, such as the tag not closed, and ensure the validity of the code.
 H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AMH5 improves web user experience with multimedia support, offline storage and performance optimization. 1) Multimedia support: H5 and elements simplify development and improve user experience. 2) Offline storage: WebStorage and IndexedDB allow offline use to improve the experience. 3) Performance optimization: WebWorkers and elements optimize performance to reduce bandwidth consumption.
 Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMHTML5 code consists of tags, elements and attributes: 1. The tag defines the content type and is surrounded by angle brackets, such as. 2. Elements are composed of start tags, contents and end tags, such as contents. 3. Attributes define key-value pairs in the start tag, enhance functions, such as. These are the basic units for building web structure.
 Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AMHTML5 is a key technology for building modern web pages, providing many new elements and features. 1. HTML5 introduces semantic elements such as, , etc., which enhances web page structure and SEO. 2. Support multimedia elements and embed media without plug-ins. 3. Forms enhance new input types and verification properties, simplifying the verification process. 4. Offer offline and local storage functions to improve web page performance and user experience.
 H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
H5 Code: Best Practices for Web DevelopersApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMBest practices for H5 code include: 1. Use correct DOCTYPE declarations and character encoding; 2. Use semantic tags; 3. Reduce HTTP requests; 4. Use asynchronous loading; 5. Optimize images. These practices can improve the efficiency, maintainability and user experience of web pages.
 H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AM
H5: The Evolution of Web Standards and TechnologiesApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AMWeb standards and technologies have evolved from HTML4, CSS2 and simple JavaScript to date and have undergone significant developments. 1) HTML5 introduces APIs such as Canvas and WebStorage, which enhances the complexity and interactivity of web applications. 2) CSS3 adds animation and transition functions to make the page more effective. 3) JavaScript improves development efficiency and code readability through modern syntax of Node.js and ES6, such as arrow functions and classes. These changes have promoted the development of performance optimization and best practices of web applications.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor




