Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >The difference between using Map and ForEach
The difference between using Map and ForEach
- php中世界最好的语言Original
- 2018-03-23 14:28:472073browse
This time I will bring you the difference between using Map and ForEach. What are the precautions when using Map and ForEach. The following is a practical case, let’s take a look.
If you already have experience with JavaScript, you may already know these two seemingly identical methods: Array.prototype.map() and Array.prototype.forEach().
So, what is the difference between them?
Definition
Let’s first take a look at the definitions of Map and ForEach on MDN:
forEach(): executes a provided function for each element function once for each array element).
map(): Creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array).
What is the difference? The forEach() method does not return the execution result, but undefined. In other words, forEach() will modify the original array. The map() method will get a new array and return it.
Example
An array is provided below. If we want to double each element in it, we can use map and forEach to achieve the goal.
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
ForEach
Note that forEach will not return a meaningful value.
We directly modify the value of arr in the callback function.
arr.forEach((num, index) => {
return arr[index] = num * 2;
});
The execution results are as follows:
// arr = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Map
let doubled = arr.map(num => {
return num * 2;
});
The execution results are as follows:
// doubled = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Execution speed comparison
jsPref is a very good website for comparing the execution speed of different JavaScript functions.
Here are the test results of forEach() and map():
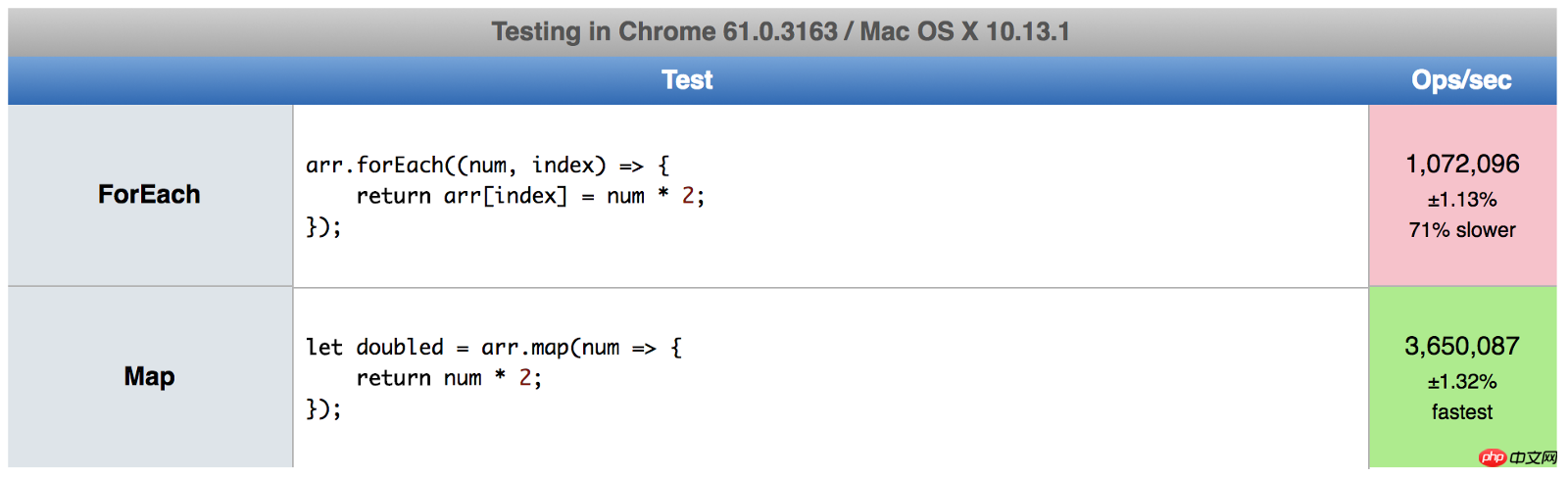
As you can see, the execution speed of forEach() on my computer is map() is 70% slower. The execution results of everyone's browser will be different. You can use the following link to test it out: Map vs. forEach - jsPref.
JavaScript is so flexible (gui) and flexible (yi) that you don’t know if there is a bug. You might as well connect to Fundebug for online real-time monitoring.
Understanding from a functional perspective
If you are used tousing functionsfor programming, then you will definitely like to use map(). Because forEach() will change the value of the original array, and map() will return a brand new array, the original array will not be affected.
Which one is better?
Depends on what you want to do.
forEach is suitable when you don't plan to change the data, but just want to do something with the data - such as saving it to a database or printing it out.
let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];
arr.forEach((letter) => {
console.log(letter);
});
// a
// b
// c
// d
map() is suitable when you want to change the data value. Not only is it faster, but it returns a new array. The advantage of this is that you can use compound (composition) (map(), filter(), reduce(), etc. in combination) to play more tricks.
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; let arr2 = arr.map(num => num * 2).filter(num => num > 5); // arr2 = [6, 8, 10]
We first use map to multiply each element by 2, and then filter out those elements greater than 5. The final result is assigned to arr2.
Core Points
What can be done with forEach(), map() can also be used. The reverse is also true.
map() will allocate memory space to store the new array and return it, while forEach() will not return data.
forEach() allows the callback to change the elements of the original array. map() returns a new array.
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
The effect of displaying the loading circle before the image is loaded
Why choose Node.js for web application development
The above is the detailed content of The difference between using Map and ForEach. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

