Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >How to use the prototype of Object object in JS
How to use the prototype of Object object in JS
- php中世界最好的语言Original
- 2018-03-23 09:52:162549browse
This time I will bring you how to use the prototype of the Object object in JS. What are the precautions when using the prototype of the Object object in JS. The following is a practical case. Let’s take a look. take a look.
Object concept
In JavaScript, all reference types are objects. For example, in function Foo () {}, Foo itself is a reference to an object.
Create objectMethod literal method new ConstructorFunction declaration Object.create
Literal object
Javascript language level quickly creates instances of objects
var obj = {foo: 'foo', bar: 'bar'}; // Object对象字面量
var obj2 = [obj, 'foo', 'bar']; // Array数组字面量
var obj3 = /^[a-zA-Z0-9]$/; // RegExp正则字面量
var obj4 = function(){}; // Function函数字面量
new constructor
Through the constructor of the built-in object, or a custom function. Using the new operator, create an object and execute the constructor method.
var obj = new Object();
var obj2 = new Array(1000);
var obj3 = new RegExp('^[a-zA-Z0-9]$');
var obj4 = new Function('a', 'b', 'return a + b;');
Function declaration
The object created by function declaration. Function belongs to a special object.
function Foo() {}
Foo instanceof Object;
Foo instanceof Function;
Object.create
Pass in an object as the prototype of the returned object, create a new object, and point the prototype of the new object to the passed in object.
var foo = {
'foo': 'foo',
'bar': 'bar'
};
var o = Object.create(foo); // o.proto = foo
console.log(o.foo); // o.proto.foo
Use Object.create(null) You can return a dictionary object.
var o = Object.create(null); o instanceof Object; // return false; o.toString(); // Uncaught TypeError
Object prototype
Every Objects have a built-in proto attribute that points to the prototype attribute of the function that constructed it. The constructor's
prototype.constructor points to the constructor Function native. The process of searching for an object's attributes consists of the following parts:
Search for the data descriptor (writable, value) or access descriptor (getter, setter) of the object's attributes. If found, return the corresponding value. If the query cannot be found, proceed to step 2. Find whether the value of the object property is explicitly defined (can be detected by Object.getOwnPropertyNames). If the object property is defined, the defined value is returned. If not, proceed to step 3. Find the hidden prototype of the objectprotoThe properties of the object, the rules are the same as steps 1 and 2. If it has not been found, repeat step 3 until proto is null.
The specific case is shown in the figure below:
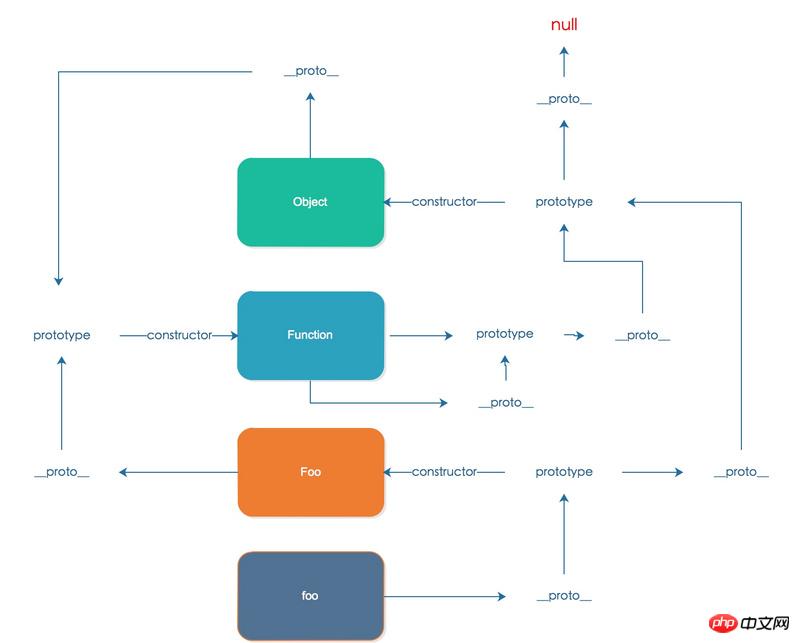
#Detecting object prototype
Test an object in its prototype chain Whether there is a prototype attribute of a constructor in
instanceof Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf
instanceof
operator, language-level detection of the prototype of the object Whether the chain contains the prototype of the constructor
function Foo () {}
Foo instanceof Function; // return true
Foo instanceof Object; // return true
Simulationinstanceof Find whether the constructor of the object's prototype chain contains the passed-in constructor, proto In some specific browsing The device has a function attribute that is exposed to the user
function Bar () {}
function isInstanceof (obj, Constructor) {
if (obj === null) {
return false;
}
// 忽略 string, number, boolean, null, undefined 类型干扰
if (!~['object', 'function'].indexOf(typeof obj)) {
return false;
}
var prototype = obj.proto;
while(prototype) {
if (prototype.constructor === Constructor) {
return true;
}
prototype = prototype.proto;
}
return false;
}
isInstanceof(Bar, Function);
isInstanceof(Bar, Object);
isPrototypeOf
The prototype object of the constructor is used to detect whether there is a constructor in the prototype chain of the target object. Prototype object.
function Baz () {}
var baz = new Baz();
Baz.prototype.isPrototypeOf(baz);
Function.prototype.isPrototypeOf(baz);
Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf(baz);
Get the object prototype Object.getPrototypeOf proto
var o = {};
var prototype = Object.getPrototypeOf(o);
console.log(prototype === Object.prototype); // return true
// 部分浏览器有效
var o2 = {};
console.log(o2.proto === Object.prototype); // return true
Set the object prototype Object.create Object.setPrototypeOf
Object.create
Return an object and set its prototype
function Foo () {}
function Bar () {}
Foo.prototype.foo = 'foo';
Bar.prototype = Object.create(Foo.prototype);
Bar.prototype.constructor = Bar; // 修正原型链的constructor
var o = new Bar();
console.log(o.foo); // return foo;
console.log(o instanceof Bar); // return true
Object.setPrototypeOf
Set the implicit prototype of the object directlyproto
function Foo () {}
Foo.prototype.name = 'foo';
var o = Object.create(null);
Object.setPrototypeOf(o, Foo.prototype);
console.log(o.name); // return foo
Summary
Objects have many knowledge points that test developers. It’s not easy to fully understand and sort it out. I will give a detailed introduction to object inheritance later. Thank you for your support of Script House.
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
Angular2 parent-child component communication method
Detailed explanation of asymmetric encryption of Node.js
CSS3 realizes tilt and rotation animation effects
The above is the detailed content of How to use the prototype of Object object in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

